- 4.37.1 Financial Products Specialty
- 4.37.1.1 Program Scope and Objectives
- 4.37.1.1.1 Background
- 4.37.1.1.2 Authority
- 4.37.1.1.3 Roles and Responsibilities
- 4.37.1.1.4 Program Management and Review
- 4.37.1.1.5 Program Controls
- 4.37.1.1.6 Terms and Acronyms
- 4.37.1.1.7 Related Resources
- 4.37.1.2 Financial Products Specialty (FPS) Program History
- 4.37.1.3 FPS Program Overview
- 4.37.1.3.1 Director, Financial Institutions and Products (FIP)
- 4.37.1.3.2 Financial Products (FP) Territory Manager
- 4.37.1.3.3 FP Team Manager
- 4.37.1.3.4 FP Specialists
- 4.37.1.3.5 FP High Income Initiative Cadre
- 4.37.1.4 Criteria and Procedures for Referrals to FP
- 4.37.1.4.1 Referrals
- 4.37.1.4.2 Mandatory FP Specialist Referrals
- 4.37.1.4.3 Voluntary FP Specialist Referrals
- 4.37.1.5 FP Specialist’s Report
- 4.37.1.5.1 Preparation of FP Specialist's Report
- 4.37.1.5.2 Reviewing and Routing of FP Specialist's Report
- Exhibit 4.37.1-1 Sample Financial Products Specialist’s Report Cover Sheet
- 4.37.1.1 Program Scope and Objectives
Part 4. Examining Process
Chapter 37. Financial Products and Transactions
Section 1. Financial Products Specialty
4.37.1 Financial Products Specialty
Manual Transmittal
July 28, 2025
Purpose
(1) This transmits revised IRM 4.37.1, Financial Products and Transactions, Financial Products Specialty.
Material Changes
(1) IRM 4.37.1.1: Policy owner information was updated and contact information added.
(2) IRM 4.37.1.1.1: Background updated with new content to comply with IRM 1.11.2. Prior information moved to new IRM 4.37.1.2, Financial Products Specialty (FPS) Program History.
(3) IRM 4.37.1.1.3: The subsection was updated with new content to comply with IRM 1.11.2. The prior information was moved to new IRM 4.37.1.3, FPS Program Overview subsection.
(4) Prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.1 information was moved to new IRM 4.37.1.3.1, Director, Financial Institutions and Products (FIP). The information included instructions to staff and was moved out of the internal controls subsection.
(5) Prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.2 information was moved to new IRM 4.37.1.3.2, Financial Products (FP) Territory Manager. The information included instructions to staff and was moved out of the internal controls subsection.
(6) Prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.3 information was moved to new IRM 4.37.1.3.3, FP Team Manager. The information included instructions to staff and was moved out of the internal controls subsection.
(7) Prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.4 information was moved to new IRM 4.37.1.3.4, FP Specialists. The information included instructions to staff and was moved out of the internal controls subsection.
(8) Prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.5 information was moved to new IRM 4.37.1.3.5, FP High Income Initiative Cadre. The information included instructions to staff and was moved out of the internal controls subsection.
(9) IRM 4.37.1.1.4: Updated wording in paragraph (2) for clarity.
(10) IRM 4.37.1.1.6: Acronyms table was moved to this subsection from prior Exhibit 4.37.1-2. Prior Exhibit 4.37.1-2 was removed. The move to this subsection was for compliance with IRM 1.11.2.2.4, Address Management and Internal Controls.
(11) IRM 4.37.1.2: New subsection with prior information moved from IRM 4.37.1.1.1.
(12) IRM 4.37.1.2: Removed "Debt or equity determinations on hybrid financial instruments" from the list under paragraph (10) because it would be considered in the other items listed.
(13) IRM 4.37.1.3: New subsection with prior information from IRM 4.37.1.1.3. The information was moved out of the internal controls subsection because it included instructions to staff.
(14) IRM 4.37.1.3.1: New subsection with information moved from prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.1. The information was moved out of the internal controls subsection because it included instructions to staff.
(15) IRM 4.37.1.3.2: New subsection with information moved from prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.2. The information was moved out of the internal controls subsection because it included instructions to staff.
(16) IRM 4.37.1.3.3: New subsection with information moved from prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.3. The information was moved out of the internal controls subsection because it included instructions to staff.
(17) IRM 4.37.1.3.4: New subsection with information moved from prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.4. The information was moved out of the internal controls subsection because it included instructions to staff.
