Internal Revenue Bulletin: 2025-30
July 21, 2025
These synopses are intended only as aids to the reader in identifying the subject matter covered. They may not be relied upon as authoritative interpretations.
This document announces a second notice obsoleting IRB guidance documents. In Notice 2025-22, 2025-19 I.R.B. 1427, nine IRB guidance documents were obsoleted. This notice will obsolete 83 pieces of guidance, which were identified for obsolescence by the Associate Offices.
This procedure provides specifications for the private printing of red-ink substitutes for the 2025 revisions of certain information returns. This procedure will be reproduced as the next revision of Publication 1179. Revenue Procedure 2024-29 is superseded.
NOTE. This revenue procedure will be reproduced as the next revision of IRS Publication 1179, General Rules and Specifications for Substitute Forms 1096, 1098, 1099, 5498, and Certain Other Information Returns.
Forms and instructions. (Also, Part 1, sections 101, 162(f), 170, 199A, 220, 223, 401(a), 403(a), 403(b), 408, 408A, 457(b), 529, 529A, 530, 853A, 892, 1400Z-1, 1400Z-2, 1441, 6041, 6041A, 6042, 6043, 6044, 6045, 6047, 6049, 6050A, 6050B, 6050D, 6050E, 6050H, 6050J, 6050N, 6050P, 6050Q, 6050R, 6050S, 6050U, 6050W, 6050X, 6050Y, 6071, 1.402A-2, 1.408-5, 1.408-7, 1.408-8, 1.408A-7, 1.671-5(e), 1.1441-1 through 1.1441-5, 1.1471-4, 1.6041-1, 1.6042-2, 1.6042-4, 1.6043-4, 1.6044-2, 1.6044-5, 1.6045-1, 1.6045-2, 1.6045-3, 1.6045-4, 1.6047-1, 1.6047-2, 1.6049-4, 1.6049-6, 1.6049-7, 1.6050A-1, 1.6050B-1, 1.6050D-1, 1.6050E-1, 1.6050H-1, 1.6050H-2, 1.6050J-1T, 1.6050N-1, 1.6050P-1, 1.6050S-1, 1.6050S-3, 1.6050W-1, 1.6050W-2, 1.6050X-1, 1.6050Y-1, 1.6050Y-2, and 1.6050Y-3.)
This notice publishes the 2025 calendar-year inflation adjustment factor for the section 45U zero-emission nuclear power production credit, as well as the inflation adjustment factors and corresponding applicable amounts for the section 45V clean hydrogen production credit and the section 45Z clean fuel production credit. The inflation adjustment factors (applicable to sections 45U, 45V, and 45Z) and the applicable amounts (in the case of sections 45V and 45Z) are used to determine the amount of the credit allowable under sections 45U, 45V, and 45Z.
Provide America’s taxpayers top-quality service by helping them understand and meet their tax responsibilities and enforce the law with integrity and fairness to all.
The Internal Revenue Bulletin is the authoritative instrument of the Commissioner of Internal Revenue for announcing official rulings and procedures of the Internal Revenue Service and for publishing Treasury Decisions, Executive Orders, Tax Conventions, legislation, court decisions, and other items of general interest. It is published weekly.
It is the policy of the Service to publish in the Bulletin all substantive rulings necessary to promote a uniform application of the tax laws, including all rulings that supersede, revoke, modify, or amend any of those previously published in the Bulletin. All published rulings apply retroactively unless otherwise indicated. Procedures relating solely to matters of internal management are not published; however, statements of internal practices and procedures that affect the rights and duties of taxpayers are published.
Revenue rulings represent the conclusions of the Service on the application of the law to the pivotal facts stated in the revenue ruling. In those based on positions taken in rulings to taxpayers or technical advice to Service field offices, identifying details and information of a confidential nature are deleted to prevent unwarranted invasions of privacy and to comply with statutory requirements.
Rulings and procedures reported in the Bulletin do not have the force and effect of Treasury Department Regulations, but they may be used as precedents. Unpublished rulings will not be relied on, used, or cited as precedents by Service personnel in the disposition of other cases. In applying published rulings and procedures, the effect of subsequent legislation, regulations, court decisions, rulings, and procedures must be considered, and Service personnel and others concerned are cautioned against reaching the same conclusions in other cases unless the facts and circumstances are substantially the same.
The Bulletin is divided into four parts as follows:
Part I.—1986 Code. This part includes rulings and decisions based on provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986.
Part II.—Treaties and Tax Legislation. This part is divided into two subparts as follows: Subpart A, Tax Conventions and Other Related Items, and Subpart B, Legislation and Related Committee Reports.
Part III.—Administrative, Procedural, and Miscellaneous. To the extent practicable, pertinent cross references to these subjects are contained in the other Parts and Subparts. Also included in this part are Bank Secrecy Act Administrative Rulings. Bank Secrecy Act Administrative Rulings are issued by the Department of the Treasury’s Office of the Assistant Secretary (Enforcement).
Part IV.—Items of General Interest. This part includes notices of proposed rulemakings, disbarment and suspension lists, and announcements.
The last Bulletin for each month includes a cumulative index for the matters published during the preceding months. These monthly indexes are cumulated on a semiannual basis, and are published in the last Bulletin of each semiannual period.
This notice continues the process of eliminating extraneous and unnecessary Internal Revenue Bulletin (I.R.B.) guidance by identifying and obsoleting 83 I.R.B. guidance documents.
On January 31, 2025, the President issued Executive Order 14192, Unleashing Prosperity Through Deregulation (E.O. 14192). The purpose of E.O. 14192 includes reducing the economic burden caused by regulation. To further this goal, E.O. 14192 directs agencies to, among other requirements, identify ten existing regulations to be repealed for each regulation publicly proposed for notice and comment or otherwise promulgated.
On February 19, 2025, the President issued Executive Order 14219, Ensuring Lawful Governance and Implementing the President’s ‘Department of Government Efficiency’ Deregulatory Initiative (E.O. 14219). The purpose of E.O. 14219 includes eliminating “overbearing and burdensome” regulations and other guidance documents, and “ending Federal overreach.” To further these goals, E.O. 14219 directs agency heads to coordinate with the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) Team Leads and the Office of Management and Budget to identify regulations and other guidance documents to be eliminated.
Accordingly, the Department of the Treasury (Treasury Department) and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) have undertaken a review of regulations and I.R.B. guidance issued under the Internal Revenue Code1 to identify guidance to be eliminated. This review is ongoing. In Notice 2025-22, 2025-19 I.R.B. 1427, nine I.R.B. guidance documents were obsoleted.
In this notice, 83 I.R.B. guidance documents are being obsoleted. These guidance documents no longer provide useful information, and clarifying their status as obsolete will streamline administration of the tax laws; reduce the volume of guidance that taxpayers and their advisors need to review for compliance with the tax laws; and increase clarity of the tax law. The Treasury Department and the IRS anticipate revoking or obsoleting additional similar guidance documents in the near future.
.01 Notice 2008-83, Application of Section 382(h) to Banks, 2008-42 I.R.B. 905, was repealed by Congress. This notice provides that, for purposes of section 382(h), any deduction properly allowed after a section 382 ownership change to a bank with respect to losses on loans or bad debts (including any deduction for a reasonable addition to a reserve for bad debts) is not treated as a built-in loss or as a deduction that is attributable to periods before the change date. In section 1261 of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, Public Law 111-5, 123 Stat. 115 (2009), Congress repealed this notice for ownership changes after January 16, 2009, except for ownership changes (i) pursuant to a written binding contract entered into on or before that date, or (ii) pursuant to a written agreement entered into on or before that date described in a public announcement or a Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) filing.
.02 The following guidance relates to section 341, which was repealed temporarily by section 302(e)(4)(A) of the Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003, Public Law 108-27, 117 Stat. 752 (2003), and permanently by section 102 of the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, Public Law 112-240, 126 Stat. 2313 (2013):
(1) Rev. Proc. 77-27, 1977-2 C.B. 537. This revenue procedure modifies prior revenue procedures regarding the issuance of private letter rulings to provide that ruling requests under repealed section 341 will be considered under certain circumstances.
(2) Rev. Rul. 79-235, Collapsible Corporations; Holding Period; Property Acquired by Exchange, 1979-2 C.B. 135. This revenue ruling addresses the application of section 341(d)(3) following certain nontaxable exchanges.
(3) Rev. Rul. 79-226, Collapsible Corporations; Sale of Property Constructed Within 3 Years of Liquidation, 1979-2 C.B. 134. This revenue ruling addresses whether certain property should be considered in applying section 341.
(4) Rev. Rul. 77-306, Collapsible Corporations; “Construction” or “Production” from Lease, 1977-2 C.B. 103. This revenue ruling addresses whether a corporate owner-lessor is considered as engaged in the “construction” or “production” of property under section 341(b)(2)(A) by virtue of a particular lease.
(5) Rev. Rul. 73-500, Collapsible Corporation; Sale of “Substantially All of the Properties”, 1973-2 C.B. 113. This revenue ruling addresses whether “substantially all of the properties” of a corporation were sold within the meaning of section 341(e)(4).
(6) Rev. Rul. 73-378, Collapsible Corporation; Reorganization; Exchange and Sale of Stock, 1973-2 C.B. 113. This revenue ruling addresses whether section 341(a) applies to (i) gain realized by an individual on the exchange of his stock in a collapsible corporation for stock in a noncollapsible corporation qualifying as a reorganization under section 368(a)(1)(C), or (ii) gain realized and recognized by him on the sale of his stock in the noncollapsible corporation.
(7) Rev. Rul. 72-422, 1972-2 C.B. 211. This revenue ruling addresses whether the dollar amount expended for alterations in connection with an existing structure is determinative of whether a taxpayer has engaged in “construction” within the meaning of section 341.
(8) Rev. Rul. 72-48, 1972-1 C.B. 102. This revenue ruling addresses whether a corporation that has realized one-third of the taxable income to be derived from property it has produced or purchased is “collapsible” within the meaning of section 341(b).
(9) Rev. Rul. 72-24, 1972-1 C.B. 102. This revenue ruling addresses whether the exception in section 341(e)(1) to treatment as a collapsible corporation applies to a foreign corporation.
(10) Rev. Rul. 71-353, 1971-2 C.B. 243. This revenue ruling addresses whether the term “beneficiary,” as used in section 544(a)(1), has the same meaning for purposes of determining stock ownership of a collapsible corporation under section 341 as that term has for purposes of sections 318 and 1563 and the regulations thereunder.
(11) Rev. Rul. 70-397, 1970-2 C.B. 80. This revenue ruling addresses whether any portion of the gain realized upon the partial liquidation of a collapsible corporation is subject to section 341(a) under the circumstances described.
(12) Rev. Rul. 70-93, 1970-1 C.B. 71. This revenue ruling addresses the computation of the amount of gain that is not subject to repealed section 341(a) by reason of the limitation in section 341(d)(3) under the circumstances described.
(13) Rev. Rul. 69-378, 1969-2 C.B. 49. This revenue ruling addresses whether a corporation engaged in “construction” within the meaning of section 341 and, if so, the date such construction was completed under the circumstances described.
(14) Rev. Rul. 69-33, 1969-1 C.B. 100. This revenue ruling addresses the requirements of section 341(f)(3)(B) with regard to an agreement from a transferee corporation.
(15) Rev. Rul. 69-32, 1969-1 C.B. 100. This revenue ruling addresses the time and manner for a corporation to consent to the provisions of section 341(f)(2).
(16) Rev. Rul. 68-476, 1968-2 C.B. 139. This revenue ruling addresses whether the gain realized by a shareholder upon the sale of stock in a collapsible corporation must be considered gain from the sale or exchange of a capital asset under the circumstances described.
(17) Rev. Rul. 68-472, 1968-2 C.B. 138. This revenue ruling addresses whether the restoration of a damaged building is “construction” within the meaning of section 341 under the circumstances described.
(18) Rev. Rul. 64-125, 1964-1 C.B. 131. This revenue ruling addresses whether the three-year rule of section 341(d)(3) applies under the circumstances described.
.03 The following guidance relates to Code provisions repealed or amended by Public Law 115-97, 131 Stat. 2054 (2017), commonly known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA):
(1) Notice 2005-38, Section 965—Limitations on Dividends Received Deduction and Other Guidance, 2005-22 I.R.B. 1100. This notice provides guidance concerning limitations on the amounts of dividends that a corporation may treat as eligible for the one-time dividends received deduction under former section 965, including the effects of certain corporate transactions on such limitations. Section 965 was amended by section 14103 of the TCJA.
(2) Notice 2005-10, Domestic Reinvestment Plans and Other Guidance Under Section 965, 2005-6 I.R.B. 474. This notice provides guidance related to the one-time dividends received deduction under former section 965 for certain cash dividends from controlled foreign corporations, including general principles and specific guidance on domestic reinvestment plans and investments in the United States. Section 965 was amended by section 14103 of the TCJA.
(3) Rev. Rul. 2003-34, Special Estimated Tax Payments, 2003-17 I.R.B. 813. This revenue ruling provides guidance on how to discontinue using section 847 in a tax year after having taken a deduction under section 847 in a prior tax year. Section 847 was repealed by section 13516 of the TCJA for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017.
(4) Rev. Rul. 76-414, Capital Gains; Alternative Tax; Sale of Patent by Corporate Taxpayer, 1976-2 C.B. 248. This revenue ruling addresses whether a corporation’s gain from the sale of a patent qualifies for the alternative tax described in section 1201 as a “subsection (d) gain” as defined in section 1201(d)(1). Section 1201 was repealed by section 13001(b)(2)(A) of the TCJA.
(5) Rev. Rul. 62-3, 1962-1 C.B. 92. This revenue ruling addresses whether a mutual insurance company is required to substitute the alternative method of taxation under section 1201(a), if applicable, in lieu of the computation under section 821(a)(1) before comparing the results of section 821(a)(1) with the results of section 821(a)(2). Section 1201 was repealed by section 13001(b)(2)(A) of the TCJA.
(6) Rev. Rul. 56-247, 1956-1 C.B. 383. This revenue ruling addresses whether the alternative tax provided in section 1201(a) in the case of a corporation and section 1201(b) in the case of other taxpayers is applied to taxable long-term capital gain unreduced by excess statutory deductions or credits over ordinary income where a taxpayer’s statutory deductions or credits exceed his ordinary income. Section 1201 was repealed by section 13001(b)(2)(A) of the TCJA .
(7) Announcement 78-170, based on News Release IR-2049 dated October 31, 1978. This announcement provides the proper computation of the alternative tax under section 1201 and changes to Part V of Schedule D (Form 1040) under the Revenue Act of 1978 in anticipation of a technical correction made by Congress in 1980. Section 1201 was repealed by section 13001(b)(2)(A) of the TCJA .
.04 The following guidance relates to section 1034, which was repealed by section 312(b) of the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997, Public Law 105-34, 111 Stat. 788 (1997):
(1) Rev. Rul. 78-136, Sale of Residence; Replacement Period; Armed Forces; Divorced Spouse, 1978-1 C.B. 259. This revenue ruling addresses the application of the suspension of the replacement period provided by section 1034(h) to spouses that sold their jointly owned principal residence and later divorce after one of the spouses commences to serve on extended active duty with the Armed Forces prior to the expiration of the replacement period.
(2) Rev. Rul. 75-238, 1975-1 C.B. 257. This revenue ruling addresses the application of the non-recognition provisions of section 1034 to gains realized by a husband and wife from the sale of their former principal residences purchased prior to marriage when they purchase and occupy a new residence as their principal residence after marriage.
(3) Rev. Rul. 74-250, Residence Replaced by Two Residences; Husband and Wife Separated, 1974-1 C.B. 202. This revenue ruling addresses the application of the nonrecognition provisions of section 1034 to gain realized by a husband and wife from the sale of their principal residence where they have agreed to live apart and each purchased and occupied a separate replacement residence.
(4) Rev. Rul. 56-396, 1956-2 C.B. 298. This revenue ruling addresses whether a taxpayer that deferred reporting gain on the sale of his principal residence under the provisions of section 1034 may make an election to use the installment method to report gain on the sale of the residence on an amended return if the taxpayer did not replace the residence during the period specified in section 1034(a).
.05 The following guidance relates to other amended or repealed Code provisions:
(1) Notice 2011-76, Due Dates for Filing Form 706, Form 706-NA, or Form 8939, Extension of Time to Pay Estate Tax, and Penalty Relief for Recipients of Property Acquired from Decedents Who Died in 2010, 2011-40 I.R.B. 479. This document provides due dates for filing Forms 706 and 706-NA, United States Estate (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return, or Form 8939, Allocation of Increase in Basis for Property Acquired From a Decedent, for recipients of property acquired from decedents who died in 2010. Section 1022, concerning the treatment of property acquired from a decedent dying after December 31, 2009, was repealed by section 301(a) of the Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010, Public Law 111-312, 124 Stat. 3296 (2010).
(2) Notice 88-7, Application of Section 382(l)(5)(D) to Certain Transactions in Which the Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corporation Establishes a Federal Mutual Domestic Building and Loan Association, 1988-4 I.R.B. 20. This notice announces the intention to promulgate regulations clarifying the effect of section 382(l)(5)(D) on certain transactions in which the Federal Savings and Loan Insurance Corporation places defaulted thrift institutions into receivership as part of its Management Consignment Program pursuant to its authority under 12 U.S.C. 1729(a) and (b). 12 U.S.C. 1729 was repealed by section 407 of the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989, Public Law 101-73, 103 Stat. 183 (1989).
(3) Rev. Proc. 83-79, 1983-43 I.R.B. 45. This revenue procedure provides a method of computing estimated tax payments under section 6153. Section 6153 was repealed by section 412 of the Deficit Reduction Act of 1984, Public Law 98-369, 98 Stat. 494 (1984).
(4) Rev. Rul. 82-35, Farms; Special Use Value; Liens, 1982-10 I.R.B. 13. This revenue ruling provides that the section 2011 credit, used under section 2032A(c)(2)(C) in computing what would have been the estate tax liability but for the section 2032A election, is derived with respect to three different types of state death tax statutes. The computation is made for the purpose of determining the amount of the lien imposed by section 6324B. Section 2011 was repealed by section 221(a)(95)(A)(i) of the Tax Increase Prevention Act of 2014, Public Law 113-295, 128 Stat. 4010 (2014).
(5) Rev. Rul. 82-10, Bond Premium Amortization; Yield Method, 1982-2 I.R.B. 6. This revenue ruling holds that the yield method is a reasonable method of amortizing bond premium under section 171(b)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1954. However, section 171(b)(3) was amended by section 1803(a)(11)(A) of the Tax Reform Act of 1986, Public Law 99-514, 100 Stat. 2085 (1986), to eliminate the reasonable method standard and to require, except as provided in regulations, the use of a constant yield method to amortize bond premium.
(6) Rev. Rul. 81-146, Valuation; Special Use and Eligible Joint Interest Elections, 1981-20 I.R.B. 5. This ruling provides that the portion of an eligible joint interest includible in a decedent’s gross estate under section 2040(c) is computed using the fair market value as the “value of such interest” under section 2040(c)(1)(A), even though the estate has elected the special use valuation for the interest under section 2032A. Section 2040(c) was repealed by section 403(c)(3)(A) of Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981, Public Law 97-34, 95 Stat. 172 (1981).
(7) Rev. Rul. 74-231, Maximum Tax on Earned Income; Partnership, 1974-1 C.B. 240. This revenue ruling addresses the character of income earned by a partnership for services rendered and how each partner takes his distributive share of partnership items into account for purposes of computing his maximum tax on earned income under section 1348 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1954. Section 1348 was repealed by section 101(c) of the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981.
(8) Rev. Rul. 63-30, 1963-1 C.B. 50. This revenue ruling provides guidance on claiming additional first-year depreciation under section 179 prior to its amendment by section 202(a) of the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981.
(9) Rev. Rul. 55-71, 1955-1 C.B. 110. This revenue ruling provides that the Federal excise tax on jewelry, furs, and related articles of personal property is a relevant factor that should be considered in determining the fair market value of such property for Federal estate and gift tax purposes. The excise tax on the items enumerated in the ruling was repealed by section 221(a)(103)(A) of the Tax Increase Prevention Act of 2014.
.06 The following guidance relates to amended or repealed regulations:
(1) Notice 2025-3, Transitional Relief Under Sections 3403, 3406, 6721, 6722, 6651, and 6656 with Respect to the Reporting of Information and Backup Withholding on Digital Assets Under Section 6045 for Digital Asset Brokers Providing Trading Front-End Services, 2025-4 I.R.B. 488. This notice provides certain transitional relief to certain decentralized industry participants treated as brokers (DeFi brokers) under section 6045 and Treasury Decision 10021 for sales of digital assets effected in calendar years 2027 and 2028, to provide these DeFi brokers with additional time to develop appropriate systems to comply with the application of the reporting requirements under section 6045 to DeFi brokers. Pursuant to Public Law 119-5, 139 Stat. 48 (2025), and operation of the Congressional Review Act, Treasury Decision 10021 has no force or effect.
(2) Rev. Rul. 76-243, Allocation of Income; Advance Charter Hire Payment, 1976-1 C.B. 134. This revenue ruling addresses whether the IRS may make a section 482 adjustment when a taxpayer entered into a voluntary contractual arrangement with a foreign jurisdiction that limited payments to the taxpayer from its foreign subsidiary in the foreign jurisdiction. The regulations at issue in the revenue ruling, section 1.482-1(d)(6) (1968), were replaced by section 1.482-1(h)(2) (1994) following an amendment to section 482 in 1986.
.07 The following guidance relates to former section 29, which provided a credit relating to facilities producing coke or coke gas (other than from petroleum-based products). Congress redesignated section 29 as section 45K in section 1322(a)(1) of the Energy Policy Act of 2005, Public Law 109-58, 119 Stat. 594 (2005). The last remaining element of the section 29 credit expired on December 31, 2013.