(18) IRM 4.37.1.3.5: New subsection with information moved from prior IRM 4.37.1.1.3.5. The information was moved out of the internal controls subsection because it included instructions to staff.
(19) IRM 4.37.1.4: Moved the second sentence of paragraph (1) to a Note to highlight that the mandatory referral criteria is on SRS.
(20) Prior Exhibit 4.37.1-2 was removed and the acronyms table in the prior exhibit was added to IRM 4.37.1.1.6. The move from this subsection was for compliance with IRM 1.11.2.2.4, Address Management and Internal Controls.
(21) Subsections with numbering changes only are listed below:
| Old IRM Cite | New IRM Cite | IRM Subsection Title |
|---|---|---|
| 4.37.1.2 | 4.37.1.4 | Criteria and Procedures for Referrals to FP |
| 4.37.1.2.1 | 4.37.1.4.1 | Referrals |
| 4.37.1.2.2 | 4.37.1.4.2 | Mandatory FP Specialist Referrals |
| 4.37.1.2.3 | 4.37.1.4.3 | Voluntary FP Specialist Referrals |
| 4.37.1.3 | 4.37.1.5 | FP Specialist’s Report |
| 4.37.1.3.1 | 4.37.1.5.1 | Preparation of FP Specialist's Report |
| 4.37.1.3.2 | 4.37.1.5.2 | Reviewing and Routing of FP Specialist's Report |
(22) Editorial updates and link updates were made throughout.
Effect on Other Documents
IRM 4.37.1 dated March 06, 2023 is superseded.Audience
Financial products specialists and their managers in Large Business & International (LB&I).Effective Date
(07-28-2025)Ronald H. Hodge II
Assistant Deputy Commissioner Compliance Integration
Large Business and International Division
-
Purpose: Define the Financial Products Specialty (FPS) program. Describe the organization of the specialty area and provide roles and responsibilities. Describe how the specialty program coordinates with the LB&I Examination Process (LEP) including issue management and related definitions.
-
Audience: Financial products (FP) specialists and their managers in Large Business & International (LB&I).
-
Policy Owner: LB&I Policy under the Strategy, Policy, and Governance office in the Assistant Deputy Commissioner Compliance Integration (ADCCI) organization and the Director, Enterprise Activities Practice Area.
-
Program Owner: Director, Financial Institutions and Products (FIP) is responsible for the administration, procedures, and updates related to the FPS program.
-
Primary Stakeholders: LB&I executives, senior managers, frontline managers, program analysts, FPS employees and other IRS employees who may request the services of an FP specialist.
-
Contact Information: To recommend changes or to make any other suggestions to this IRM section, contact the IRM author or see SPDER’s IMD Contacts List by referencing guidelines provided in IRM 1.11.6.5, Providing Feedback About an IRM Section - Outside of Clearance. A request or inquiry can also be made on the LB&I Policy Gateway.
-
The FPS program’s primary responsibility is to support field examinations focusing on financial products tax issues. Field employees in the FPS program consist of FP specialists.
-
FP specialists are experienced revenue agents that have completed special training in financial instruments and terminology, financial industry practices, and the taxation of financial instruments and markets. While the primary activity of FP specialists is supporting large and medium sized corporate and partnership examinations, they also work on assigned projects requiring this expertise across all operating divisions.
-
By law, the IRS has the authority to conduct examinations under Title 26, Internal Revenue Code, Subtitle F - Procedure and Administration, Chapter 78, Discovery of Liability and Enforcement of Title, Subchapter A, Examination and Inspection, which includes but is not limited to:
-
IRC 7602, Examination of books and witnesses
-
IRC 7605, Time and place of examination
-
-
All IRS personnel have the responsibility to ensure all taxpayer rights are protected and observed. See IRM 4.10.1.2, Taxpayer Rights and Pub 1, Your Rights as a Taxpayer.
-
For additional information see IRM 4.10, Examination of Returns, and IRM 4.46, LB&I Examination Process.
-
The Director, Enterprise Activities Practice Area, is responsible for the policies and procedures in this IRM section.
-
The Director, FIP, is responsible for providing oversight of FP territory managers and the policies and procedures in the IRM. See IRM 4.37.1.3.1, Director, Financial Institutions and Products (FIP), for additional information.
-
FP territory managers (TTMs) supervise FP team managers (TMs). FP TTMs are responsible for providing oversight and administration for the procedures in this IRM. See IRM 4.37.1.3.2, Financial Products (FP) Territory Manager, for additional information.
-
FP TMs supervise FP specialists. FP TMs are responsible for monitoring and overseeing work of the FP specialists. See IRM 4.37.1.3.3, FP Team Manager, for additional information.
-
FP specialists are responsible for developing and resolving financial products tax issues for cases assigned. See IRM 4.37.1.3.4, FP Specialist, for additional information.
-
The FPS program seeks to identify, develop, and resolve financial products tax issues that are:
-
National in scope
-
Significant in dollars
-
Important to tax administration
-
Important for uniform and consistent treatment
-
-
FPS participates in the LB&I Examination Process (LEP), generally as issue team members and issue team managers. FPS collaborates with the geographic practice area managers in review of potential tax risks. FPS efficiently performs the examination of financial products and related transactions. This provides for a quality work product and a minimization of burden to both the LB&I examination team and the taxpayer.
-
FPS accumulates and disseminates examination techniques, information about tax avoidance and evasion schemes, and other information useful in planning and conducting examinations.
-
FPS monitors the progress and results of issues through various information management systems.
-
FPS works closely with geographic practice area exam teams, international examiners, subject matter experts within the practice networks, and the Office of Chief Counsel in order to achieve FPS objectives and goals.
-
The Issue Management System (IMS) is a case management application sponsored by LB&I. IMS provides case management functionality to LB&I, SB/SE specialty groups, and Appeals. IMS is used to monitor various elements of FPS inventory. For example, status of Information Document Requests (IDRs), approving examination plans, risk analysis, and Notice of Proposed Adjustment (NOPAs).
-
FP management periodically reviews reports using the Issue Based Management Information System (IBMIS). IBMIS is a reporting tool containing day-to-day information gathered on the Audit Information Management System (AIMS). The system provides team managers, territory managers, executives, and analysts a centralized system for managing case information for tracking, planning, and reporting.
-
The table below defines commonly used acronyms in this IRM:
Acronym Term ADCCI Assistant Deputy Commissioner Compliance Integration CAP Compliance Assurance Process CBF Case-Built File FIP Financial Institutions and Products FP Financial Products FPS Financial Products Specialty HII High Income Initiative IMS Issue Management System ISCP Issue Selection and Collaboration Process LB&I Large Business and International LCC Large Corporate Compliance LEP LB&I Examination Process REIT Real Estate Investment Trust REMIC Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduit RIC Regulated Investment Company SRS Specialist Referral System TM Team Manager TTM Territory Manager UIL Uniform Issue List WP Workpaper
-
The FPS program evolved from tax shelters involving commodity, option and government security straddles into a vast array of complex tax issues.
-
FPS can impact all types of tax examinations, including examinations of:
-
Individuals
-
Partnerships
-
Corporations
-
Exempt Organizations
-
Employee Plans
-
Estates/Trusts
-
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
-
Real Estate Mortgage Investment Conduits (REMICs)
-
Regulated Investment Companies (RICs)
-
-
Financial products are instruments utilized in the global marketplace. They include, but are not limited to, conventional financial instruments such as:
-
Stocks
-
Bonds
-
Loans and Mortgages
-
Foreign Currency
-
Financial Contracts related to Physical Commodities
-
-
Financial products also include derivatives, such as:
-
Forward Contracts
-
Option Contracts
-
Futures Contracts
-
Notional Principal Contracts (swaps)
-
Mortgage-Backed Securities
-
Structured Notes
-
Hybrid and/or Synthetic Securities
-
-
Derivative securities markets have revolutionized how capital is raised and risk is managed. Financial products are primarily marketed by investment bankers and securities firms. Inter-bank lending and borrowing, foreign exchange trading and security sales occur in global markets, twenty-four hours a day.
-
Financial arrangements include re-packaging financial products into new products or hedging existing products. Transactions often arbitrage different tax laws that exist in the U.S. and foreign markets.
-
Financial products often involve the financing of business, the business’s products, or services rendered by a business. Financial products may also be used to manage product risk, for example, the hedging of foreign currency risk in a global business.
-
Generally, issues center around functions handled by the Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer, Comptroller, or any other department responsible for worldwide funding, risk management, investing or refinancing, rather than the tax department.
-
Financial products tax issues may exist for the dealer who creates and markets transactions, and also for the customer or end user of the product or transaction. Issues can be geographic. For example, there may be many dealer issues in locations with major financial centers and few or no dealer issues in locations where there are no major financial markets.