(1) Rev. Proc. 2004-27, 2004-17 I.R.B. 831. This revenue procedure permits certain owners of royalty interests to claim the credit for producing fuel from a nonconventional source in the taxable year in which they receive the income from the sale of qualified fuel, rather than in a prior taxable year in which the owner of the operating interest sold the qualified fuel.
(2) Rev. Proc. 2001-34, Qualified Fuel Under Section 29(c)(1)(C), 2001-22 I.R.B. 1293. This procedure modifies Rev. Proc. 2001-30, 2001-19 I.R.B. 1163, regarding the circumstances under which the IRS will issue private letter rulings regarding solid synthetic fuels produced from coal.
(3) Rev. Rul. 94-48, Section 29 Credit; Production Attributable to Net Profits Interest, 1994-29 I.R.B. 5. This revenue ruling holds that the production attributable to a net profits interest under section 29(d)(3) is the production required to be sold to produce that portion of the gross sales from the property that is equal to the amount of income received by the holder of the net profits interest.
(4) Rev. Rul. 93-54, Section 29 Credit; Recompletions, 1993-27 I.R.B. 4. This revenue ruling holds that if a well that is drilled after December 31, 1979, and before January 1, 1993, is recompleted after January 1, 1993, to produce fuel that is a qualified fuel under section 29 and if the recompletion does not involve additional drilling to deepen or extend the well, the fuel produced as a result of the recompletion qualifies for the section 29 credit.
(5) Rev. Rul. 93-46, Section 29 Credit; Royalty Owners, 1993-25 I.R.B. 6. This revenue ruling holds that the owner of a royalty interest is allowed an allocable share of the section 29 credit where the mineral in which the royalty owner has an interest is a qualified fuel when extracted.
(6) Rev. Rul. 90-70, Credit for Producing Fuel from a Nonconventional Fuel Source, 1990-35 I.R.B. 4. This revenue ruling holds that, for the purposes of the section 29 credit, a well is considered to have been “drilled” before January 1, 1991, if the well was “spudded in” before that date and there has been continual drilling since the spudding.
(7) Rev. Rul. 86-127, Credit for Producing Fuel from a Nonconventional Source, 1986-44 I.R.B. 4. This revenue ruling modifies and supersedes Rev. Rul. 86-19, 1986-7 I.R.B. 4, to correct the scope of the categories of deregulated national gas that do not constitute qualified fuels for purposes of the section 29 credit.
(8) Rev. Rul. 86-100, Credit for Producing Fuel from a Nonconventional Source, 1986-35 I.R.B. 4. This revenue ruling holds that a liquid coal-water mixture is not a synthetic fuel produced from coal and is, therefore, not a qualified fuel eligible for the section 29 credit.
(9) Rev. Rul. 86-2, Credit for Producing Oil from a Nonconventional Source, 1986-2 I.R.B. 4. This revenue ruling holds that a taxpayer may receive the section 29 credit for the sale of natural gas during part of a calendar year, notwithstanding that during the same calendar year the taxpayer made other sales from the same wells under the incentive pricing provisions of section 107 of the Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978.
(10) Rev. Rul. 85-77, Nonconventional Fuel Source Credit; Price-Support Payments, 1985-24 I.R.B. 4. This revenue ruling holds that price-support payments that a taxpayer receives for the sale of qualified fuel do not reduce the taxpayer’s section 29 credit.
(11) Announcement 2004-42, Credit for Producing Fuel from a Nonconventional Source, 2004-17 I.R.B. 840. This announcement explains that the I.R.B. version of Rev. Proc. 2004-27 differs from the version that was advance released on April 5, 2004, in that all references to the cash method of accounting have been removed.
(12) Announcement 2003-70, Section 29 – Test Procedures and Significant Chemical Change, 2003-46 I.R.B. 1090. This announcement announces that the IRS will resume ruling on the issue of significant chemical change for synthetic fuels for purposes of section 29.
(13) Announcement 2003-46, 2003-30 I.R.B. 222. This announcement informs the public that the IRS is currently reviewing information regarding test procedures and results that have been presented as evidence that fuel underwent a significant chemical change, and that until the review is complete rulings on the question of significant chemical change will be suspended for requests relying on the procedures and results being reviewed.
(14) Announcement 90-31, Credit for Producing Fuel from a Nonconventional Source – Oil Produced from Tar Sands, 1990-10 I.R.B. 28. This announcement solicits written comments from interested persons regarding the circumstances under which oil would qualify for the section 29 credit for production from tar sands.
.08 The following guidance is obsolete because the subject matter is now covered by final regulations:
(1) Notice 2011-82, Guidance on Electing Portability of Deceased Spousal Unused Exclusion Amount, 2011-42 I.R.B. 516. This notice provides guidance to executors of estates of decedents dying after December 31, 2010, of the need to file Form 706 within the time prescribed by law (including extensions) to elect to allow the decedent’s surviving spouse to take advantage of the deceased spouse’s unused exclusion amount. Regulations implementing the provisions of section 2010(c) are found in sections 20.2010-1 to -3.
(2) Notice 2003-8, Information Reporting for Securities Futures Contracts, 2003-4 I.R.B. 310. This notice delays information reporting requirements under section 6045 regarding securities futures contracts until further notice from the IRS. This reporting is now required by section 1.6045-1.
(3) Notice 2000-62, Returns Relating to Payments of Qualified Tuition and Related Expenses, and to Payments of Interest on Education Loans, 2000-51 I.R.B. 587. This notice announces that eligible education institutions and certain persons receiving payments of student loan interest may continue to report the same information under section 6050S. These, and additional requirements, are now prescribed by section 1.6050S-1.
(4) Notice 96-12, Mark to Market for Securities Dealers: The Dealer-Customer Relationship, 1996-10 I.R.B. 29. This notice provides guidance on whether a taxpayer’s transactions with related persons, including members of the taxpayer’s consolidated group, may be transactions with customers for purposes of section 475. This issue is addressed in section 1.475(c)-1.
(5) Rev. Rul. 75-424, Real Estate Investment Trust; Mortgages on Microwave Transmission Property, 1975-2 C.B. 269. This revenue ruling addresses whether, for purposes of qualifying as a real estate investment trust (REIT), certain assets relating to the construction of microwave transmission systems are “real estate assets.” Whether such assets qualify as real property and, therefore, as real estate assets for purposes of section 856 is now addressed in section 1.856-10.
(6) Rev. Rul. 71-286, 1971-2 C.B. 263. This revenue ruling addresses whether, for purposes of qualifying as a REIT, air rights over real property are considered “interests in real property” and “real estate assets.” Whether such rights qualify as interests in real property and, therefore, as real estate assets for purposes of section 856 is now addressed in section 1.856-10.
(7) Rev. Rul. 69-94, 1969-1 C.B. 189. This revenue ruling addresses whether, for purposes of qualifying as a REIT, certain railroad properties are “real estate assets.” Whether such property qualifies as real property and, therefore, as a real estate asset for purposes of section 856 is now addressed in section 1.856-10.
(8) Rev. Rul. 59-109, 1959-1 C.B. 168. This revenue ruling provides that a sale of a partner’s interest in a partnership is the sale of a capital asset under section 741 unless section 751 applies. This rule is now prescribed in section 1.741-1(a).
(9) Rev. Rul. 56-6, 1956-1 C.B. 660. This revenue ruling provides guidance that deficiencies in Federal income taxes assessed against the decedent resulting from nonrecognition of his minor son as a member of a partnership are deductible from decedent’s gross estate in the full amount paid by decedent’s estate. The deductibility of a decedent’s income tax liability is now addressed in section 20.2053-6(f).
(10) Rev. Rul. 54-444, 1954-2 C.B. 300. This revenue ruling provides guidance on the optional valuation date to be used in respect of certain assets received in the liquidation of corporate stock held among the assets of an estate under the Internal Revenue Code of 1939. This issue is now addressed in section 20.2032-1.
.09 The following guidance relates to past tax years and is not applicable to current or future tax years:
(1) Notice 2016-75, Section 45R – 2016 Guidance with Respect to the Tax Credit for Employee Health Insurance Expenses of Certain Small Employers, 2016-51 I.R.B. 832. This notice addressed situations in which a lack of qualified health plans in the counties in which the employer operates prevented an otherwise qualifying small employer from claiming a tax credit under section 45R for 2016.
(2) Notice 2016-20, Qualified Zone Academy Bond Allocations for 2015 and 2016, 2016-9 I.R.B. 362. This notice sets forth the maximum face amount of Qualified Zone Academy Bonds that may be issued for each State for the calendar years 2015 and 2016 under section 54E(c)(2).
(3) Notice 2015-11, Qualified Zone Academy Bond Allocations for 2014, 2015-8 I.R.B. 618. This notice sets forth the maximum face amount of Qualified Zone Academy Bonds that may be issued for each State for the calendar year 2014 under section 54E(c)(2).
(4) Notice 2015-8, Section 45R – 2015 Guidance with Respect to the Tax Credit for Employee Health Insurance Expenses of Certain Small Employers, 2015-6 I.R.B. 589. This notice addressed situations in which a lack of qualified health plans in the counties in which the employer operates prevented an otherwise qualifying small employer from claiming a tax credit under section 45R for 2015.
(5) Notice 2014-6, Section 45R – Transition Relief with Respect to the Tax Credit for Employee Health Insurance Expenses of Certain Small Employers, 2014-2 I.R.B. 279. This notice addressed situations in which a lack of qualified health plans in the counties in which the employer operates prevented an otherwise qualifying small employer from claiming a tax credit under section 45R for 2014.
(6) Notice 2013-3, Qualified Zone Academy Bond Allocations for 2012 and 2013, 2013-7 I.R.B. 484. This notice sets forth the maximum face amount of Qualified Zone Academy Bonds that may be issued for each State for the calendar years 2012 and 2013 under section 54E(c)(2).
(7) Notice 2012-21, Extension of Time to File an Estate Tax Return Solely to Elect Portability of a Deceased Spousal Unused Exclusion Amount, 2012-10 I.R.B. 450. This notice grants the executor of a qualifying estate a six-month extension of time until 15 months after the decedent’s date of death to file Form 706 on which to make an election under section 2010(c). This guidance is no longer needed and expired on its own terms because it only applied to a decedent whose date of death was after December 31, 2010, and before July 1, 2011. Final regulations were issued implementing the provisions of section 2010(c).
(8) Notice 2011-88, Postponement of Backup Withholding Requirement for Payment Card and Third Party Network Payments Made Under Section 6050W, 2011-46 I.R.B. 748. This notice provides that backup withholding of section 6050W payments will not be required for calendar year 2011.
(9) Notice 2010-11, Extension of Temporary Suspension of AHYDO Rules, 2010-4 I.R.B. 326. This notice extends to December 31, 2010, the temporary suspension of the rules for certain applicable high yield discount obligations pursuant to section 163(e)(5)(F), which permits such suspension if the Secretary of the Treasury or his delegate determines that such suspension is appropriate in light of distressed conditions in the debt capital markets.
(10) Notice 2005-89, Temporary Relief for Certain REITs and Taxable REIT Subsidiaries that Provide Accommodations to Persons Affected by Hurricanes Katrina and Rita, 2005-49 I.R.B. 1077. This notice provides that, for a period of six months beginning on August 28, 2005, the IRS will not treat a hotel, motel, or other establishment that otherwise satisfies the definition of “lodging facility” under section 856(d)(9) as other than a “lodging facility” if it is used to provide temporary housing to certain persons affected by Hurricane Katrina or Hurricane Rita, provided certain recordkeeping requirements are satisfied.
(11) Rev. Proc. 2019-34, 2019-35 I.R.B. 669. This revenue procedure provides simplified procedures for an insurance company to obtain automatic consent to change its method of accounting to comply with sections 807 and 848, as amended by the TCJA, for the first taxable year beginning after December 31, 2017.
(12) Rev. Proc. 2011-19, Qualified Zone Academy Bond Allocations for 2011, 2011-6 I.R.B. 465. This revenue procedure sets forth the maximum face amount of Qualified Zone Academy Bonds that may be issued for each State for the calendar year 2011 under section 54E(c)(2).
(13) Rev. Proc. 80-49, 1980-45 I.R.B. 29. This document provides procedures for the partial revocation of a section 2032A election made on or before August 30, 1980. The effective date for making a partial election under these procedures has expired.
(14) Rev. Rul. 82-62, Valuation; Special Use Value; Retroactive Election, 1982-15 I.R.B. 12. This revenue ruling provides that estates that previously were eligible for, but did not timely elect, section 2032A valuation cannot retroactively elect special use valuation under section 421(k)(5) of the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981. This guidance only applied to estate tax returns filed between July 28, 1980, and February 17, 1982.
(15) Announcement 91-58, New Form 706-QDT for Reporting and Paying Estate Tax with Respect to Qualified Domestic Trust; Due Date is September 16, 1991, 1991-15 I.R.B. 39. This document announces a new Form 706 QDT for reporting and paying estate tax with respect to a qualified domestic trust. The due date was September 16, 1991.
.10 The following guidance requested comments from the public and the guidance is no longer needed:
(1) Notice 2013-48, Application of Wash Sale Rules to Money Market Fund Shares, 2013-31 I.R.B. 120. This notice requests comments on a proposed revenue procedure that would establish a de minimis exception to the wash sale rules of section 1091 for certain redemptions of shares of money market funds that, under regulations proposed by the SEC, would no longer maintain a constant share price.
(2) Notice 2011-73, Request for Comments on Health Coverage Affordability Safe Harbor for Employers (Section 4980H), 2011-40 I.R.B. 474. This notice requests comments on a proposed safe harbor, which could be incorporated in future proposed regulations, for determining the affordability of coverage under an eligible employer sponsored plan for purposes of an employer’s potential assessable payment under section 4980H(b).
.11 Notice 2008-94, Guidance on §§ 162(m)(5) and 280G(e) of the Internal Revenue Code, 2008-44 I.R.B. 1070, provided guidance on certain executive compensation provisions of the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, Public Law 110-343, 122 Stat. 3765 (2008), which added sections 162(m)(5) and 280G(e) to the Code, and specifically applied to the Troubled Asset Relief Program, which is no longer operative.
-
Notice 2025-3 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2016-75 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2016-20 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2015-11 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2015-8 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2014-6 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2013-48 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2013-3 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2012-21 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2011-88 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2011-82 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2011-76 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2011-73 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2010-11 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2008-94 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2008-83 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2005-89 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2005-38 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2005-10 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2003-8 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 2000-62 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 96-12 is obsoleted.
-
Notice 88-7 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Proc. 2019-34 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Proc. 2011-19 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Proc. 2004-27 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Proc. 2001-34 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Proc. 83-79 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Proc. 80-49 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Proc. 77-27 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 2003-34 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 94-48 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 93-54 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 93-46 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 90-70 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 86-127 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 86-100 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 86-2 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 85-77 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 82-62 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 82-35 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 82-10 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 81-146 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 79-235 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 79-226 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 78-136 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 77-306 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 76-414 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 76-243 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 75-424 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 75-238 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 74-250 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 74-231 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 73-500 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 73-378 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 72-422 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 72-48 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 72-24 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 71-353 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 71-286 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 70-397 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 70-93 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 69-378 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 69-94 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 69-33 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 69-32 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 68-476 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 68-472 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 64-125 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 63-30 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 62-3 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 59-109 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 56-396 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 56-247 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 56-6 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 55-71 is obsoleted.
-
Rev. Rul. 54-444 is obsoleted.
-
Announcement 2004-42 is obsoleted.
-
Announcement 2003-70 is obsoleted.
-
Announcement 2003-46 is obsoleted.
-
Announcement 91-58 is obsoleted.
-
Announcement 90-31 is obsoleted.
-
Announcement 78-170 is obsoleted.
This notice was drafted by the Office of the Associate Chief Counsel (Procedure and Administration). For further information, contact the Office of the Associate Chief Counsel (Procedure and Administration) at (202) 317-3400 (not a toll-free number).
1 Unless otherwise specified, all “Section” or “§” references are to sections of the Internal Revenue Code (Code) of 1986 or the Internal Revenue Regulations (CFR Title 26).
This notice publishes the inflation adjustment factors and applicable amounts, as appropriate, for calendar year 2025 for the zero-emission nuclear power production credit under § 45U of the Internal Revenue Code (Code) (the § 45U credit), the credit for production of clean hydrogen under § 45V of the Code (the § 45V credit), and the clean fuel production credit under § 45Z of the Code (the § 45Z credit). These inflation adjustment factors and applicable amounts, as appropriate, are used to determine the corresponding credit amounts under §§ 45U, 45V, and 45Z of the Code.
.01 Section 45U.
Section 45U was added to the Code by section 13105 of the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA), enacted as Pub. L. 117-169, 136 Stat. 1818, 1929 (August 16, 2022), to provide an income tax credit for producing electricity at a qualified nuclear power facility.
Section 45U(a) provides that, for purposes of § 38, the § 45U credit for any taxable year is an amount equal to the amount by which the product of 0.3 cents (the amount provided in § 45U(a)(1)(A)), multiplied by the kilowatt hours of electricity produced by the taxpayer at a qualified nuclear power facility, and sold by the taxpayer to an unrelated person during the taxable year, exceeds the reduction amount for that taxable year.
Section 45U(b)(2) defines the reduction amount as the lesser of the amount determined under § 45U(a) before application of the reduction amount, or the amount equal to 16 percent of the excess of, subject to other rules regarding the treatment of certain receipts, the gross receipts from any electricity produced by such facility (including any electricity services or products provided in conjunction with the electricity produced by such facility) and sold to an unrelated person during such taxable year, over the amount equal to the product of 2.5 cents (the amount provided in § 45U(b)(2)(A)(ii)(II)(aa)), multiplied by the kilowatt hours of electricity determined in § 45U(a).
Section 45U(c)(1) provides that the 0.3 cent amount in § 45U(a)(1)(A) and the 2.5 cent amount in § 45U(b)(2)(A)(ii)(II)(aa) are each adjusted by multiplying such amounts by the inflation adjustment factor (as determined under § 45(e)(2), by substituting “2023” for “1992” in § 45(e)(2)(B)) for the calendar year in which the sale of electricity (as defined in § 45U(b)(3)) occurred. If the 0.3 cent and 2.5 cent amounts, as increased under § 45U(c)(1), are not multiples of 0.05 cent and 0.1 cent, respectively, then such amounts are rounded to the nearest multiples of 0.05 cent and 0.1 cent, respectively.
.02 Section 45V.
Section 45V was added to the Code by IRA section 13204, 136 Stat. at 1935, to provide an income tax credit for producing qualified clean hydrogen.
Section 45V(a) provides that, for purposes of § 38, the § 45V credit for any taxable year is an amount equal to the product of (1) the kilograms of qualified clean hydrogen produced by the taxpayer during such taxable year at a qualified clean hydrogen production facility during the 10-year period beginning on the date such facility was originally placed in service, and (2) the applicable amount as determined under § 45V(b) with respect to such hydrogen.
Section 45V(b)(1) provides that, for purposes of § 45V(a)(2), the applicable amount is an amount equal to the applicable percentage of $0.60. If the amount so determined is not a multiple of 0.1 cent, then such amount is rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.1 cent.
Section 45V(b)(2) provides that, for purposes of § 45V(b)(1), the applicable percentage is determined based on the lifecycle greenhouse gas emissions (lifecycle GHG emissions) rate of the process used to produce any qualified clean hydrogen as follows: (i) if the lifecycle GHG emissions rate is not greater than 4 kilograms of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) per kilogram of hydrogen, and not less than 2.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, then the applicable percentage is 20 percent; (ii) if the lifecycle GHG emissions rate is less than 2.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, and not less than 1.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, then the applicable percentage is 25 percent; (iii) if the lifecycle GHG emissions rate is less than 1.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, and not less than 0.45 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, then the applicable percentage is 33.4 percent; and (iv) if the lifecycle GHG emissions rate is less than 0.45 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, then the applicable percentage is 100 percent.
Section 45V(b)(3) provides that the $0.60 amount in § 45V(b)(1) is adjusted by multiplying such amount by the inflation adjustment factor (as determined under § 45(e)(2), by substituting “2022” for “1992” in § 45(e)(2)(B)) for the calendar year in which the qualified clean hydrogen is produced. If any amount as increased under § 45V(b)(3) is not a multiple of 0.1 cent, then such amount is rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.1 cent.
.03 Section 45Z.
Section 45Z was added to the Code by IRA section 13704, 136 Stat. at 1997, to provide an income tax credit for producing clean transportation fuel.
Section 45Z(a)(1) provides that, for purposes of § 38, the § 45Z credit for any taxable year is an amount equal to the product of (i) the applicable amount per gallon (or gallon equivalent) with respect to any transportation fuel which is produced by the taxpayer at a qualified facility and sold by the taxpayer in a specific manner during the taxable year, and (ii) the emissions factor for such fuel as determined under § 45Z(b).
Section 45Z(a)(2) and (3) provide the applicable amounts for transportation fuels. For transportation fuel that is not a sustainable aviation fuel (non-SAF transportation fuel), the applicable amount is 20 cents (under § 45Z(a)(2)(A)), or $1.00 (under § 45Z(a)(2)(B)). For transportation fuel that is a sustainable aviation fuel (SAF transportation fuel), the applicable amount is 35 cents (under § 45Z(a)(3)(A)(i)), or $1.75 (under § 45Z(a)(3)(A)(ii)). Section 45Z(a)(2) refers to the lower amounts for each type of fuel as the base amount and to the higher amounts as the alternative amount. A taxpayer uses the alternative amount if it produces transportation fuel at a qualified facility that satisfies certain prevailing wage and apprenticeship requirements.
Section 45Z(c)(1) provides that for calendar years beginning after 2024, the applicable amounts in § 45Z(a)(2) and (3) must each be adjusted by multiplying such amounts by the inflation adjustment factor for the calendar year in which the sale of the transportation fuel occurs. If any amount as increased under § 45Z(c)(1) is not a multiple of 1 cent, then such amount is rounded to the nearest multiple of 1 cent. Section 45Z(c)(2) provides that the inflation adjustment factor for the § 45Z credit is the inflation adjustment factor determined and published by the Secretary of the Treasury or his delegate pursuant to § 45Y(c), determined by substituting “calendar year 2022” for “calendar year 1992” in § 45Y(c)(3).