-
Financial product tax issues involve consideration of the following:
-
Character
-
Amount
-
Timing
-
Source
-
-
Analyzing a financial products issue begins with a series of questions such as:
-
What is the financial product?
-
Where is it traded?
-
Is it traded on an exchange?
-
Is it traded at all?
-
Why was the transaction done?
-
Who is the taxpayer?
-
What is the economic effect of the financial product?
-
-
The FPS program provides an organizational structure that is flexible and allows for the timely identification and dissemination of information in a uniform and consistent manner.
-
The FPS program is organized under FIP which is within the Enterprise Activities Practice Area of the LB&I Division. The FPS program is responsible for providing technical expertise across all operating divisions.
-
The FPS is supported by the FIP director, TTMs, TMs, and FP specialists located throughout the country.
-
FP specialists are revenue agents who possess broad expertise in tax law and who have been given special training in financial instruments and terminology, financial industry practices and the taxation of financial instruments and markets. FP specialists serve as issue team members within the LEP. See IRM 4.46.1.1.3.5, Issue Team Member Roles and Responsibilities.
-
Within LB&I, the issue-based examination process is intended to facilitate execution and decision making in a collaborative process where all parties work together to resolve issues at the earliest appropriate point in an examination. All practice areas of LB&I share an equal responsibility in conducting a thorough examination. See IRM 4.46.1.1.3, Roles and Responsibilities.
-
The following subsections list FPS positions that are directly involved in FP issue examinations and procedures:
-
The FIP director provides management oversight of the FPS program and of the FIP practice networks.
-
The FIP director ensures the FPS program provides:
-
Recommendations for policy and legislative changes.
-
Uniform and consistent treatment of industry issues.
-
Timely technical assistance to the field.
-
Financial marketplace research and analysis.
-
-
The FIP director has a responsibility to:
-
Plan for budgeting, staffing and training.
-
Develop measures to gauge and monitor program effectiveness.
-
Develop and monitor management information systems.
-
Coordinate and conduct visits to territories and teams.
-
Control nationally coordinated projects.
-
Develop and recommend referral criteria.
-
Develop position descriptions.
-
Maintain a directory of FPS program personnel.
-
-
The FIP director oversees design and delivery of FPS training programs, in coordination with Learning & Education.
-
To provide FPS program oversight, the FIP director will:
-
Issue guidelines and procedures.
-
Assist territories to achieve uniform direction.
-
Provide technical and administrative assistance when necessary.
-
Resolve differences between territories/operating divisions.
-
Act as liaison between the field and other national functions.
-
-
The FIP director communicates directly with the FP TTMs and TMs when warranted.
-
Additional FIP director responsibilities include:
-
Plan the expansion of FPS to improve efficiency.
-
Ensure matters of importance related to the FPS program are timely brought to the attention of the Enterprise Activities Practice Area director, including recommendations for improvement.
-
Promote effective communication within the FPS program regarding financial products tax issues.
-
-
A FP TTM is responsible for their respective territory to achieve maximum utilization of specialist staff days and case coverage.
-
A FP TTM periodically conducts workload studies to determine the number and location of FP specialists needed for their territory.
-
The following duties are specific to how a FP TTM supports the FPS program within their territory.
-
Issue written FPS program procedures.
-
Provide for adequate training, both internal and external.
-
Conduct periodic group and case visits to evaluate the effectiveness of the FPS program.
-
Ensure teams within the territory are responding timely to mandatory and voluntary case referrals.
-
Ensure FP TMs and specialists are actively engaged in the examination process.
-
Ensure the director is timely informed of the status of all FPS program projects including those crossing territory lines.
-
Ensure the FPS program data contained in various information systems is complete, accurate and updated timely.
-
Provide new FP TMs and FP specialists with managerial and technical assistance, as applicable, including on-the-job training.
-
Ensure the FP TMs timely evaluate their FP specialists.
-
Adhere to IRM 4.46.1.3, Principles of Collaboration.
-
-
A FP TM will follow the fundamental responsibilities provided in:
-
IRM 1.4.1, Management Roles and Responsibilities.
-
IRM 4.46.1.1.3.2, Issue Manager Roles and Responsibilities.
-
IRM 4.46.1.1.3.3, Manager of Team Members Who Are Not Designated as Case Manager or Issue Manager.
-
IRM 4.46.1.3, Principles of Collaboration.
-
-
In addition, a FP TM will:
-
Advise the FP TTM of staffing, funding, and training needs.
-
Support the LB&I issue selection and collaboration process (ISCP).