.04 Sections 45(e)(2)(B) and 45Y(c)(3).
Sections 45(e)(2)(B) and 45Y(c)(3) define the term inflation adjustment factor as, with respect to a calendar year, a fraction the numerator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for the preceding calendar year and the denominator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for the calendar year 1992. The term GDP implicit price deflator means the most recent revision of the implicit price deflator for the gross domestic product as computed and published by the Department of Commerce before March 15 of the calendar year.
.01 2025 Section 45U Inflation Adjustment Factor.
For purposes of § 45U(c)(1), for sales of electricity occurring in calendar year 2025, the inflation adjustment factor is a fraction the numerator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for 2024 (125.234) and the denominator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for 2023 (122.273), which yields an inflation adjustment factor of 1.0242.
For sales of electricity occurring in calendar year 2025, the amount provided in § 45U(a)(1)(A) is 0.3 cents (0.3 cents (or $0.003) x 1.0242, then rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.05 cent). The amount provided in § 45U(b)(2)(A)(ii)(II)(aa) is 2.6 cents (2.5 cents (or $0.025) x 1.0242, then rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.1 cent).
.02 2025 Section 45V Inflation Adjustment Factor and Applicable Amount.
For purposes of § 45V(b)(3), for qualified clean hydrogen produced in calendar year 2025, the inflation adjustment factor is a fraction the numerator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for 2024 (125.234) and the denominator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for 2022 (118.026), which yields an inflation adjustment factor of 1.0611.
For qualified clean hydrogen produced in calendar year 2025, the applicable amount determined under § 45V(b)(1) is the product of $0.637 ($0.60 x 1.0611, then rounded to the nearest multiple of 0.1 cent) and the applicable percentage, which depends on the lifecycle GHG emissions rate of the qualified clean hydrogen production process. Thus, for qualified clean hydrogen produced through a process that results in a lifecycle GHG emissions rate of:
(i) not greater than 4 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, and not less than 2.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, the applicable amount is $0.127;
(ii) less than 2.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, and not less than 1.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, the applicable amount is $0.159;
(iii) less than 1.5 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, and not less than 0.45 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, the applicable amount is $0.213; and
(iv) less than 0.45 kilograms of CO2e per kilogram of hydrogen, the applicable amount is $0.637.
.03 2025 Section 45Z Inflation Adjustment Factor and Applicable Amount.
For purposes of § 45Z(c), for transportation fuel sold in calendar year 2025, the inflation adjustment factor is a fraction the numerator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for 2024 (125.234) and the denominator of which is the GDP implicit price deflator for 2022 (118.026), which yields an inflation adjustment factor of 1.0611.
For non-SAF transportation fuel sold in calendar year 2025, the base amount in § 45Z(a)(2)(A) is 21 cents (20 cents x 1.0611, then rounded to the nearest cent). The alternative amount in § 45Z(a)(2)(B) is $1.06 ($1.00 x 1.0611, then rounded to the nearest cent).
For SAF transportation fuel sold in calendar year 2025, the base amount in § 45Z(a)(3)(A)(i) is 37 cents (35 cents x 1.0611, then rounded to the nearest cent). The alternative amount in § 45Z(a)(3)(A)(ii) is $1.86 ($1.75 x 1.0611, then rounded to the nearest cent).