-
Timely assign or reject referrals on the Specialist Referral System (SRS).
-
Ensure FP referrals are addressed as early as possible and that FP specialist participation does not delay completion of the examination.
-
Timely update and verify the accuracy of data in information reporting systems.
-
Communicate to the director, through the TTM, any new or unusual tax issues, examination techniques and tax avoidance schemes as soon as they are discovered or developed.
-
Ensure the Quality Review and Analysis (QRA) auditing standards are followed and measurements are monitored.
-
Support local Appeals and Counsel offices with FP specialists when required, for example for litigation support.
-
Evaluate FP specialists timely.
-
Encourage regular written feedback from the referring team or group manager regarding the performance of the FP specialists assigned to a case.
-
Be involved in the FP portion of cases including, where possible and if schedule permits, case visits, exam planning meetings, mid-cycle reviews, issue resolution meetings with the taxpayer, and post audit critique meetings.
-
Ensure FP specialists complete all required examination steps and forms, including audit plans, risk analyses, examination reports, and post audit critiques.
-
Review and approve all required forms and reports to be issued.
-
Ensure FP specialists correctly report all time related to their assigned cases.
-
Provide knowledgeable FP specialists to teach training classes for FP program training and for awareness training for other IRS personnel.
-
Ensure key FP issues are coordinated with the corresponding practice networks.
-
-
FP specialists have the following duties and responsibilities:
-
Provide specialized technical expertise to all business units within the IRS.
-
Provide accountability for efficient, objective and professional expertise leading to the timely completion and resolution of financial product tax issues.
-
Participate as a team member in the examination process, which includes planning the examination, performing risk analyses, prioritizing issues, and determining the time required.
-
Attend meetings with the examination team and taxpayer, as necessary.
-
Prepare and discuss IDRs with the taxpayer.
-
Work with the team manager, team coordinator, and other team members or revenue agents to develop and resolve financial product tax issues.
-
Work to resolve conflicts within the team and elevating conflicts, as necessary, to the FP TM.
-
Provide feedback about the examination to the FP TM.
-
Coordinate with the corresponding practice networks, the Office of Chief Counsel, and the Office of Appeals, as needed.
-
-
For LB&I cases, FP specialists will adhere to IRM 4.46.1.1.3.5, Issue Team Member Roles and Responsibilities, and to IRM 4.46, LB&I Examination Process.
-
The role of the FP High Income Initiative (HII) Cadre is to assist examiners in addressing FP related questions and identify the most effective resources available to address identified issues.
-
Resources may include inquiries to the FIP practice networks or referrals to assign a FP specialist to the case.
-
FPS workload is assigned through the Specialist Referral System (SRS).
-
FPS workload is identified through various processes.
-
Cases may be identified by case managers or their designee. See IRM 4.46.3.2.1, LB&I Examination Issue Selection and Collaboration Process (ISCP) and IRM 4.46.3.2.6.1, Specialist Referrals.
-
If a revenue agent starts a case without an FP specialist already assigned, the revenue agent can make a referral to FP in the SRS.
-
For workload identified through the campaign selection process, the FP specialist will be involved in various campaigns on an as-needed basis.
-
-
Large Corporate Compliance (LCC) cases are a mandatory FPS referral at the beginning of the examination to allow the FP specialist to participate during the planning phase.
-
HII cases are a mandatory FP SRS referral for all new starts, including related pick-ups, as of June 21, 2022.
-
The FPS program encourages referrals. Returns not requiring mandatory referrals may be referred if FP specialist assistance is appropriate. Examiners should make referrals as early as possible upon identification of a FP issue. Informal assistance is available to determine if a referral should be made. Informal assistance may not be used in lieu of mandatory referral requirements.
-
Although not identified as mandatory referrals on SRS, the FPS program recommends that case-built file (CBF) assignments be made for Form 1065 partnerships and joint ventures with assets greater than $10 million in order for an initial risk assessment to be conducted.
-
This subsection covers the preparation, review and routing of the FP specialist’s report.
-
FP specialists will follow IRM 4.46.6.2, Workpaper Organization and Considerations. This includes the workpaper (WP) naming convention and the requirement to have documents uploaded to IMS.
-
Upon completing an assignment, the FP specialist will prepare an FP specialist's report. The report will be prepared for all referrals, including no changes.
-
The FP specialist's report will use the proper forms required in IRM 4.46.6, Workpaper and Reports Resources, and IRM 4.10.8, Report Writing, depending on the nature of the referral.