The principal authors of this notice are Whitney Brady, Glenn Kats, and Jennifer Golden of the Office of Associate Chief Counsel (Energy, Credits, and Excise Tax). For further information regarding this notice contact Whitney Brady at (202) 317-6325, Glenn Kats at (202) 317-3995, or Jennifer Golden at (202) 317-6855 (not toll-free numbers).
| PART 1 – GENERAL INFORMATION | |
|---|---|
| Section 1.1 – Overview of Revenue Procedure 2025-22 / What’s New | 201 |
| Section 1.2 – Definitions | 205 |
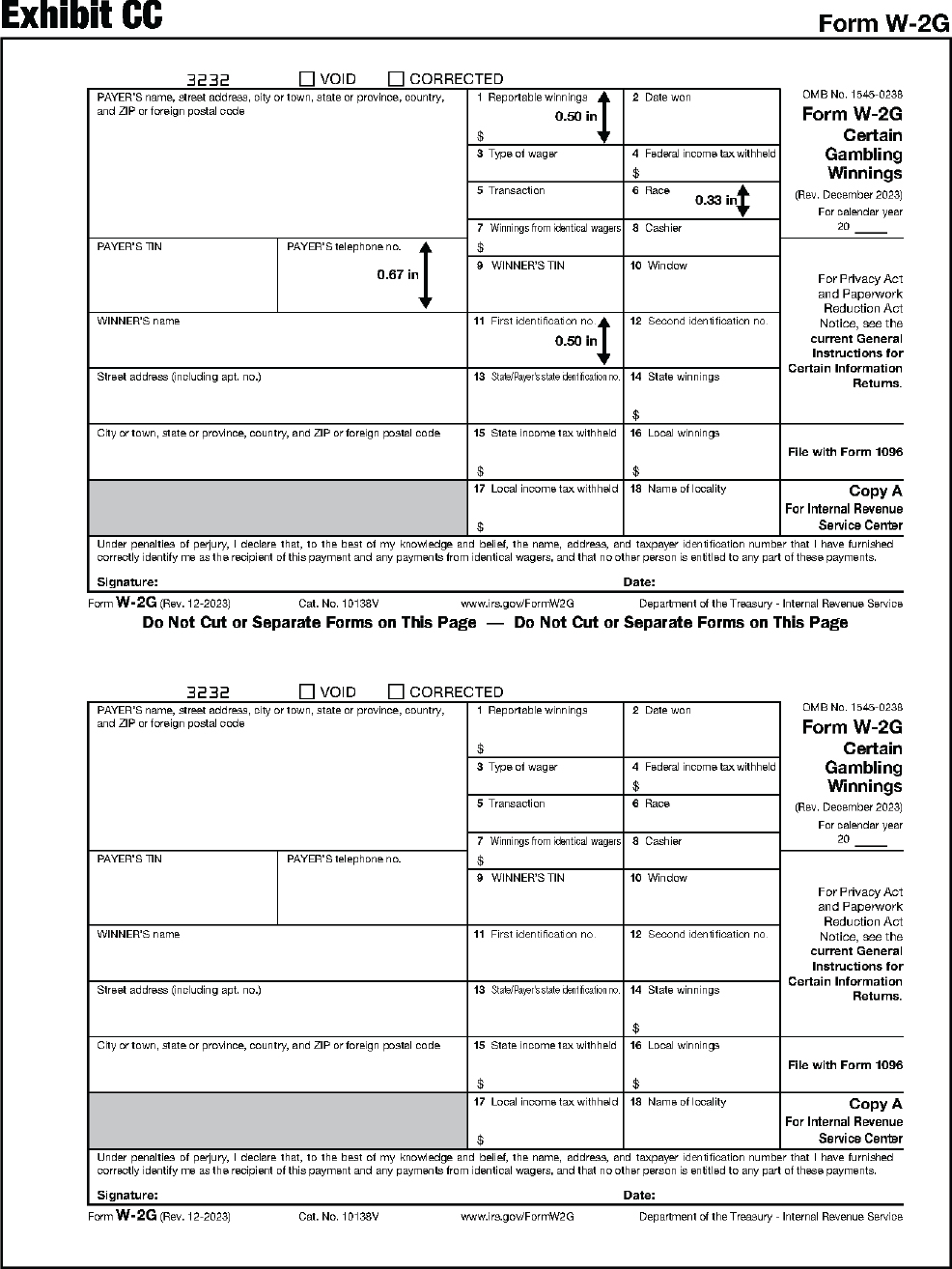
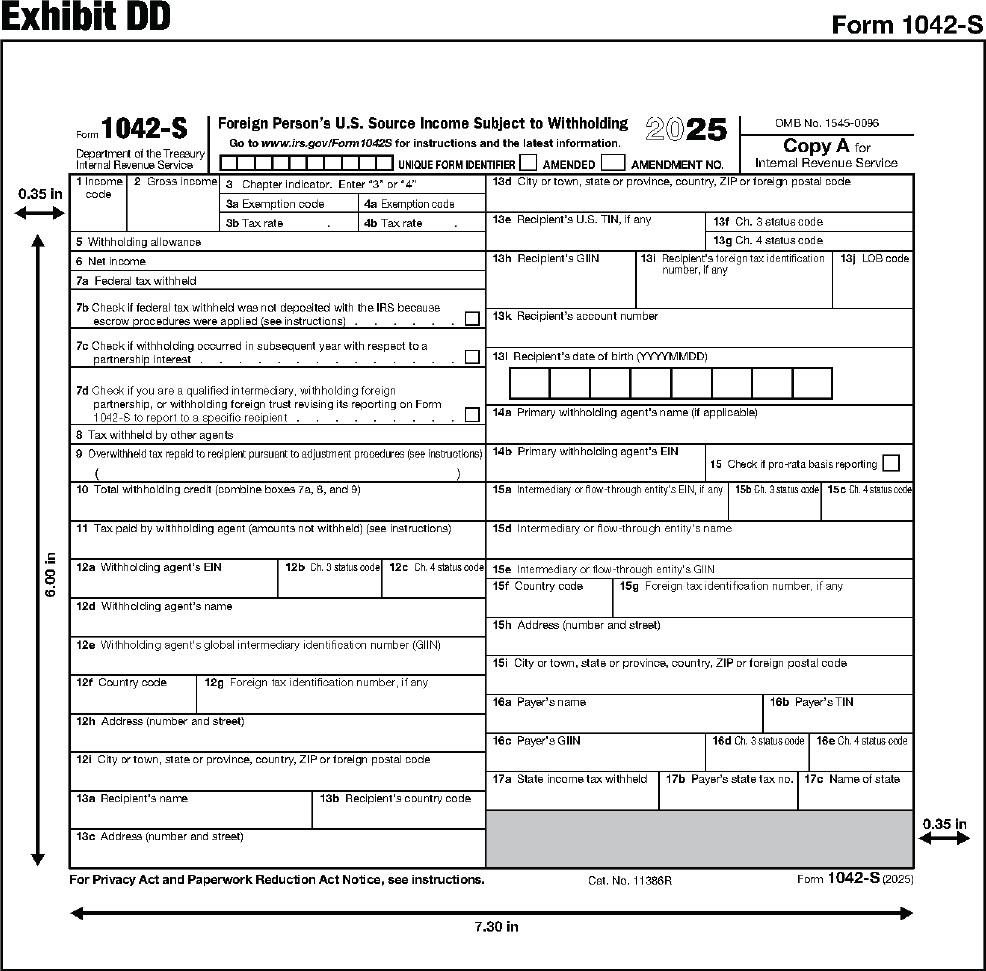
| Section 1.3 – General Requirements for Acceptable Substitute Forms 1096, 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, W-2G, and 1042-S | 206 |
| PART 2 – SPECIFICATIONS FOR SUBSTITUTE FORMS 1096 AND COPIES A OF FORMS 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, AND 5498 (ALL FILED WITH THE IRS) | |
| Section 2.1 – Specifications | 209 |
| Section 2.2 – Instructions for Preparing Paper Forms That Will Be Filed With the IRS | 214 |
| PART 3 – SPECIFICATIONS FOR SUBSTITUTE FORM W-2G (FILED WITH THE IRS) | |
| Section 3.1 – General | 216 |
| Section 3.2 – Specifications for Copy A of Form W-2G | 216 |
| PART 4 – SUBSTITUTE STATEMENTS TO FORM RECIPIENTS AND FORM RECIPIENT COPIES | |
| Section 4.1 – Specifications | 217 |
| Section 4.2 – Composite Statements | 221 |
| Section 4.3 – Additional Information for Substitute and Composite Forms 1099-B and 1099-DA | 223 |
| Section 4.4 – Required Legends | 223 |
| Section 4.5 – Miscellaneous Instructions for Copies B, C, D, 1, and 2 | 225 |
| Section 4.6 – Electronic Delivery of Recipient Statements | 226 |
| PART 5 – ADDITIONAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR SUBSTITUTE FORMS 1097- BTC, 1098, 1099, 5498, W-2G, AND 1042-S | |
| Section 5.1 – Paper Substitutes for Form 1042-S | 228 |
| Section 5.2 – OMB Requirements for All Forms in This Revenue Procedure | 230 |
| Section 5.3 – Ordering Forms and Instructions | 231 |
| Section 5.4 – Effect on Other Revenue Procedures | 231 |
| PART 6 – EXHIBITS | |
| Section 6.1 – Exhibits of Forms in This Revenue Procedure | 231 |
The purpose of this revenue procedure is to set forth the 2025 requirements for:
-
Using official Internal Revenue Service (IRS) forms to file information returns with the IRS,
-
Preparing acceptable substitutes of the official IRS forms to file information returns with the IRS, and
-
Using official or acceptable substitute forms to furnish information to recipients.
This revenue procedure contains specifications for the following information returns.
| Form | Title |
|---|---|
| 1096 | Annual Summary and Transmittal of U.S. Information Returns |
| 1097-BTC | Bond Tax Credit |
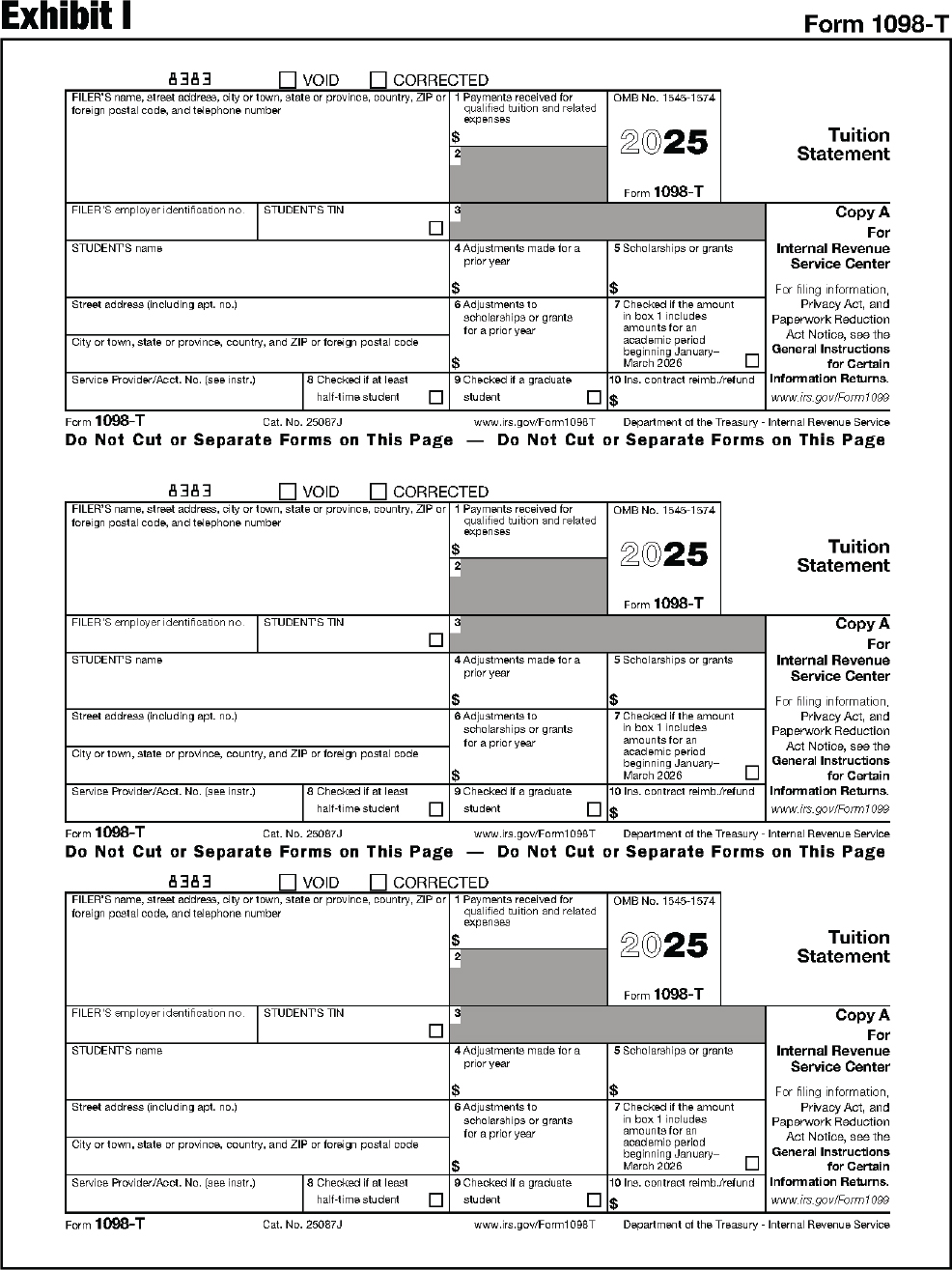
| 1098 | Mortgage Interest Statement |
| 1098-C | Contributions of Motor Vehicles, Boats, and Airplanes |
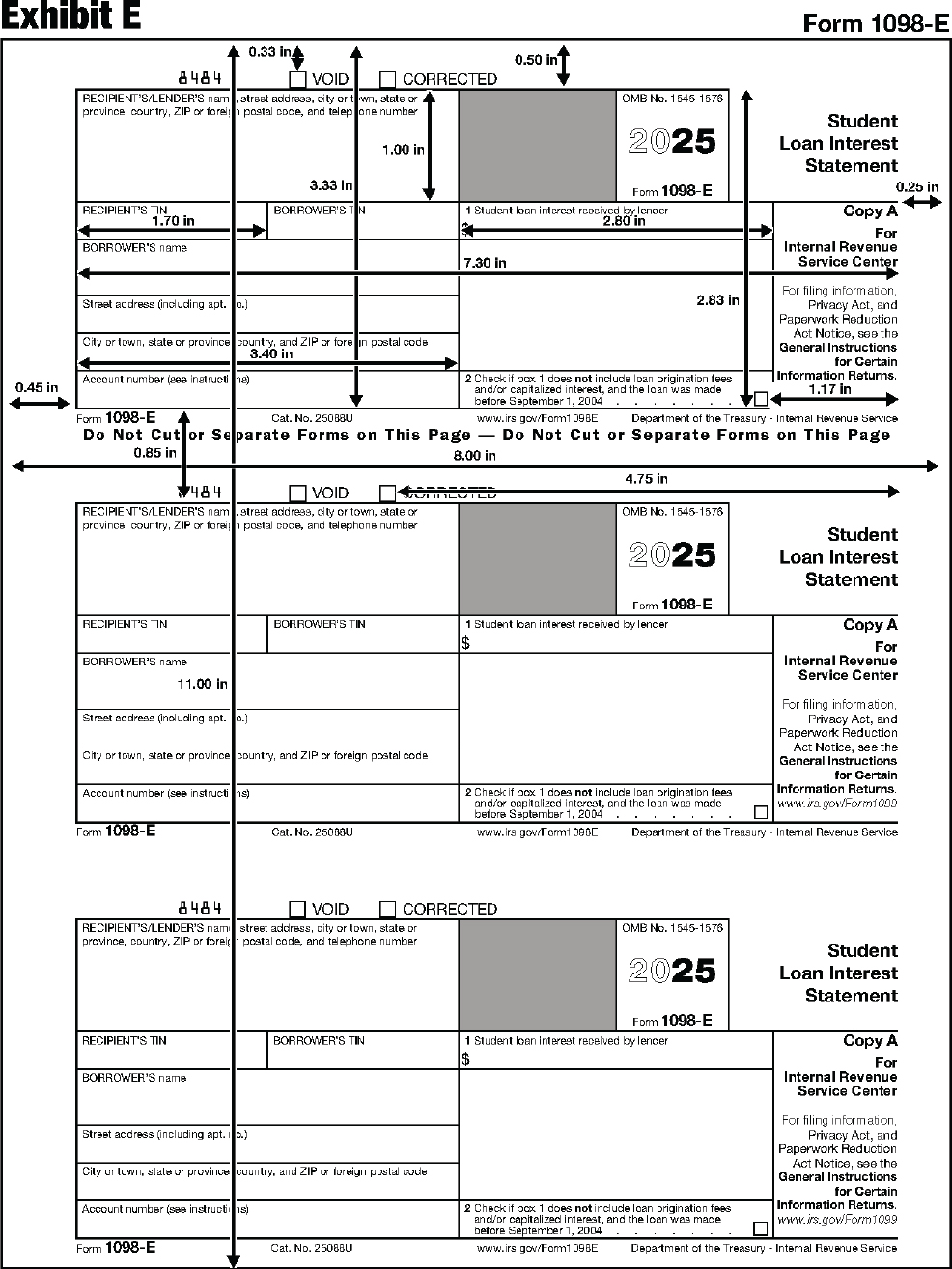
| 1098-E | Student Loan Interest Statement |
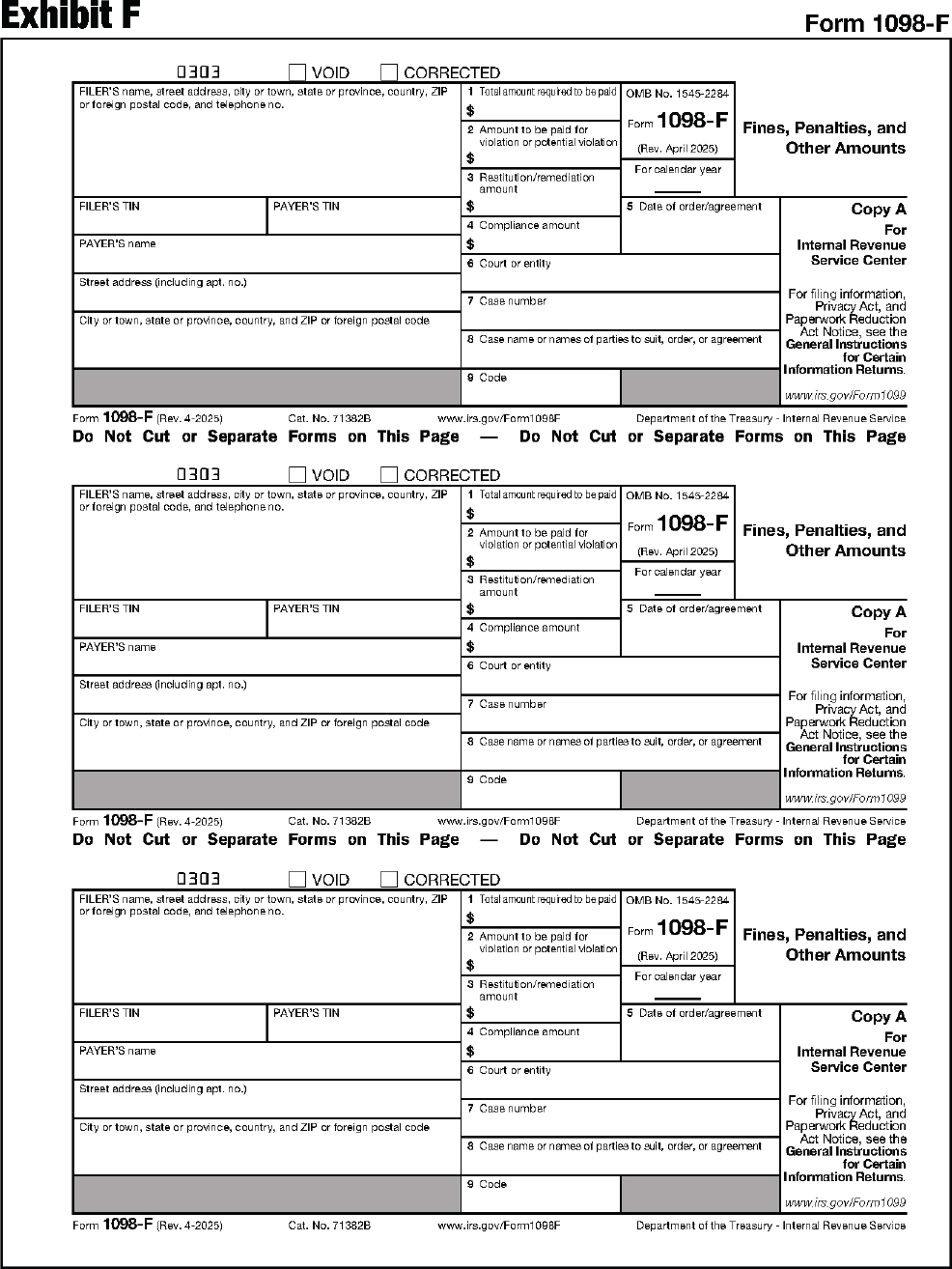
| 1098-F | Fines, Penalties, and Other Amounts |
| 1098-MA | Mortgage Assistance Payments |
| 1098-Q | Qualifying Longevity Annuity Contract Information |
| 1098-T | Tuition Statement |
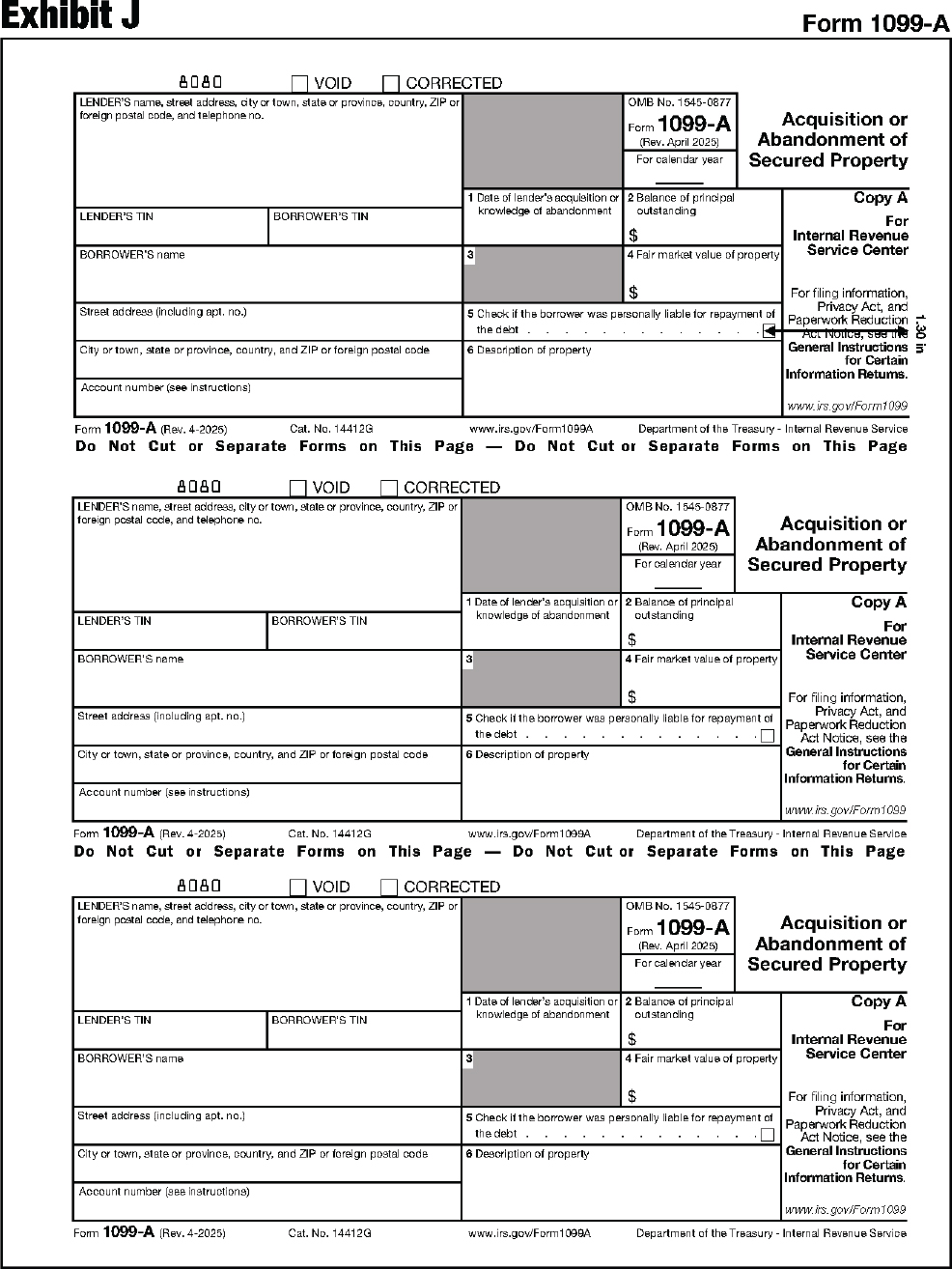
| 1099-A | Acquisition or Abandonment of Secured Property |
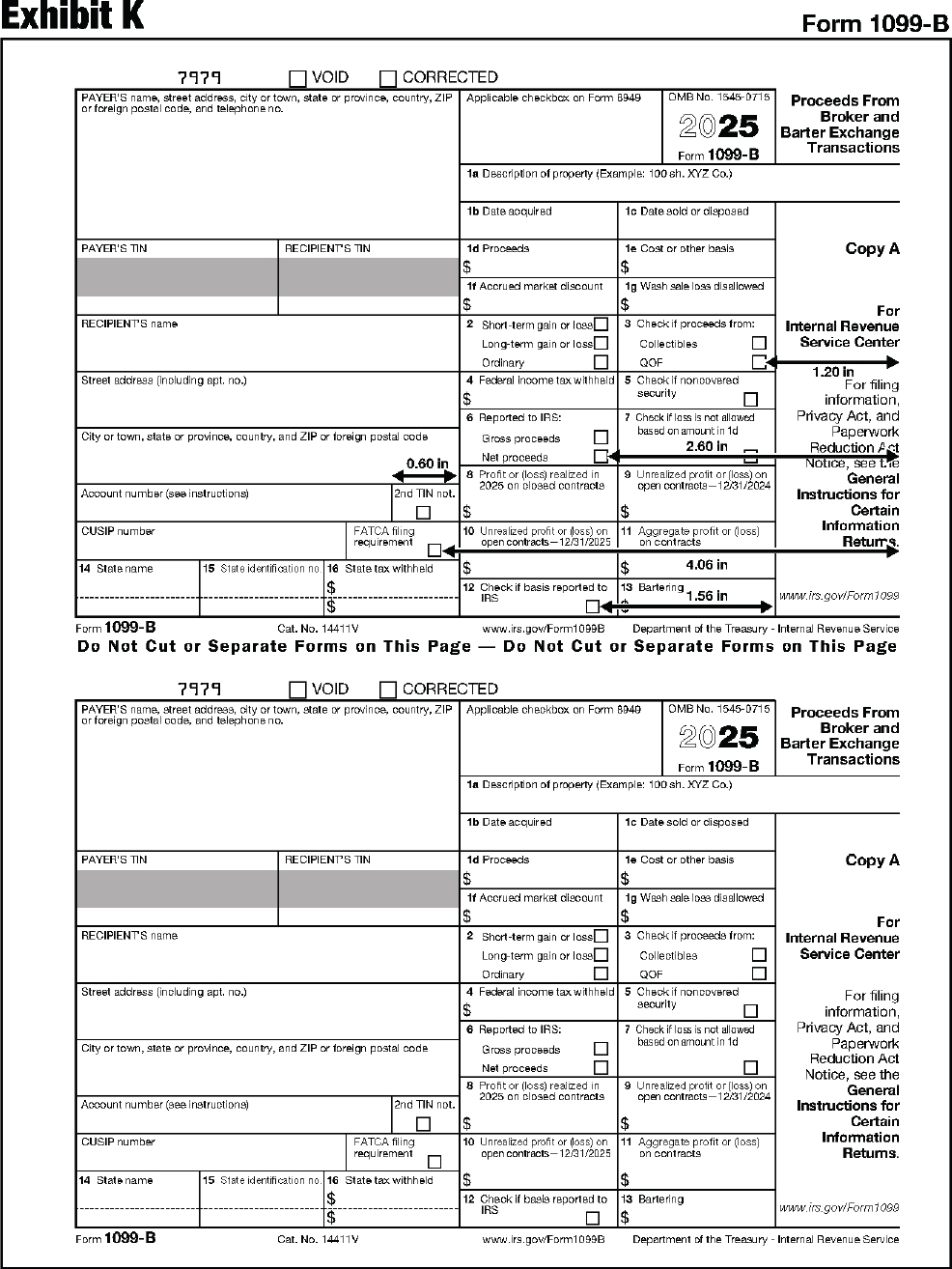
| 1099-B | Proceeds From Broker and Barter Exchange Transactions |
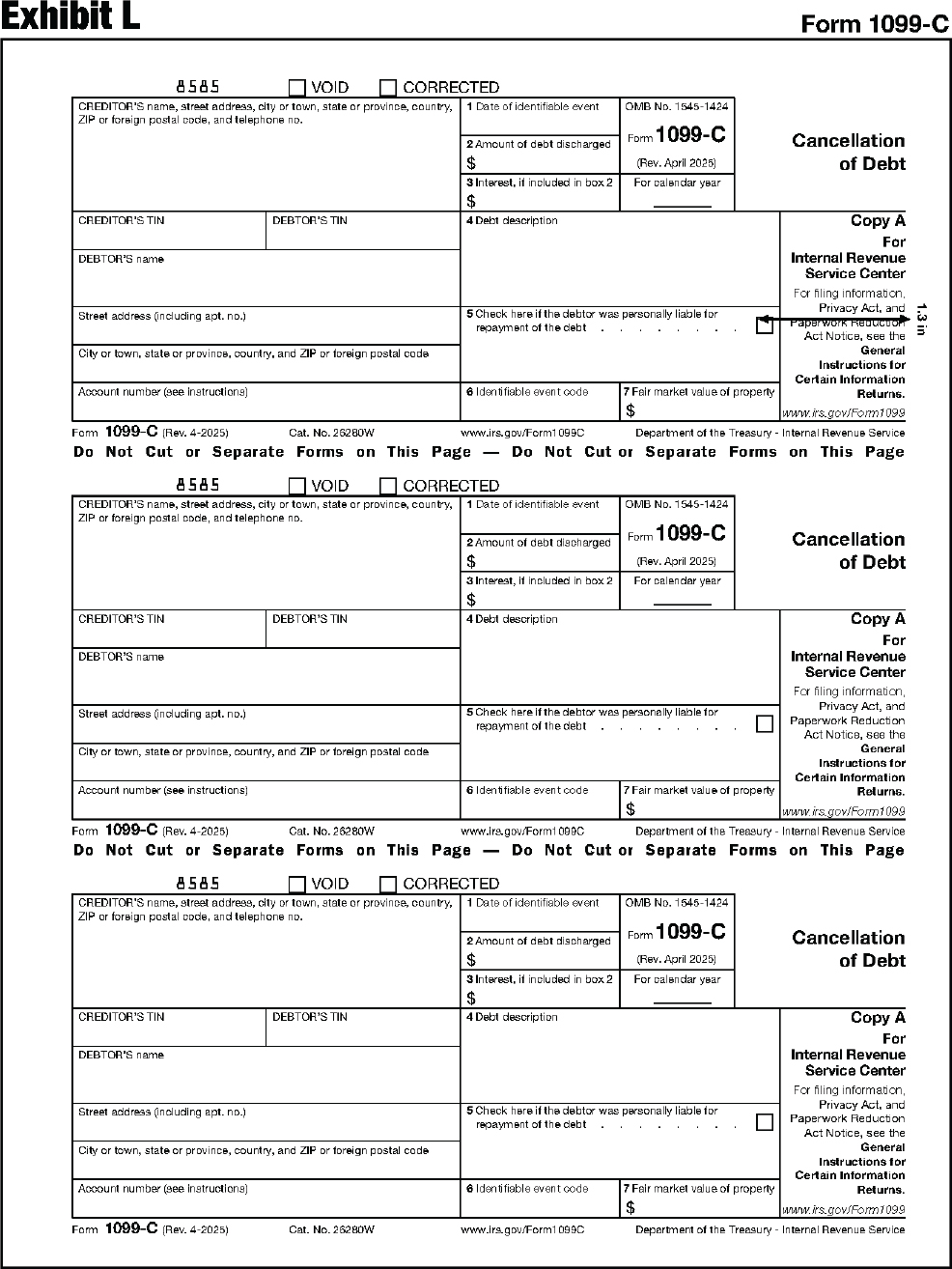
| 1099-C | Cancellation of Debt |
| 1099-CAP | Changes in Corporate Control and Capital Structure |
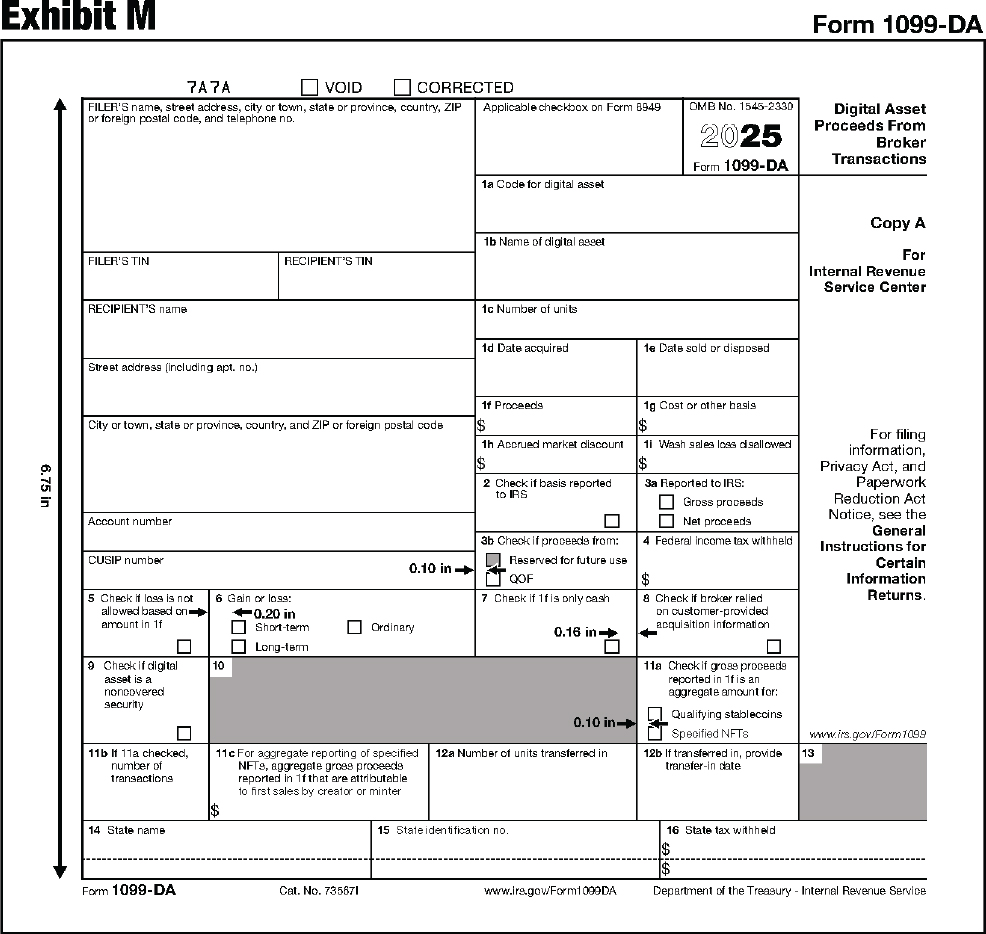
| 1099-DA | Digital Asset Proceeds From Broker Transactions |
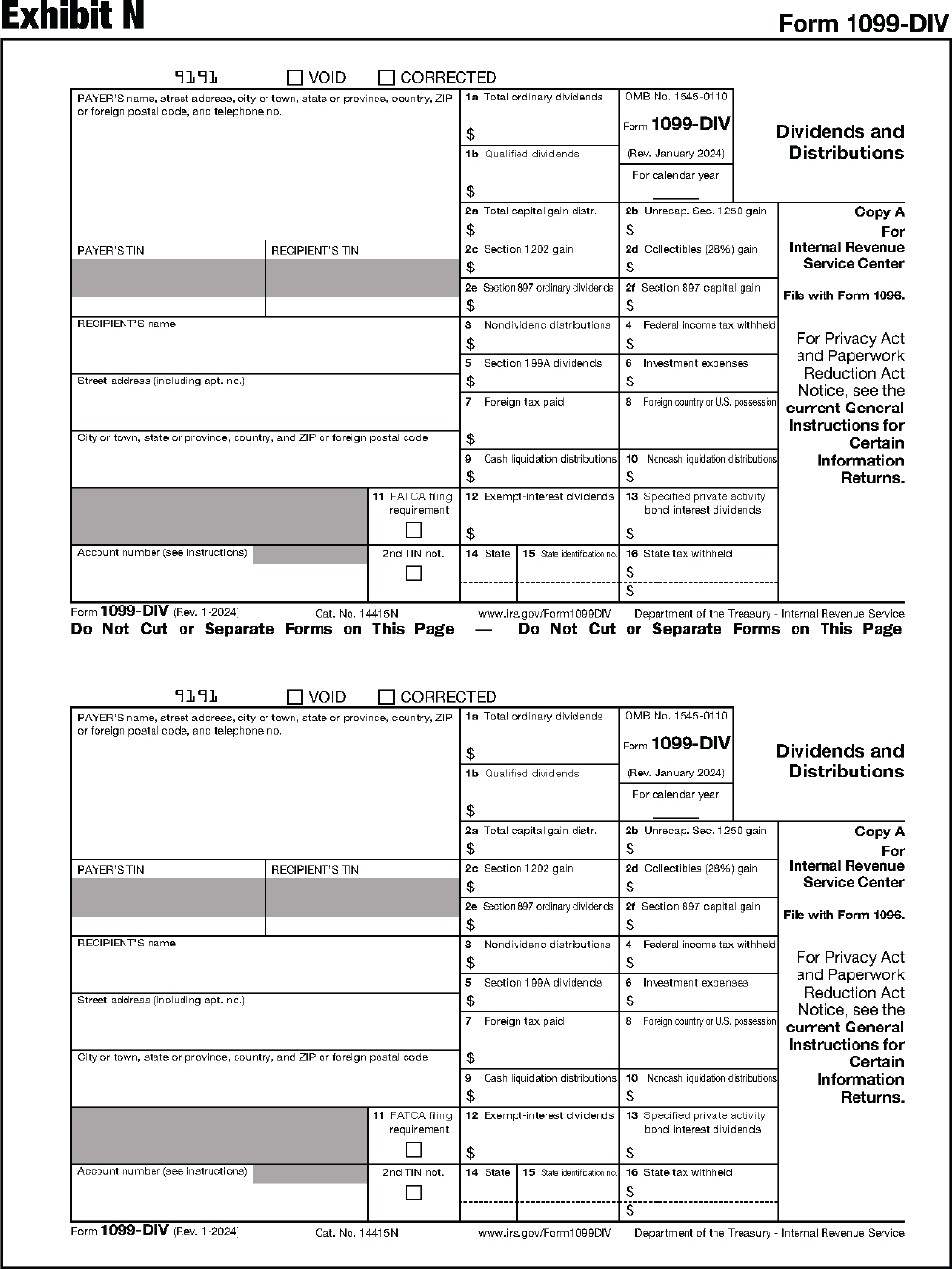
| 1099-DIV | Dividends and Distributions |
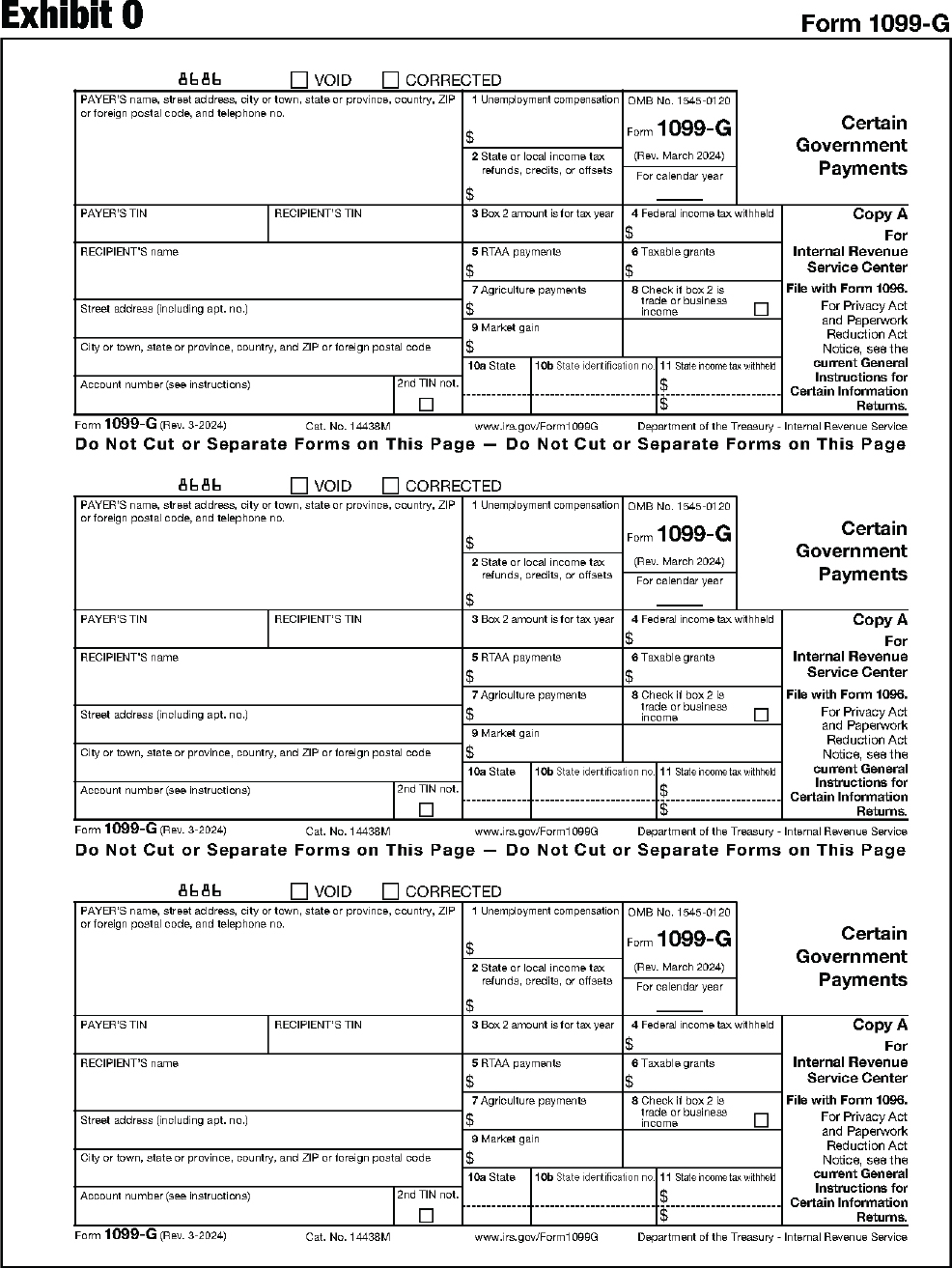
| 1099-G | Certain Government Payments |
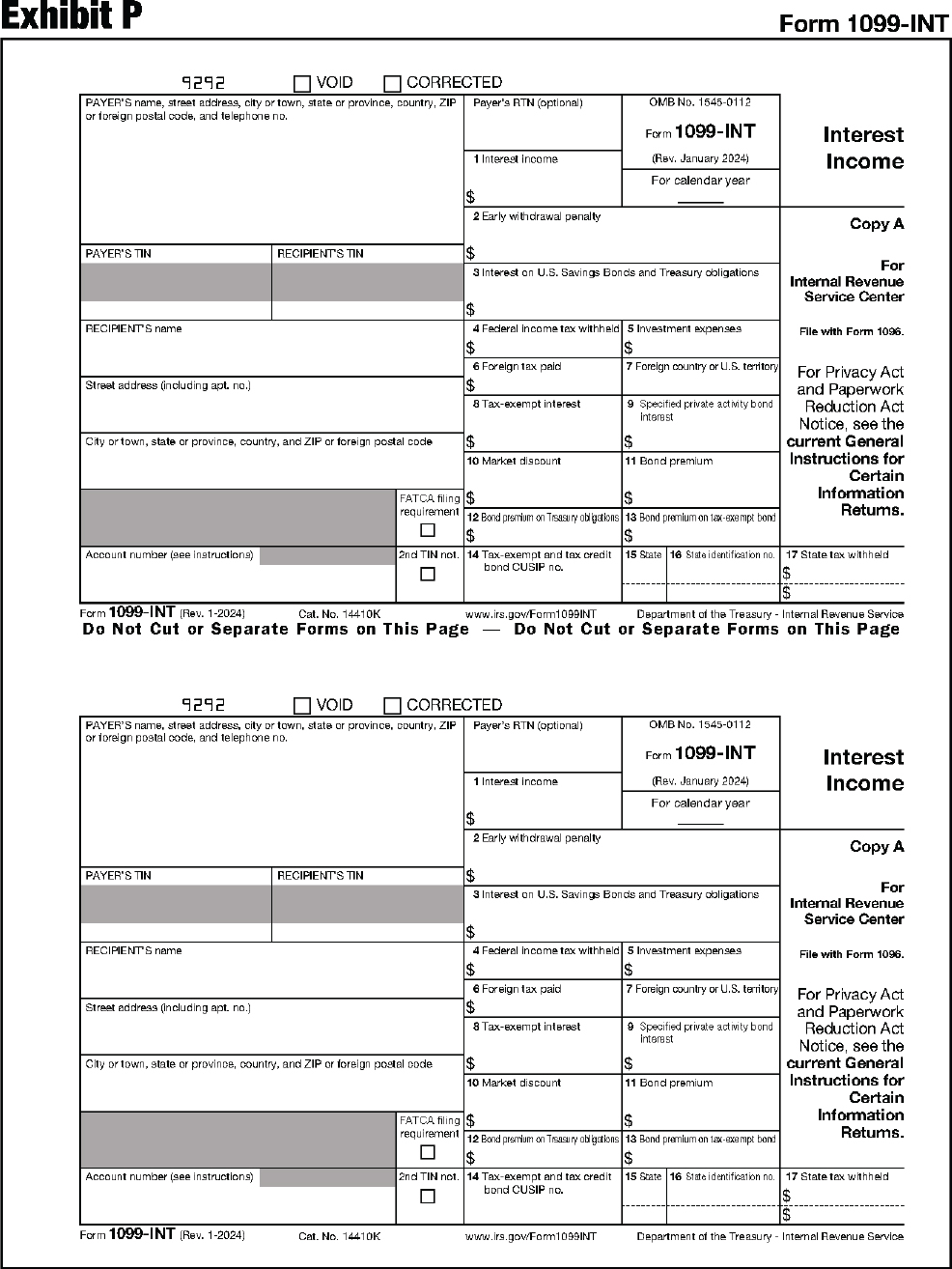
| 1099-INT | Interest Income |
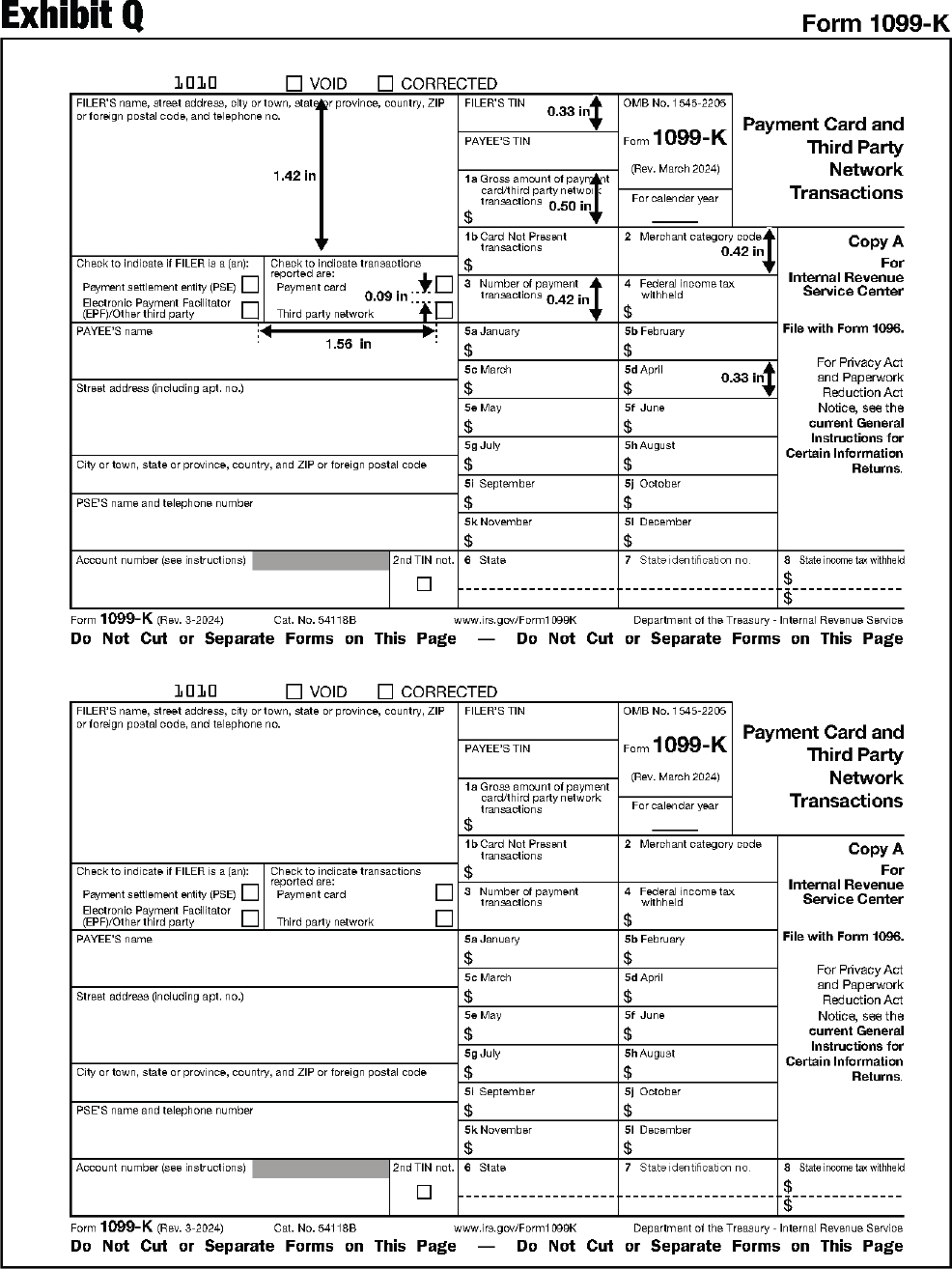
| 1099-K | Payment Card and Third Party Network Transactions |
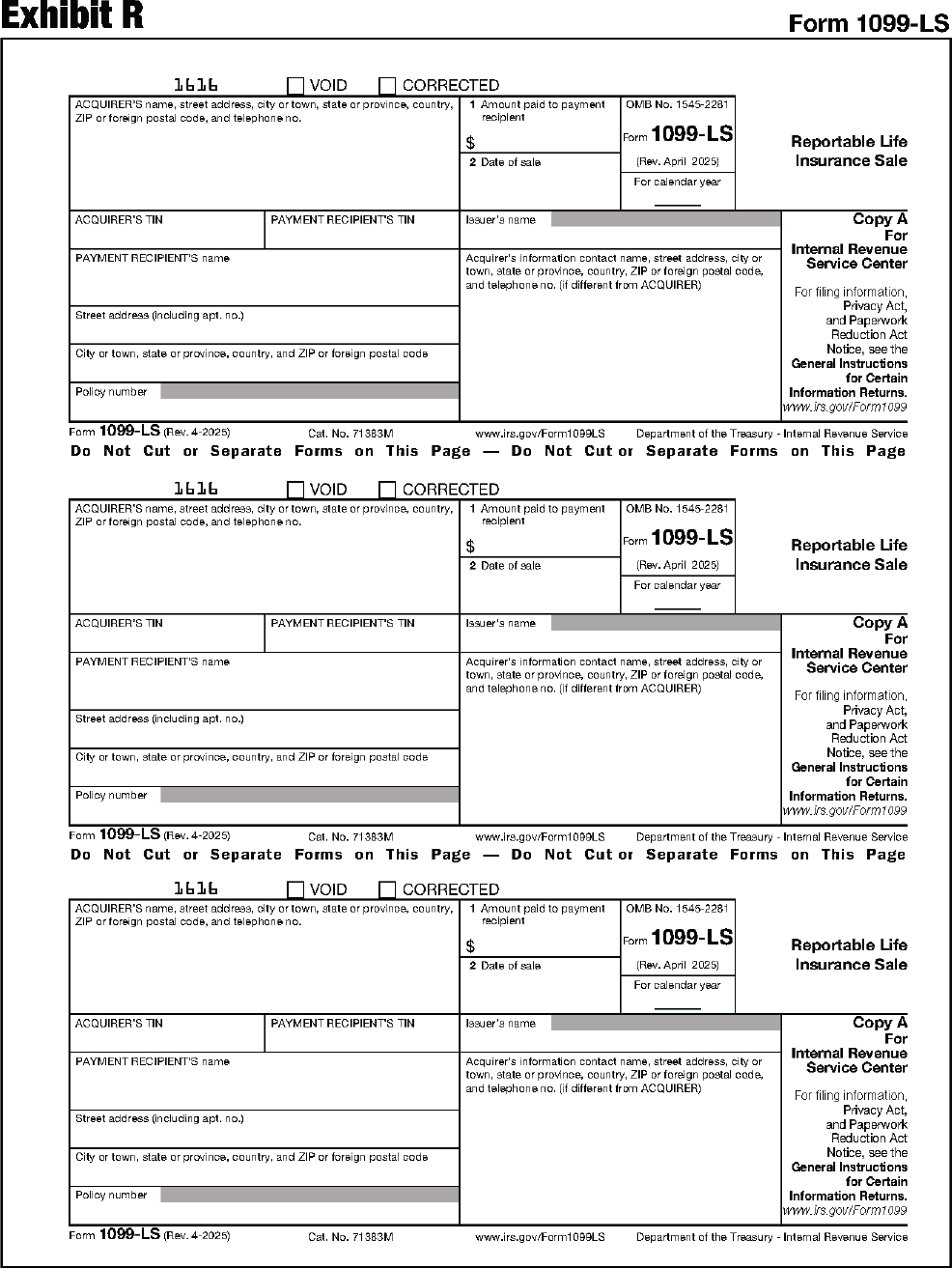
| 1099-LS | Reportable Life Insurance Sale |
| 1099-LTC | Long-Term Care and Accelerated Death Benefits |
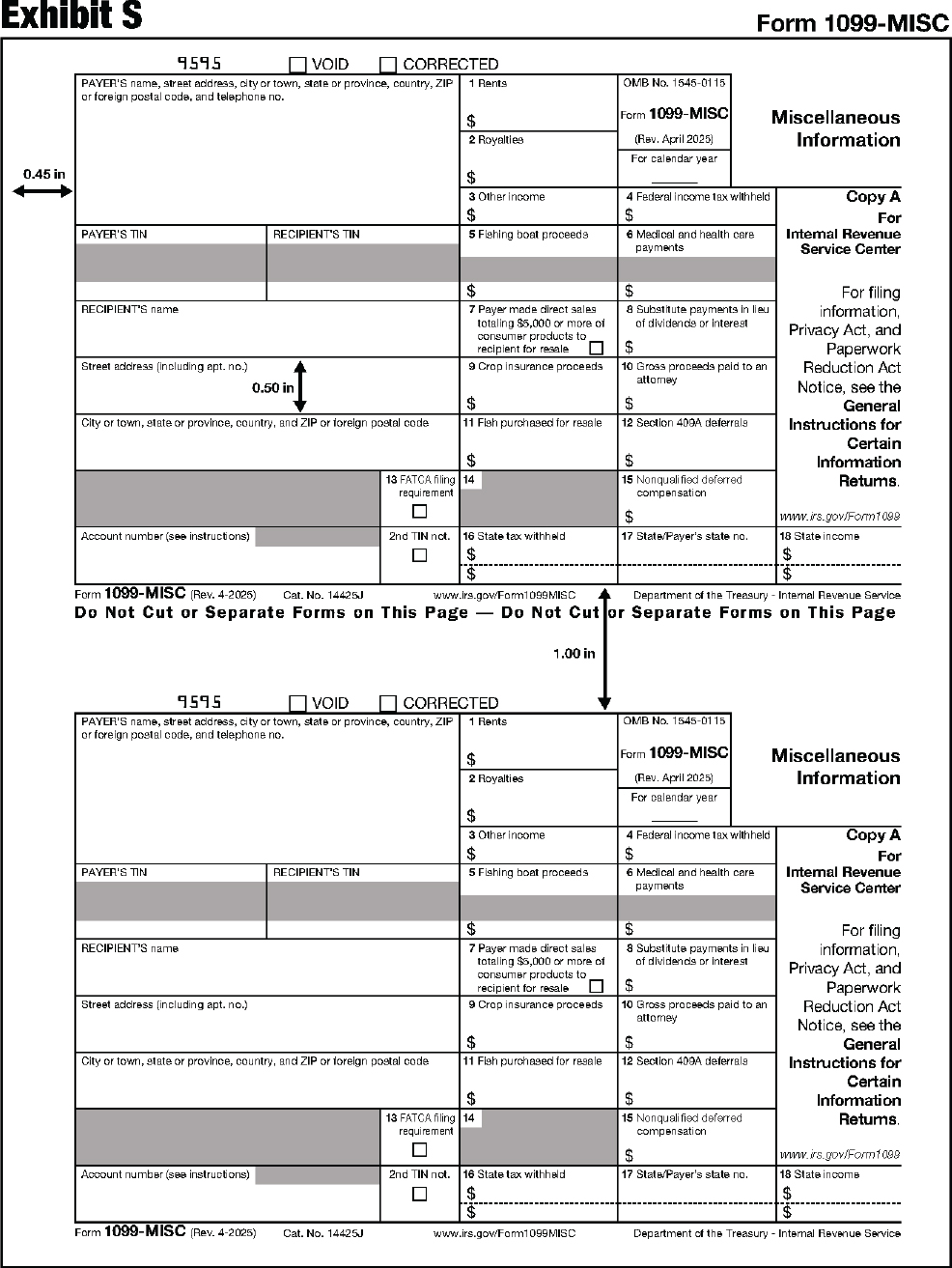
| 1099-MISC | Miscellaneous Information |
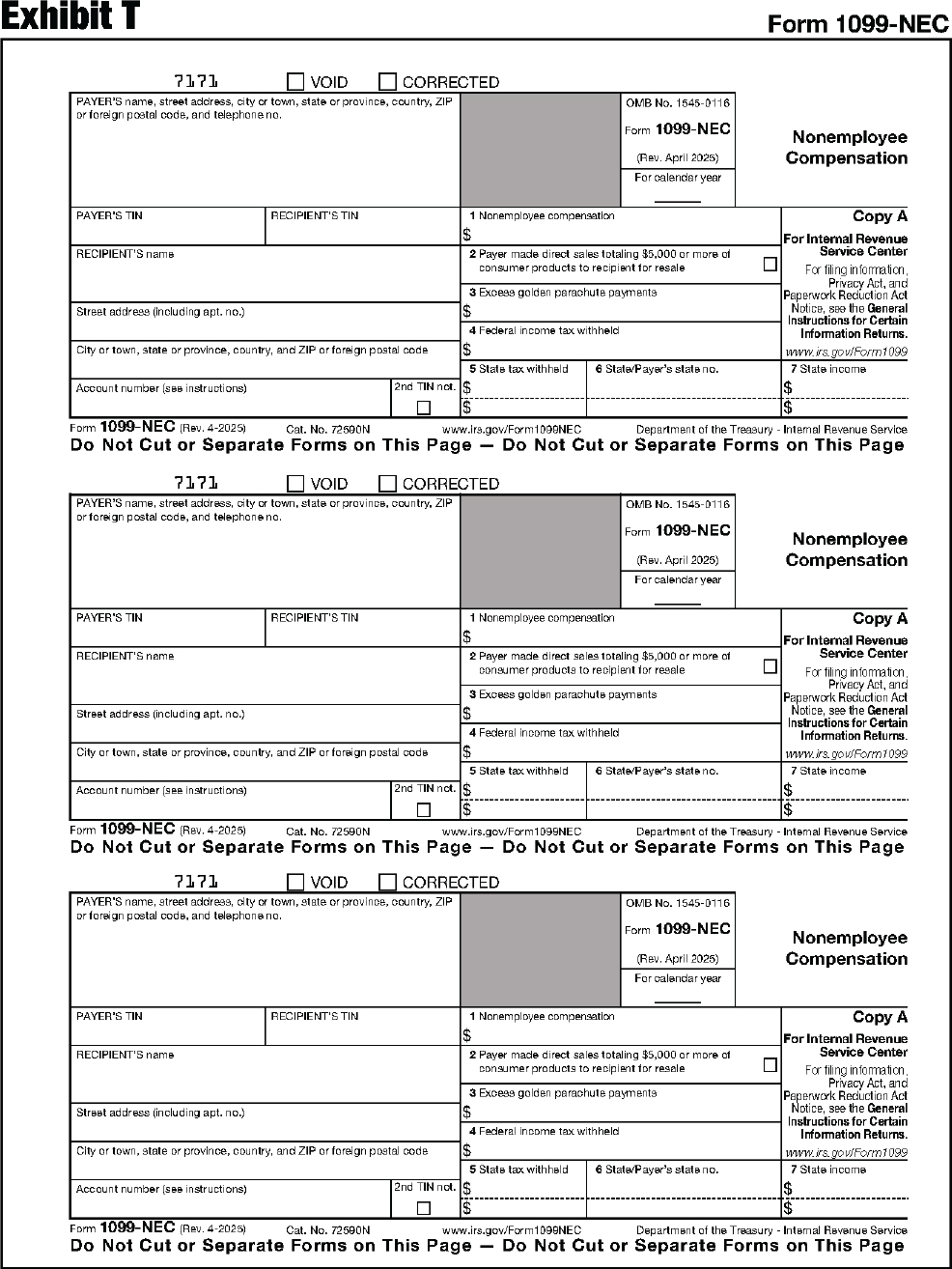
| 1099-NEC | Nonemployee Compensation |
| 1099-OID | Original Issue Discount |
| 1099-PATR | Taxable Distributions Received From Cooperatives |
| 1099-Q | Payments From Qualified Education Programs (Under Sections 529 and 530) |
| 1099-QA | Distributions From ABLE Accounts |
| 1099-R | Distributions From Pensions, Annuities, Retirement or Profit-Sharing Plans, IRAs, Insurance Contracts, etc. |
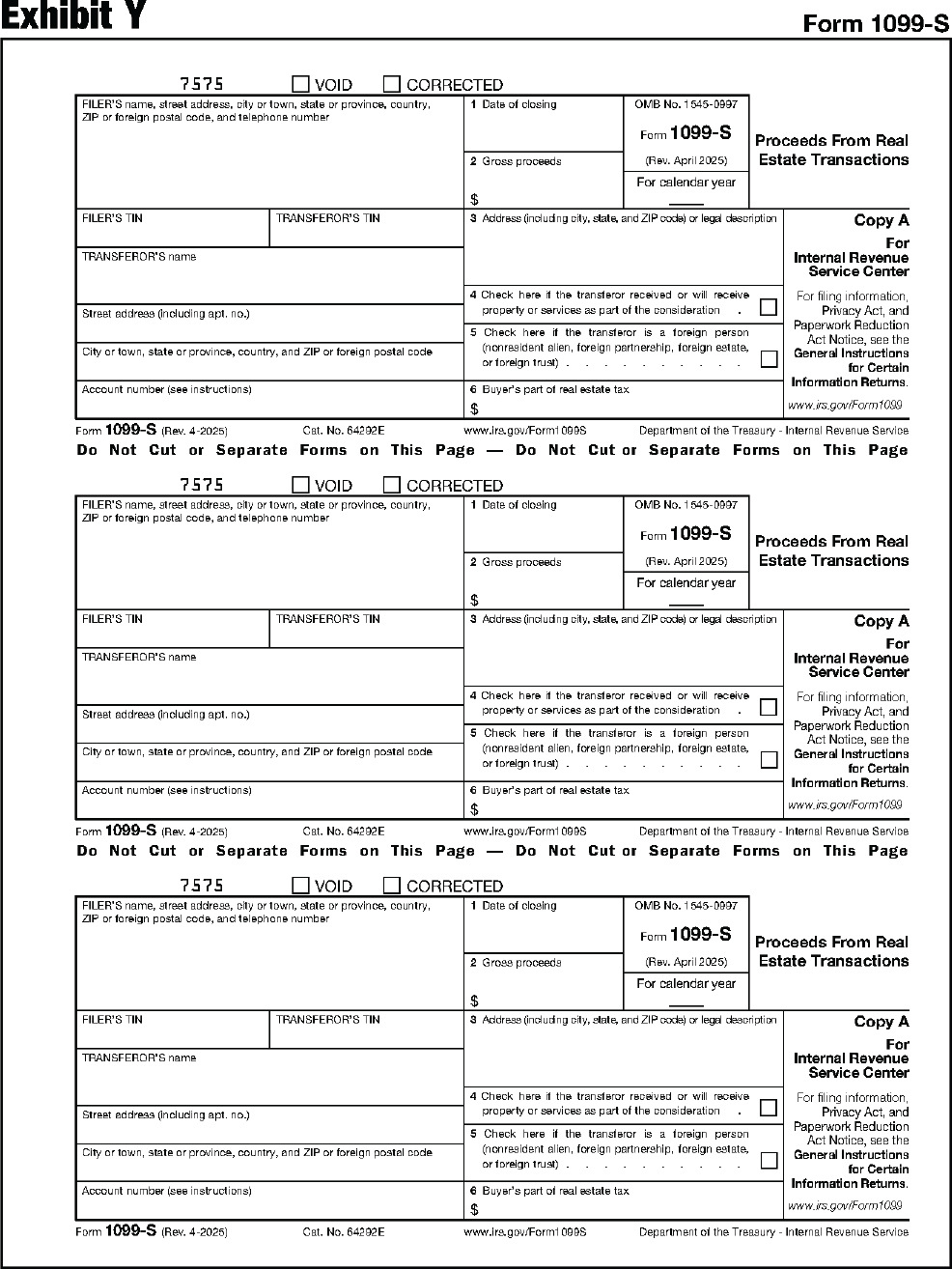
| 1099-S | Proceeds From Real Estate Transactions |
| 1099-SA | Distributions From an HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA |
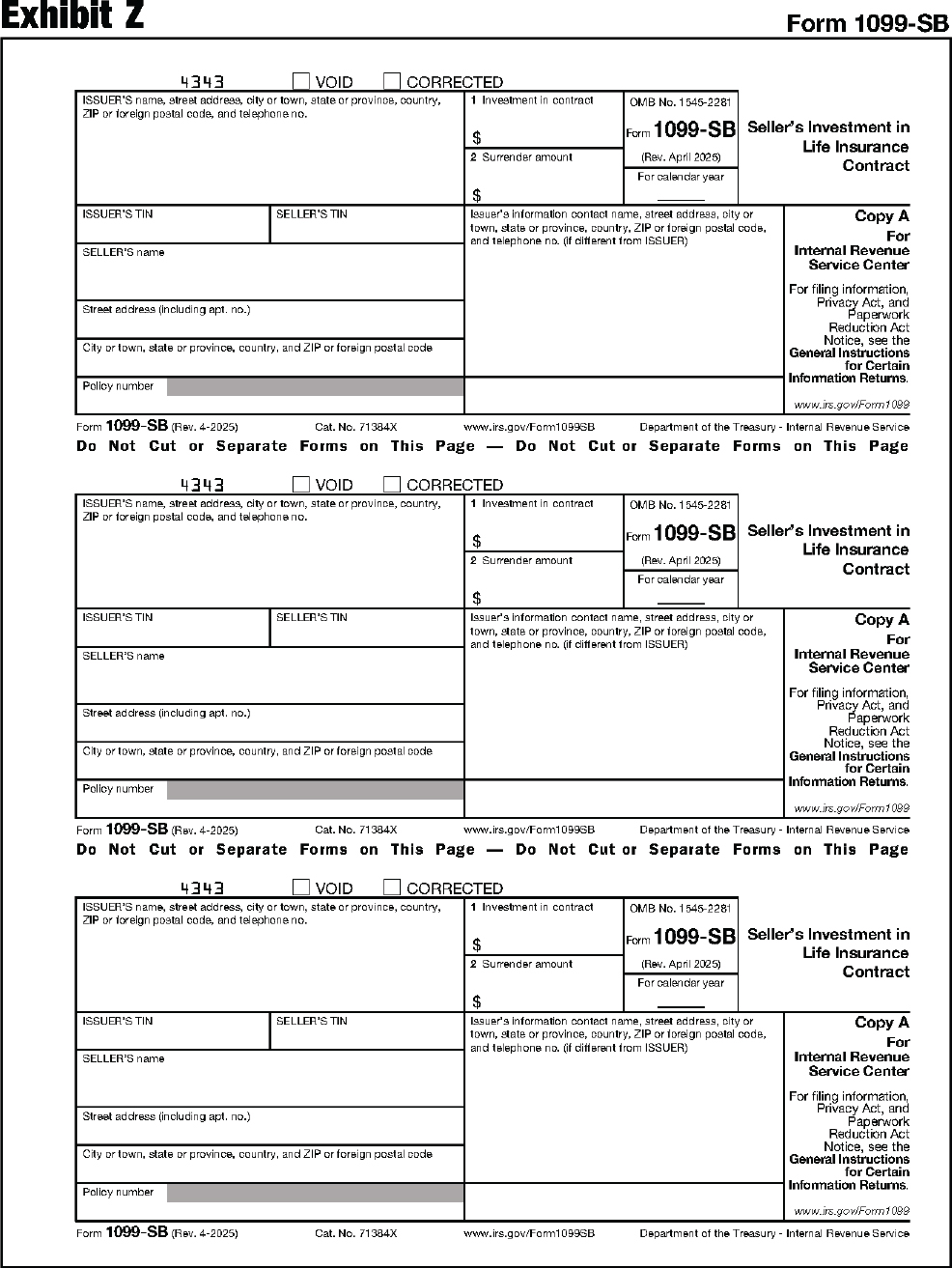
| 1099-SB | Seller's Investment in Life Insurance Contract |
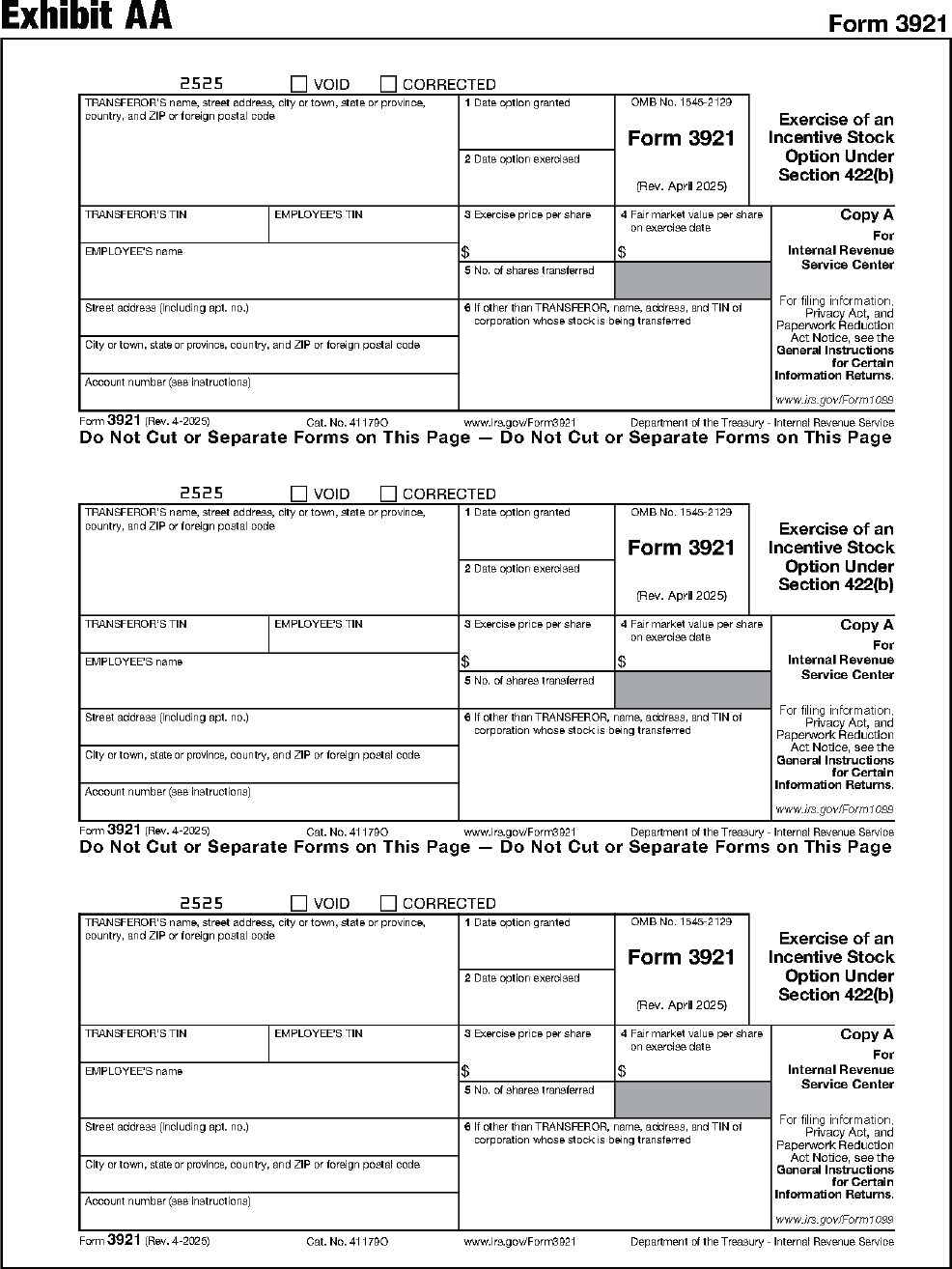
| 3921 | Exercise of an Incentive Stock Option Under Section 422(b) |
| 3922 | Transfer of Stock Acquired Through an Employee Stock Purchase Plan Under Section 423(c) |
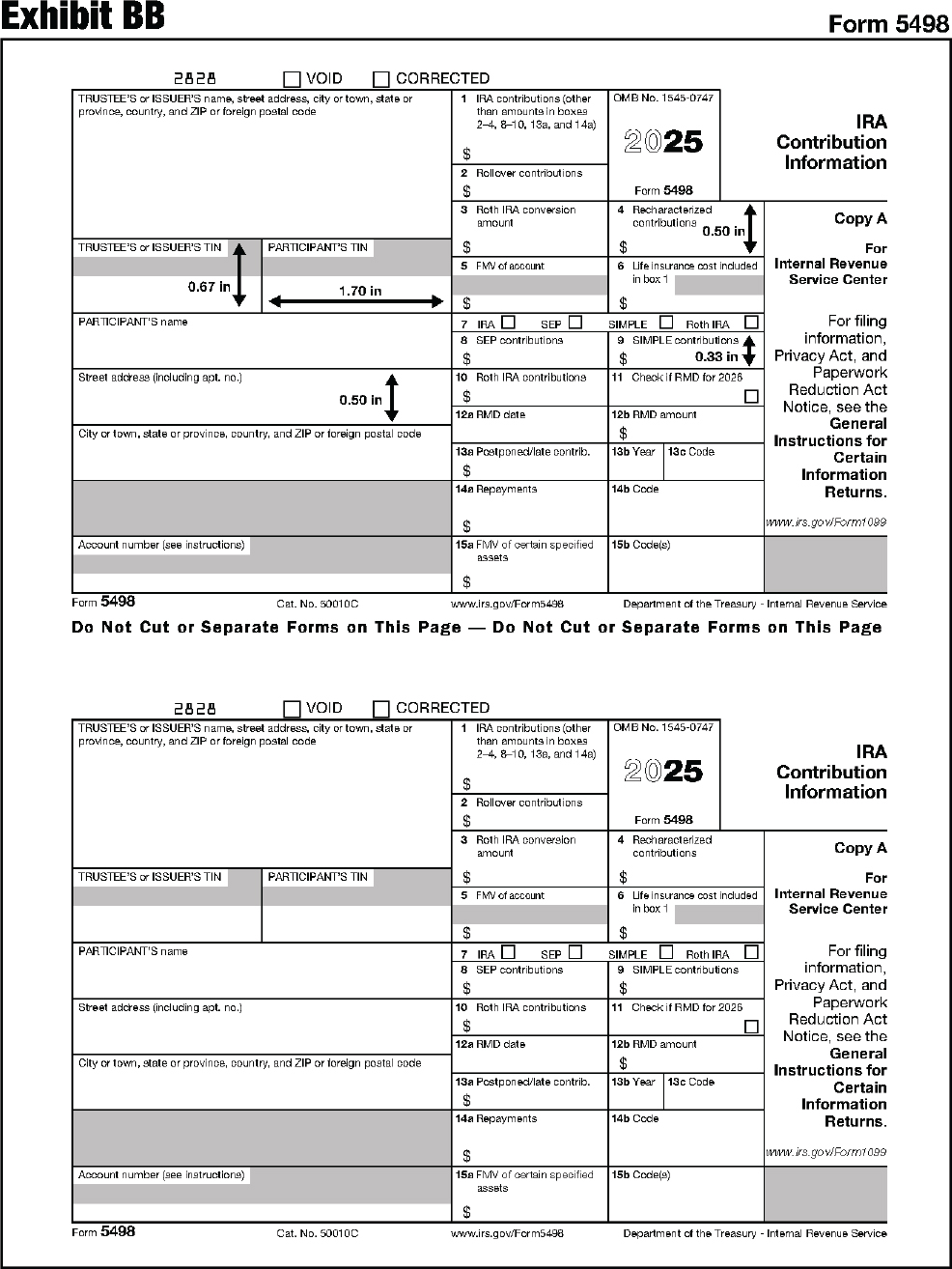
| 5498 | IRA Contribution Information |
| 5498-ESA | Coverdell ESA Contribution Information |
| 5498-QA | ABLE Account Contribution Information |
| 5498-SA | HSA, Archer MSA, or Medicare Advantage MSA Information |
| W-2G | Certain Gambling Winnings |
| 1042-S | Foreign Person’s U.S. Source Income Subject to Withholding |
For purposes of this revenue procedure, a substitute form or statement is one that is not published by the IRS. For a substitute form or statement to be acceptable to the IRS, it must conform to the official form or the specifications outlined in this revenue procedure. Do not submit any substitute forms or statements listed above to the IRS for approval. Privately published forms may not state, “This is an IRS approved form.”
Filers making payments to certain recipients during a calendar year are required by the Internal Revenue Code (the Code) to file information returns with the IRS for these payments. These filers must also provide this information to their recipients. In some cases, this also applies to payments received. See Part 4 for specifications that apply to recipient statements (generally Copy B).
In general, section 6011 of the Code authorizes the Secretary of Treasury to publish regulations that require filers to file information returns according to those regulations and the corresponding forms and instructions. A filer who is required to file 10 or more information returns during a calendar year must file those returns electronically. See Electronic filing of returns, later, for more information.
Caution. Financial institutions that are required to report payments made under chapter 3 or 4 must file Forms 1042-S electronically, regardless of the number of returns required to be filed.
Note. If you file electronically, do not file the same returns on paper.
Filers required to file fewer than 10 information returns during a calendar year are encouraged to file the information returns electronically. See the requirements for filing information returns (and providing a copy to a payee) in the current General Instructions for Certain Information Returns and the current Instructions for Form 1042-S. In addition, see the current revision of Pub. 1220, Specifications for Electronic Filing of Forms 1097, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, and W-2G, for electronic filing through the IRS Filing Information Returns Electronically (FIRE) system. Information Returns Intake System (IRIS) users should follow the specifications in Pub. 5717, Information Returns Intake System (IRIS) Taxpayer Portal User Guide.