-
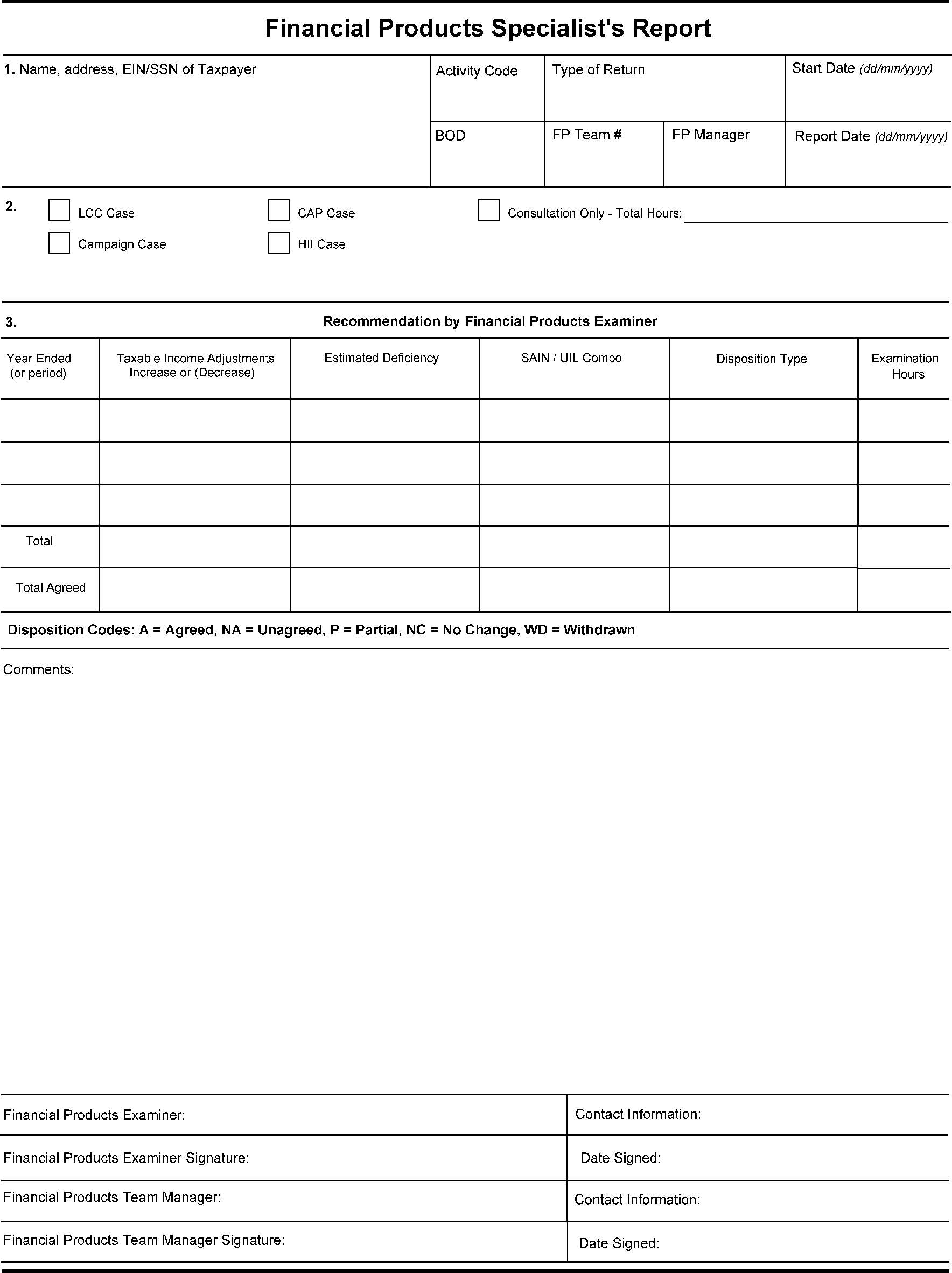
The FP report must include a cover sheet, listing administrative data such as date started, date completed, time charged and proposed adjustments by uniform issue list (UIL) code and disposition. See Exhibit 4.37.1-1 for a sample FP specialist's report cover sheet.
-
The FP specialist's report will be routed to the FP TM for review and approval.
-
The FP TM, or designee, will review and approve the FP specialist's report promptly (generally within five business days) to avoid any delay in disposition and closure of the case.
-
The final FP specialist’s report will be forwarded to the referring manager.
 )
or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
)
or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