The IRS prints and provides the forms on which various payments must be reported. See Section 5.3 for ordering forms and instructions. Alternately, filers may prepare substitute copies of these IRS forms and use such forms to report payments to the IRS.

The Internal Revenue Service/Technical Service Operation (IRS/TSO) maintains a centralized customer service call site to answer questions related to information returns (Forms W-2, W-3, W-2c, W-3c, 1099, 1096, etc.). You can reach the call site at 866-455-7438 (toll free) or outside the United States at 304-263-8700 (not a toll-free number). Deaf or hard-of-hearing customers may call any of our toll-free numbers using their choice of relay service.

Questions regarding the filing of information returns and comments/ suggestions regarding this publication can be emailed to fire@irs.gov. When you send emails concerning specific file information, include the company name and the electronic file name or Transmitter Control Code (TCC). Do not include taxpayer identification numbers (TINs) or attachments in email correspondence because electronic mail is not secure.

The IRS/TSO does not process information returns which are filed on paper forms. See Pub. 1220 for information on waivers and extensions of time.

For other tax information related to business returns or accounts, call 800-829-4933. Deaf or hard-of-hearing customers may call any of our toll-free numbers using their choice of relay service.

Further information impacting Pub. 1179, such as issues arising after its final release, will be posted on IRS.gov at IRS.gov/Pub1179.
The following changes have been made to this year’s revenue procedure. For further information about each form listed below, see the separate reporting instructions.
Removal of filer copy. In an ongoing process to reduce filer burden, we are removing the filer copy and instructions for the filer on forms.
New Form 1099-DA. Information about the new Form 1099-DA, Digital Asset Proceeds from Broker Transactions, has been added, throughout. For more information on the Form 1099-DA, go to IRS.gov/Form1099DA.
Form 1099-H. The Health Coverage Tax Credit expired on December 31, 2021. References to Form 1099-H have been removed.
Exhibits. All of the exhibits in this publication were updated to include all of the 2025 revisions of those forms that have been revised.
Editorial changes. We made editorial changes throughout, including updated references. Redundancies were eliminated as much as possible.
In addition to the general instructions, which contain general information concerning Forms 1096, 1097, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, and W-2G, specific form instructions are provided separately. Use the instructions to prepare acceptable substitutes of the official IRS forms to file information returns with the IRS.
-
Instructions for Form 1097-BTC.
-
Instructions for Form 1098.
-
Instructions for Form 1098-C.
-
Instructions for Forms 1098-E and 1098-T.
-
Instructions for Form 1098-F.
-
Instructions for Form 1098-Q.
-
Instructions for Forms 1099-A and 1099-C.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-B.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-CAP.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-DA.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-DIV.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-G.
-
Instructions for Forms 1099-INT and 1099-OID.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-K.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-LS.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-LTC.
-
Instructions for Forms 1099-MISC and 1099-NEC.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-PATR.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-Q.
-
Instructions for Forms 1099-QA and 5498-QA.
-
Instructions for Forms 1099-R and 5498.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-S.
-
Instructions for Form 1099-SB.
-
Instructions for Forms 3921 and 3922.
-
Instructions for Form 5498-ESA.
-
Instructions for Forms W-2G and 5754.
You can also obtain the latest developments for each of the forms and instructions listed here by going to their information pages at IRS.gov. See the separate instructions for each form on the webpage via the link.
Form recipient means the person to whom you are required by law to furnish a copy of the official form or information statement. The form recipient may be referred to by different names on various Forms 1099 and related forms (beneficiary, borrower, debtor, donor, employee, filer, homeowner, insured, participant, payee, payer, payer/borrower, payment recipient, policyholder, seller, shareholder, student, transferor, or, in the case of Form W-2G, the winner). See Section 1.3.4.
Filer means the person or organization required by law to file with the IRS a form listed in Section 1.1.2. A filer may be a payer, creditor, payment settlement entity, recipient of mortgage or student loan interest payments, educational institution, broker, barter exchange, or person reporting real estate transactions; a trustee or issuer of any educational or ABLE Act savings account, individual retirement arrangement, or medical savings account; a lender who acquires an interest in secured property or who has reason to know that the property has been abandoned; a corporation reporting a change in control and capital structure or transfer of stock to an employee; certain donees of motor vehicles, boats, and airplanes; or an acquirer or issuer of a life insurance contract.
Substitute form means a paper substitute of Copy A of an official form listed in Section 1.1.2 that completely conforms to the provisions in this revenue procedure.
Substitute form recipient statement means a paper or electronic statement of the information reported on a form listed in Section 1.1.2. For the remainder of this revenue procedure, we will refer to this as a “recipient statement.” This statement must be furnished to a person (form recipient), as defined under the applicable provisions of the Code and the applicable regulations.
Composite substitute statement means one in which two or more required statements (for example, Forms 1099-INT and 1099-DIV) are furnished to the recipient on one document. However, each statement must be designated separately and must contain all the requisite Form 1099 information except as provided under Section 4.2. A composite statement may not be filed with the IRS.
Paper substitutes for Form 1096 and Copy A of Forms 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, W-2G, and 1042-S that completely conform to the specifications listed in this revenue procedure may be privately printed and filed as returns with the IRS. The reference to the Department of the Treasury – Internal Revenue Service should be included on all such forms.
If you are uncertain of any specification and want it clarified, you may submit a letter citing the specification, stating your understanding and interpretation of the specification, and enclosing an example of the form (if appropriate) to:
Internal Revenue Service Attn: Substitute Forms Program C:DC:TS:CAR:MP:P:TP:TP ATSC 4800 Buford Highway Mail Stop 061-N Chamblee, GA 30341
Note. Allow at least 30 days for the IRS to respond.
You may also contact the Substitute Forms Program via email at substituteforms@irs.gov. Please enter “Substitute Forms” on the subject line.
Note. Do not send completed forms to the Substitute Forms Program via email or mail as they are unable to process those forms. Any examples/samples of substitute forms sent to the Substitute Forms Program should not contain taxpayer information.
Forms 1096, 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, W-2G, and 1042-S are subject to annual review and possible change. Therefore, filers are cautioned against overstocking supplies of privately printed substitutes.
Some Forms 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, W-2G, and 1042-S that include logos, slogans, and advertisements may not be recognized as important tax documents. A payee may not recognize the importance of the payee copy for tax reporting purposes due to the use of logos, slogans, and advertisements. Accordingly, the IRS has determined that logos, slogans, and advertising are not allowed on the payee copies of the above forms, on Copy A filed with the IRS, or on Form 1096, or on an envelope or enclosed in an envelope containing any of those documents, with the following exceptions.
-
The exact name of the payer, broker, or agent, primary trade name, trademark, service mark, or symbol of the payer, broker, or agent, an embossment or watermark on the information return and payee copies that is a representation of the name, a primary trade name, trademark, service mark, or symbol of the payer, broker, or agent, that is:
– Presented in any typeface, font, stylized fashion, or print color normally used by the payer, broker, or agent, and used in a non-intrusive manner; and
– As long as these items do not materially interfere with the ability of the recipient to recognize, understand, and use the tax information on the payee copies.
-
The IRS e-file logo on the IRS official payee copies may be included, but it is not required, on any of the substitute form copies.
-
Logos and slogans may be used on permissible enclosures, such as a check or account statement, other than information returns and payee copies.
The information return and payee copies must clearly identify the payer’s name associated with its employer identification number (EIN).
If you have comments about the restrictions on including logos, slogans, and advertising on information returns and payee copies, send your comments to:
Internal Revenue Service Attn: Substitute Forms Program C:DC:TS:CAR:MP:P:TP:TP ATSC 4800 Buford Highway Mail Stop 061-N Chamblee, GA 30341
or email them to substituteforms@irs.gov
Note. Do not send completed forms to the Substitute Forms Program via email or mail as they are unable to process those forms. Any examples/samples of substitute forms sent to the Substitute Forms Program should not contain taxpayer information.
Proposed substitutes of Copy A must be exact replicas of the official IRS form with respect to layout and content. Proposed substitutes for Copy A that do not conform to the specifications in this revenue procedure are not acceptable.
Further, if you file such forms with the IRS, you may be subject to a penalty for failure to file a correct information return under section 6721 of the Code. The amount of the penalty is based on when you file the correct information return.
Penalties. The amounts of the penalty for returns required to be filed in 2025 is shown under Penalties in part O of the 2025 General Instructions for Certain Information Returns.
Copy B and Copy C of the following forms must contain the information in Part 4 to be considered a “statement” or “official form” under the applicable provisions of the Code. The format of this information is at the discretion of the filer with the exception of the location of the tax year, the form number, the form name, and the information for composite Form 1099 statements, as outlined under Section 4.2.
Copy B of the forms below is for the following recipients.
| Form | Recipient |
|---|---|
| 1098 | For Payer/Borrower |
| 1098-C | For Donor |
| 1098-E; 1099-A | For Borrower |
| 1098-F | For Payer |
| 1098-MA | For Homeowner |
| 1098-Q | For Participant |
| 1098-T | For Student |
| 1099-C | For Debtor |
| 1099-CAP | For Shareholder |
| 1099-K | For Payee |
| 1099-LS | For Payment Recipient |
| 1099-LTC | For Policyholder |
| 1099-R; W-2G | Copy B may be required to be attached to the filer's federal income tax return. |
| 1099-S | For Transferor |
| 1099-SB | For Seller |
| All remaining Forms 1099; 1097-BTC; 1042-S | For Recipient |
| 3921; 3922 | For Employee |
| 5498; 5498-SA | For Participant |
| 5498-ESA; 5498-QA | For Beneficiary |
Copy C of the forms below is for the following recipients.
| Form | Recipient |
|---|---|
| 1098-C | For Donor’s Records |
| 1042-S | For Recipient |
| 3921 | For Corporation |
| 1099-LTC | For Insured |
| 1099-R | For Recipient’s Records |
| All other Forms 1099 | See Section 4.5.2. |
| W-2G | For Winner’s Records |
Note. On Copy C of Form 1099-LTC, you may reverse the locations of the policyholder’s and the insured’s name, street address, city, state, and ZIP code for easier mailing.
Due to the very low volume of paper Forms 1097-BTC, 1098-C, 1098-MA, 1099-CAP, 1099-LTC, 1099-Q, 1099-QA, 1099-SA, 3922, 5498-ESA, 5498-QA, and 5498-SA received and processed by the IRS each year, these forms have been converted to fillable online PDFs.
Note. The instructions for substitute Forms 1042-S, also available in a fillable online format, are found separately in Part 5.
These forms in their fillable formats can be found at IRS.gov/FormsPubs.
All the instructions regarding the substitute forms found in Part 1, and Sections 2.1.2, 2.1.7, 2.1.9, and 2.1.10, and the remainder of this publication, unless specified differently immediately below, remain in effect if you are going to produce the online fillable forms as paper or online substitute forms.
-
Copy A of privately printed substitutes of the forms listed above must be exact replicas of the official forms with respect to layout and content. Use the official form, found on IRS.gov, printed actual size on an 8½ inch by 11 inch sheet of paper. The forms will print one to a page.
-
All printing must be in high quality nongloss black ink.
-
Paper for Copy A must be white chemical wood bond, or equivalent, 20 pounds (basis 17 x 22-500), plus or minus 5% (0.05); or offset book paper, 50 pounds (basis 25 x 38-500). No optical brighteners may be added to the pulp or paper during manufacture. The paper must consist of principally bleached chemical wood pulp or recycled printed paper. It must also be suitably sized to accept ink without feathering.
Note. If you want to print the forms as they formerly appeared to save paper, with the exception of Forms 1097-BTC (printed 2-to-a-page) and 1098-C (single-form page), they are all printed 3-to-a-page. Follow the 3-to-a-page measurements in Section 6. Print the form to actual size with no scaling.
Form identifying numbers (for example, 9191 for Form 1099-DIV) must be printed in nonreflective black carbon-based ink in print positions 15 through 19 using an optical character recognition (OCR) A font. The checkboxes to the right of the form identifying numbers must be 10-point boxes. The “VOID” checkbox is in print position 25 (1.9 inches from left vertical line of the form). The “CORRECTED” checkbox is in print position 33 (2.7 inches from left vertical line of the form). Measurements are generally from the left edge of the paper, not including the perforated strip.
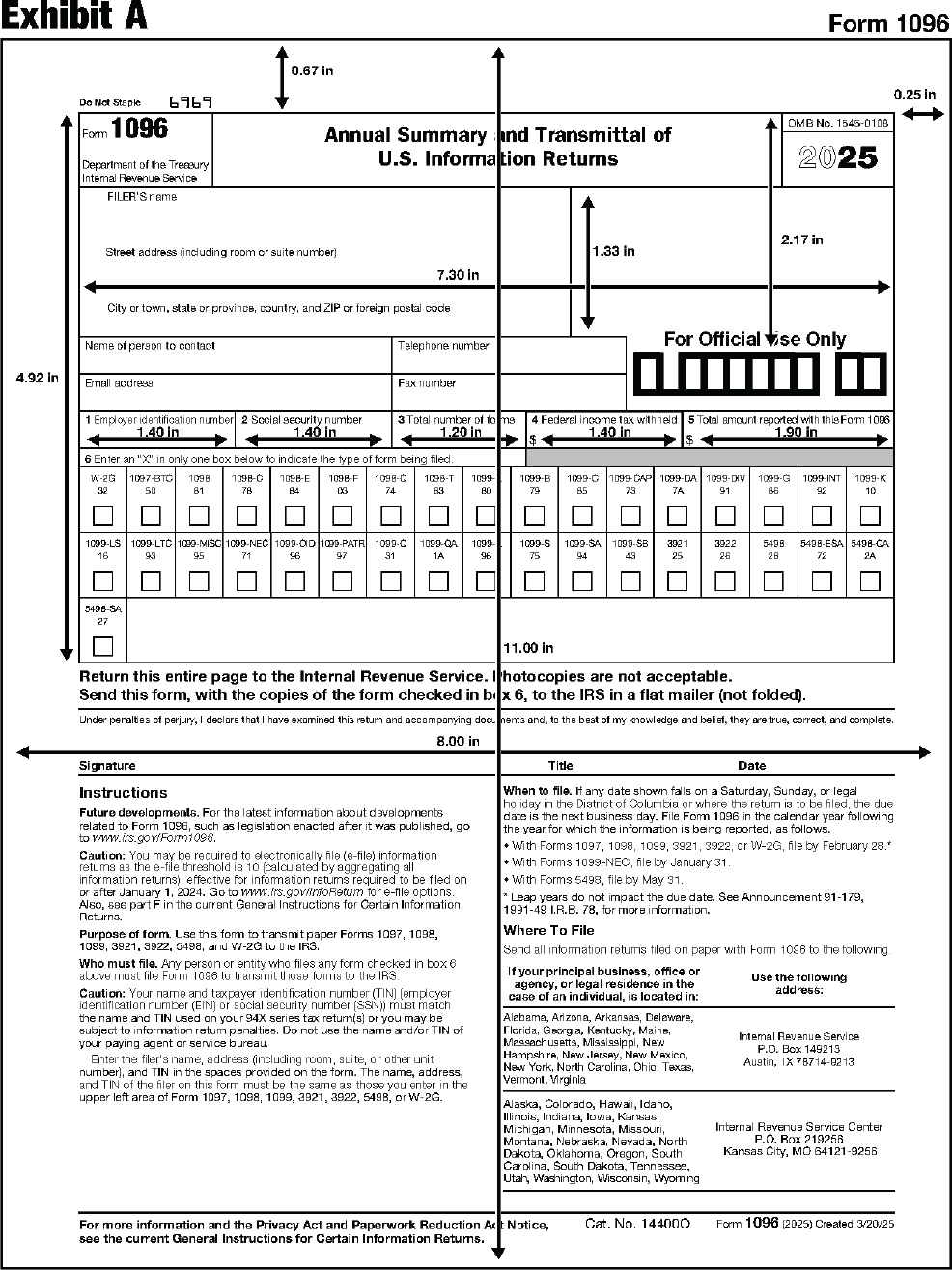
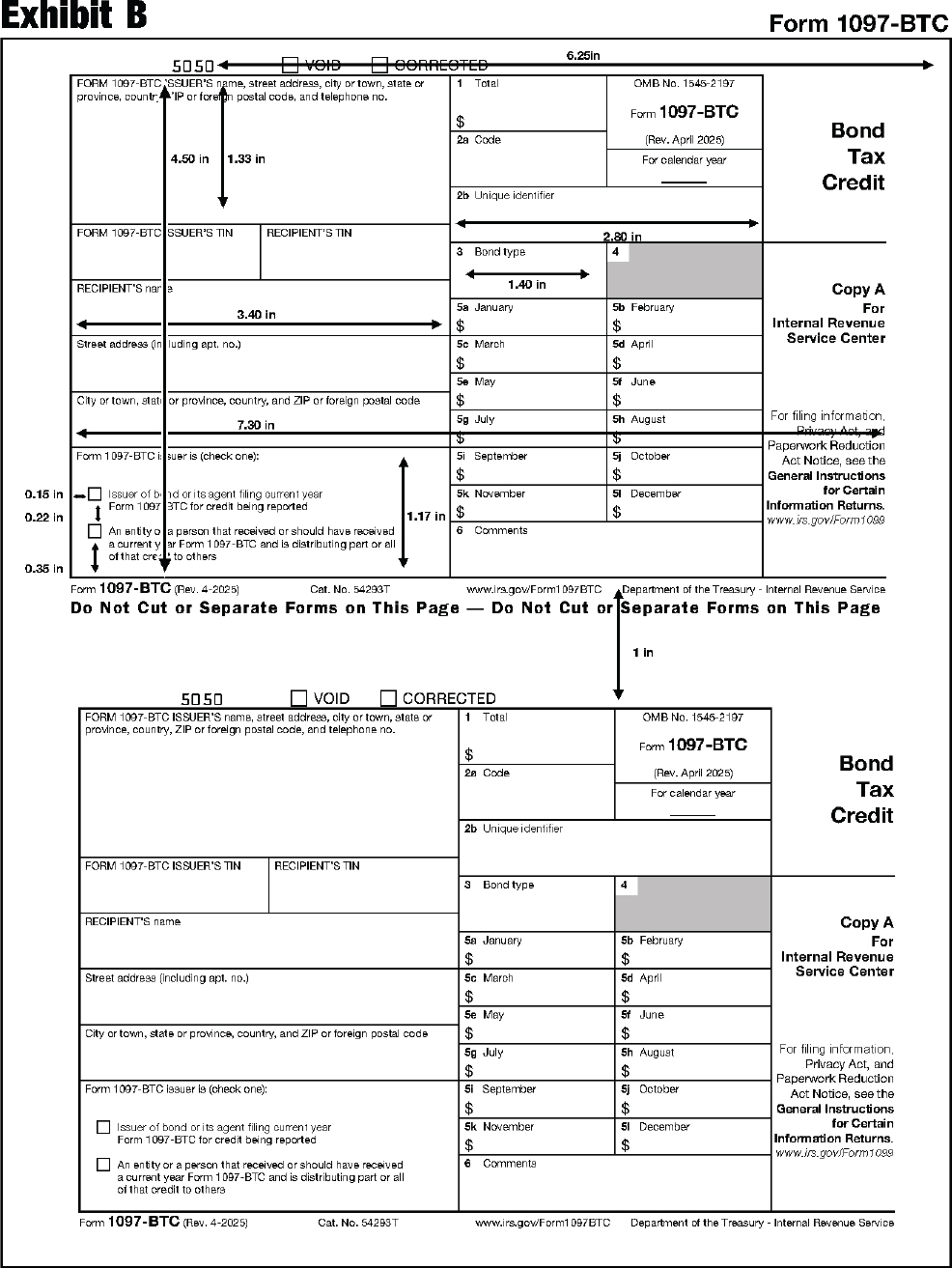
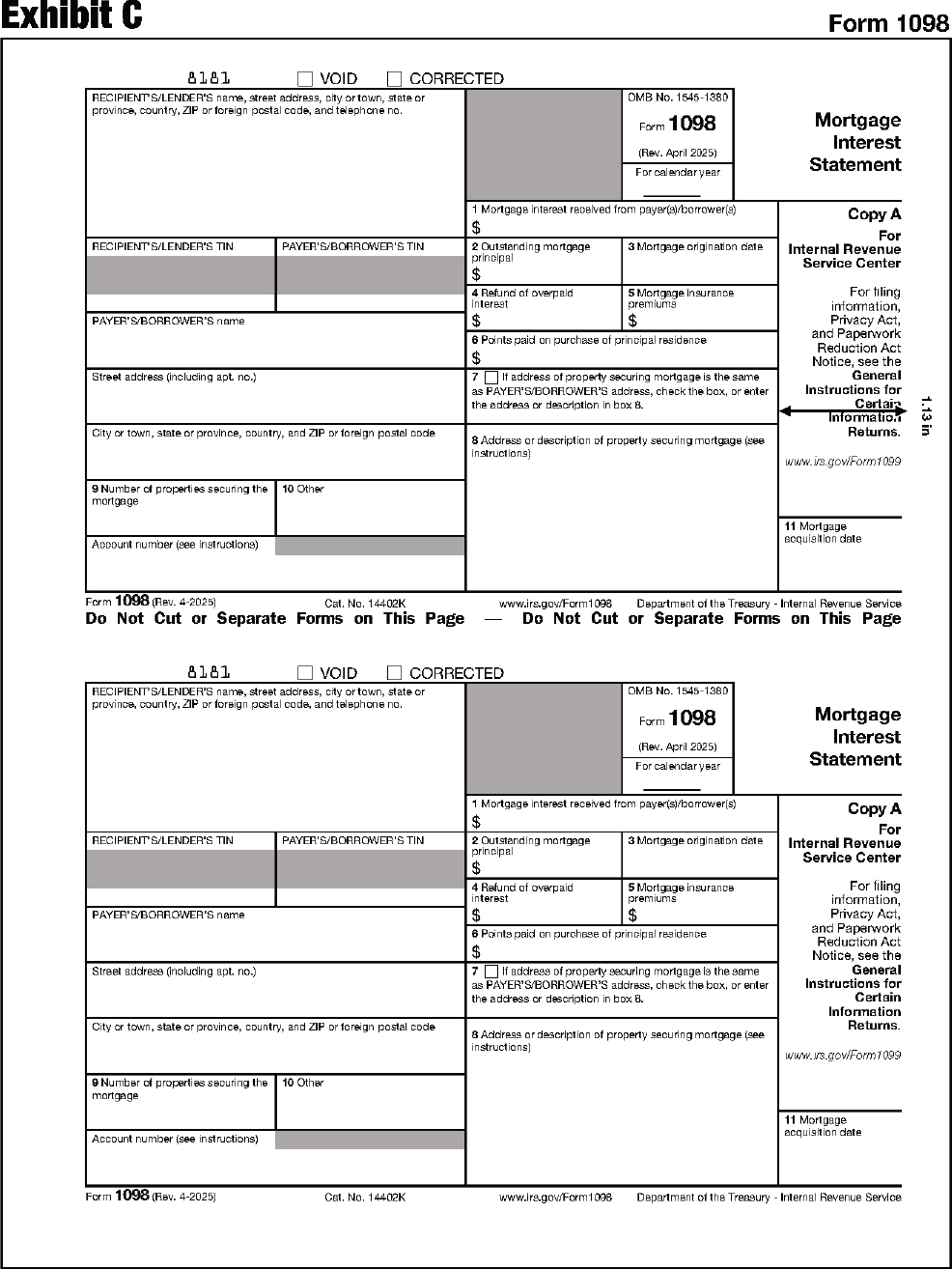
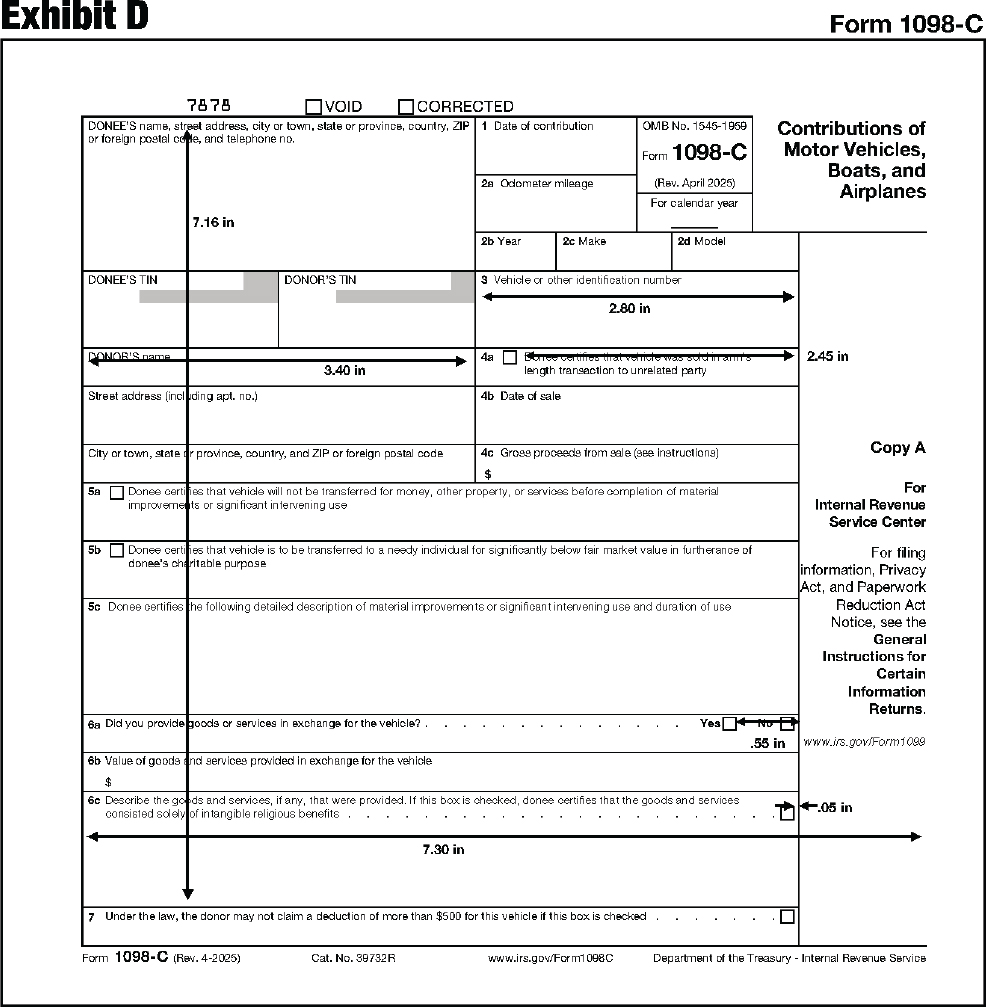
The substitute form Copy A must be an exact replica of the official IRS form with respect to layout and content. To determine the correct form measurements, see Exhibits A through DD at the end of this publication.
Hot wax and cold carbon spots are not permitted on any of the internal form plies. These spots are permitted on the back of a mailer top envelope ply.
Use of chemical transfer paper for Copy A is acceptable.
The Government Publishing Office (GPO) symbol must be deleted.
Color and paper quality for Copy A (cut sheets and continuous pinfeed forms) as specified by JCP Code 0-25, dated November 29, 1978, must be white 100% bleached chemical wood, OCR bond produced in accordance with the following specifications.
Note. Reclaimed fiber in any percentage is permitted, provided the requirements of this standard are met.
| Acidity: Ph value, average, not less than | 4.5 |
| Basis Weight: 17 x 22-500 cut sheets | 18-20 |
| Metric equivalent–g/m2 | 75 |
| A tolerance of ±5 pct. is allowed. | |
| Stiffness: Average, each direction, not less than-milligrams | 50 |
| Tearing strength: Average, each direction, not less than-grams | 40 |
| Opacity: Average, not less than-percent | 82 |
| Thickness: Average-inch | 0.0038 |
| Metric equivalent-mm | 0.097 |
| A tolerance of +0.0005 inch (0.0127 mm) is allowed. Paper cannot vary more than 0.0004 inch (0.0102 mm) from one edge to the other. | |
| Porosity: Average, not less than-seconds | 10 |
| Finish (smoothness): Average, each side-seconds | 20-55 |
| For information only, the Sheffield equivalent-units | 170-100 |
| Dirt: Average, each side, not to exceed-parts per million | 8 |
Chemical transfer paper is permitted for Copy A only if the following standards are met.
-
Only chemically backed paper is acceptable for Copy A. Front and back chemically treated paper cannot be processed properly by machine.
-
Carbon-coated forms are not permitted.
-
Chemically transferred images must be black.
All copies must be clearly legible. Fading must be minimized to assure legibility.
All print on Copy A of Forms 1098, 1098-E, 1098-F, 1098-Q, 1098-T, 1099-A, 1099-B, 1099-C, 1099-DA, 1099-DIV, 1099-G, 1099-INT, 1099-K, 1099-LS, 1099-MISC, 1099-NEC, 1099-OID, 1099-PATR, 1099-R, 1099-S, 1099-SB, 3921, and 5498; and the print on Form 1096 above the statement, “Return this entire page to the Internal Revenue Service. Photocopies are not acceptable.” must be in Flint J-6983 red OCR dropout ink or an exact match. However, the 4-digit form identifying number must be in nonreflective carbon-based black ink in OCR A font.
The shaded areas of any substitute form should generally correspond to the format of the official form.
The printing for the Form 1096 jurat statement and the text that follows may be in any shade or tone of black ink. Black ink should only appear on the lower part of the reverse side of Form 1096, where it will not bleed through and interfere with scanning.
Note. The instructions on the front and back of Form 1096, which include filing addresses, must be printed.
Separation between fields must be 0.1 inch.
Other printing requirements are discussed in Sections 2.1.6 through 2.1.10.
You must initiate, or have, a quality control program to assure OCR ink density. Readings will be made when printed on approved 20 lb. white OCR bond with a reflectance of not less than 80% (0.80). Black ink must not have a reflectance greater than 15% (0.15). These readings are based on requirements of the “BancTec IntelliScan XDS” Optical Scanner using Flint J-6983 red OCR dropout ink or an exact match.
The following testers and ranges are acceptable.
Important information: The forms produced under these specifications must be guaranteed to function properly when processed through High Speed Scan-Optics 9000 mm scanners. Forms require precision spacing, printing, and trimming.
Density readings on the solid Flint J-6983 (red) must be between the ranges of 0.95 to 0.90. The optimal scanning range is 0.93. Density readings on the solid black must be between the ranges of 112 to 108. The optimal scanning range is 110.
Note. The readings are taken using an Ex-Rite 500 series densitometer, in Status T with Absolute or – paper setting under an Illuminate 5000 Kelvin Watt Light. You must maintain print contrast specification of ink and densitometer reflectivity reading throughout the entire production run.
-
MacBeth PCM-II. The tested Print Contrast Signal (PCS) values when using the MacBeth PCM-II tester on the “C” scale must range from 0.01 minimum to 0.06 maximum.
-
Kidder 082A. The tested PCS values when using the Kidder 082A tester on the Infra Red (IR) scale must range from 0.12 minimum to 0.21 maximum. White calibration disc must be 100%. Sensitivity must be set at one (1).
-
Alternative testers must be approved by the IRS to establish tested PCS values. You may obtain approval by writing to the following address.
Internal Revenue Service Attn: Substitute Forms Program C:DC:TS:CAR:MP:P:TP:TP ATSC 4800 Buford Highway Mail Stop 061-N Chamblee, GA 30341
Type must be substantially identical in size and shape to the official form. All rules are either 1/2-point or 3/4-point. Rules must be identical to those on the official IRS form.
Note. The form identifying number must be nonreflective carbon-based black ink in OCR A font.
Generally, three Copies A of Forms 1098, 1099, 3921, and 3922 are contained on a single page (3-to-a-page), 8 inches wide (without any snap-stubs and/or pinfeed holes) by 11 inches deep.
Exceptions. Forms 1097-BTC, 1098, 1098-Q, 1099-B, 1099-DIV, 1099-INT, 1099-K, 1099-MISC, 1099-OID, 1099-R, and 5498 contain two copies on a single page (2-to-a-page). Forms 1098-C, 1099-DA, and 1042-S are single-page documents.
There is a 0.33-inch top margin from the top of the corrected box, and a 0.2- to 0.25-inch right margin, with a +/- 1/20 (0.05) inch tolerance for the right margin. If the right and top margins are properly aligned, the left margin for all forms will be correct. All margins must be free of print. See Exhibits A through DD in Part 6 for correct form measurements.
These measurements are constant for certain Forms 1098, 1099, and 5498. These measurements are shown only once in this publication, on Form 1097-BTC (Exhibit B) 2-to-a-page and on Form 1098-E (Exhibit E) 3-to-a-page.
Exceptions to these measurements, and form-specific measurements are shown on the rest of the exhibits.
The depth of the individual trim size of each 3-to-a-page form must be 32/3 inches, the same depth as the official form, unless otherwise indicated.
The depth of the individual trim size of each 2-to-a-page form is 51/2 inches.
Copy A (3-to-a-page and 2-to-a-page) of privately printed continuous substitute forms must be perforated at each 11 inches page depth. No perforations are allowed between forms on the Copy A page.
Exception. Copy A of Form W-2G may be perforated.
The words “Do Not Cut or Separate Forms on This Page” must be printed using Flint J-6983 red OCR dropout ink or an exact match (see Section 2.1.5) between the 3-to-a-page or 2-to-a-page. This statement should not be included after the last form on the page.
Separations are required between all the other individual copies in the set. Any recipient copies printed on a single sheet of paper must be easily separated. The best method of separation is to provide perforations between the individual copies. Each copy should be easily distinguished, whatever method of separation is used. See the table in Section 4.5.2 for a list of copies for each form.
Note. Perforation does not apply to printouts of copies that are furnished electronically to recipients (as described in Regulations section 31.6051-1(j)). However, these recipients should be cautioned to carefully separate any copies. See Section 4.6.1 for information on electronically furnishing statements to recipients.
You must include the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) number on Copies A and Form 1096 in the same location as on the official form.
The following Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice phrases must be printed on Copy A of the forms as follows.
-
“For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the current General Instructions for Certain Information Returns” on Forms 1099-DIV, 1099-G, 1099-INT, 1099-K, 1099-OID, and W-2G.
-
“For more information and the Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the current General Instructions for Certain Information Returns” on Form 1096.
-
“For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see instructions” on Form 1042-S.
-
“For filing information, Privacy Act, and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the General Instructions for Certain Information Returns” must be printed on all other forms listed in Section 1.1.2.
A postal indicia may be used if it meets the following criteria.
-
It is printed in the OCR ink color prescribed for the form.
-
No part of the indicia is within one print position of the scannable area.
The printer’s symbol (GPO) must not be printed on substitute Copy A. Instead, the EIN or the vendor code of the form’s printer must be entered in place of the Catalog Number (Cat. No.). The 4-digit vendor code, preceded by four zeros and a slash, for example, 0000/9876, must appear in 12-point Arial font, or a close approximation, on Copy A only of Forms 1096, 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, and W-2G. The vendor code is used to identify the forms producer. Vendor codes can be obtained free of charge from the National Association of Computerized Tax Processors (NACTP) via email at president@nactp.org. The use of a vendor code is recommended.
Note. Vendor codes from the NACTP are required by those companies producing the 1099 family of forms (Forms 1096, 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, and W-2G) as part of a product for resale to be used by multiple issuers. Issuers developing 1099 family forms to be used only for their individual companies do not require a vendor code.
The Cat. No. shown on the forms is used for IRS distribution purposes and should not be printed on any substitute forms.
The form must not contain the statement “IRS approved” or any similar statement.
Section 2.2 – Instructions for Preparing Paper Forms That Will Be Filed With the IRS
The form recipient’s name, street address, city, state, ZIP code, and telephone number (if required) should be typed or machine printed in black ink in the same format as shown on the official IRS form. The city, state, and ZIP code must be on the same line.
The following rules apply to the form recipient’s name(s).
-
The name of the appropriate form recipient must be shown on the first or second name line in the area provided for the form recipient’s name.
-
No descriptive information or other name may precede the form recipient’s name.
-
Only one form recipient’s name may appear on the first name line of the form.
-
If multiple recipients’ names are required on the form, enter on the first name line the recipient name that corresponds to the recipient TIN shown on the form. Place the other form recipients’ names on the second name line (only 2 name lines are allowable).
Because certain states require that trust accounts be provided in a different format, filers should generally provide information returns reflecting payments to trust accounts with the:
-
Trust’s EIN in the recipient’s TIN area,
-
Trust’s name on the recipient’s first name line, and
-
Name of the trustee on the recipient’s second name line.
Although handwritten forms will be accepted, the IRS prefers that filers type or machine print data entries. Also, filers should insert data as directed by shading, or in the middle of blocks, well separated from other printing and guidelines, and take measures to guarantee clear, dark black, sharp images. Photocopies are not acceptable.
Truncating payee TIN on payee statements. Where permitted, filers may truncate a payee’s TIN (social security number (SSN), individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN), adoption taxpayer identification number (ATIN), or EIN) on the payee statement (including substitute and composite substitute statements) furnished to the payee in paper form or electronically. Generally, the payee statement is that copy of an information return designated “Copy B” on the form. To truncate where allowed, replace the first 5 digits of the 9-digit number with asterisks (*) or Xs (for example, an SSN xxx-xx-xxxx would appear on the paper payee statement as ***-**-xxxx or XXX-XX-xxxx). See Treasury Decision 9675, 2014-31 I.R.B. 242, available at IRS.gov/irb/2014-31_IRB#TD-9675.
Caution. Recipient TINs must not be truncated on Copy A filed with the IRS.
Use the account number box on all Forms 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, 5498, and W-2G for an account number designation when required by the official IRS form. The account number is required if you have multiple accounts for a recipient for whom you are filing more than one information return of the same type. Additionally, the IRS encourages you to include the recipients’ account numbers on paper forms if your system of records uses the account number rather than the name or TIN for identification purposes. Also, the IRS will include the account number in future notices to you about backup withholding. If you are using window envelopes to mail statements to recipients and using reduced rate mail, be sure the account number does not appear in the window. The Postal Service may not accept these for reduced rate mail.
Exception. Form 1098-T can have third-party provider information.
-
Machine-printed forms should be printed using a 6 lines/inch option, and should be printed in 10 pitch pica (10 print positions per inch) or 12 pitch elite (12 print positions per inch). Proportional spaced fonts are unacceptable.
-
Substitute forms prepared in continuous or strip form must be burst and stripped to conform to the size specified for a single sheet before they are filed with the IRS. The size specified does not include pinfeed holes. Pinfeed holes must not be present on forms filed with the IRS.
-
Do not use a felt tip marker. The machine used to “read” paper forms generally cannot read this ink type.
-
Do not use dollar signs ($), ampersands (&), asterisks (*), commas (,), or other special characters in the numbered money boxes. Exception. Use decimal points to indicate dollars and cents (for example, 2000.00 is acceptable).
-
Do not use apostrophes (’), asterisks (*), or other special characters on the payee name line.
-
Do not fold Forms 1097-BTC, 1098, 1099, 3921, 3922, or 5498 mailed to the IRS. Mail these forms flat in an appropriately sized envelope or box. Folded documents cannot be readily moved through the machine used in IRS processing.
-
Do not staple Forms 1096 to the transmitted returns. Any staple holes near the return code number may impair the IRS’s ability to machine scan these types of documents.
-
Do not type other information on Copy A.
-
Do not cut or separate the individual forms on the sheet of forms of Copy A (except Forms W-2G).
Mail completed paper forms to the IRS Service Center shown in the instructions for Form 1096 and in the current General Instructions for Certain Information Returns. Specific information needed to complete the forms mentioned in this revenue procedure are given in the specific form instructions. A chart showing which form must be filed to report a particular payment is included in the current General Instructions for Certain Information Returns.
The following specifications give the format requirements for substitute Form W-2G (Copy A only), which is filed with the IRS.
A filer may use a substitute Form W-2G to file with the IRS (referred to as “substitute Copy A”). The substitute form must be an exact replica of the official form with respect to layout and content.
You must follow these specifications when printing substitute Copy A of the Form W-2G.
Caution. The payee’s TIN (SSN, ITIN, ATIN, or EIN) must not be truncated on Copy A of Form W-2G.
| Item | Substitute Form W-2G (Copy A) |
|---|---|
| Paper Color and Quality | Paper for Copy A must be white chemical wood bond, or equivalent, 20 pounds (basis 17 x 22-500), plus or minus 5% (0.05). The paper must consist substantially of bleached chemical wood pulp. It must be free from unbleached or ground wood pulp or post-consumer recycled paper. It must also be suitably sized to accept ink without feathering. |
| Ink Color and Quality | All printing must be in a high quality nongloss black ink. |
| Typography | The type must be substantially identical in size and shape to the official form. All rules on the document are either 1/2 point (0.007 inch), 1 point (0.015 inch), or 3 point (0.045 inch). Vertical rules must be parallel to the left edge of the document; horizontal rules to the top edge. |
| Dimensions | The official form is 8 inches wide x 51/2 inches deep, exclusive of a snap stub. Any substitute Copy A can be between 8 inches and 81/2 inches wide by 5 inches deep. The snap feature is not required on substitutes. All margins must be free of print. There is a 0.33-inch top margin from the top of the corrected box, and a 1/2-inch left margin. If the top and left margins are properly aligned, the right margin for all forms will be correct. If the substitute forms are in continuous or strip form, they must be burst and stripped to conform to the size specified for a single form. |
| Hot Wax and Cold Carbon Spots | Hot wax and cold carbon spots are not permitted on any of the internal form plies. These spots are permitted on the back of a mailer top envelope ply. |
| Printer’s Symbol | The GPO symbol must not be printed on substitute Forms W-2G. Instead, the EIN of the form’s printer must be printed in the bottom margin on the face of each individual Copy A on a sheet. The form must not contain the statement “IRS approved” or any similar statement. |
| Cat. No. | The Cat. No. shown on Form W-2G is used for IRS distribution purposes and should not be printed on any substitute forms. |
If you do not use the official IRS form to furnish statements to recipients, you must furnish an acceptable substitute statement. Information presented in substitute statements should be in a point size large enough to be easily read by recipients. To be acceptable, your substitute statement must comply with the rules in this part. If you are furnishing a substitute form, see Regulations sections 1.6042-4, 1.6044-5, 1.6049-6, and 1.6050N-1 to determine how the following statements must be provided to recipients for most Forms 1099-DIV and 1099-INT, all Forms 1099-OID and 1099-PATR, and Form 1099-MISC, or Form 1099-S for royalties. Generally, information returns may be furnished electronically with the consent of the recipient. See Section 4.6.1.
Note. A trustee of a grantor-type trust may choose to file Forms 1099 and furnish a statement to the grantor under Regulations sections 1.671-4(b)(2)(iii) and (b)(3)(ii). The statement required by those regulations is not subject to the requirements outlined in this section.
The rules in this section apply to Forms 1099-B, 1099-DA, 1099-DIV (except for section 404(k) dividends), 1099-INT (except for interest reportable under section 6041), 1099-OID, and 1099-PATR only. You may furnish form recipients with Copy B of the official Form 1099 or a substitute Form 1099 (recipient statement) if it contains the same information as the official IRS form (such as aggregate amounts paid to the form recipient; any backup withholding; the name, address, and TIN of the person making the return; and any other information required by the official form). Information not required by the official form should not be included on the substitute form except for state income tax withholding information. But see Section 4.3 regarding additional information that may be included on substitute and composite Forms 1099-B and 1099-DA, such as basis for noncovered securities.
Note. Many of the information returns now include boxes for providing state withholding information as part of the official form, with additional copies for convenience. Payers may, however, provide the state withholding information separately (such as on a separate page or section) in order to assist the payee with completing a state income tax return that requires the attachment of any information return that includes state withholding amounts and payer numbers.
Exception for supplementary information. The substitute form may include supplementary information that will assist the payee with completing the tax return. Such information could include expense and cost basis factors related to the reporting for widely held fixed investment trusts (WHFITs), as required under Regulations section 1.671-5. The substitute statement should disclose to the payee that such supplementary information is not furnished to the IRS. See Section 4.3 for additional requirements when providing supplemental information with the Forms 1099-B and 1099-DA that is not furnished to the IRS.
Forms 1099-B and 1099-DA. For transactions reportable on Form 8949, Sales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets, brokers that use substitute statements should segregate dispositions of noncovered securities from covered securities, and further segregate long-term and short-term dispositions of covered securities. They may also segregate long-term from short-term dispositions of noncovered securities, to the extent that the date acquired is known. For 2025 dispositions, the substitute Forms 1099-B and 1099-DA may have up to five separate sections, each with a heading identifying which securities are included in the list, and each separately totaled. Each section, after totaling or within the heading for the section, should indicate how to report the transactions on Form 8949, as indicated.
-
Short-term transactions for which basis is reported to the IRS—Report on Form 8949, Part I, with box A checked for Form 1099-B or Part I, with box G checked for Form 1099-DA.
-
Short-term transactions for which basis is not reported to the IRS—Report on Form 8949, Part I, with box B checked for Form 1099-B or Part I, with box H checked for Form 1099-DA.
-
Long-term transactions for which basis is reported to the IRS—Report on Form 8949, Part II, with box D checked for Form 1099-B or Part II, with box J checked for Form 1099-DA.
-
Long-term transactions for which basis is not reported to the IRS—Report on Form 8949, Part II, with box E checked for Form 1099-B or Part II, with box K checked for Form 1099-DA.
-
Transactions for which basis is not reported to the IRS and for which short-term or long-term determination is unknown (to Broker). You must determine short term or long term based on your records and report on Form 8949, Part I, with box B or box H checked, or on Form 8949, Part II, with box E or box K checked, as appropriate.
For each section, each transaction may include information not reported to the IRS, such as basis, date acquired, and gain or loss. Therefore, for short-term dispositions where basis was not reported to the IRS, basis and date acquired may be shown just as they would be shown for short-term dispositions where basis was reported to the IRS.
For 2025 dispositions, each of the applicable sections must have Sales Price and Cost or Other Basis (if known) separately totaled. Net gain or loss, if included for any of the sections, may also be totaled.
Brokers may also use substitute Form 1099-B or 1099-DA for transactions that are not directly reported on Form 8949. Examples include transactions involving regulated futures contracts, foreign currency contracts, and section 1256 option contracts. Any additional sections created for this purpose should be segregated from those transactions directly reportable on Form 8949.
The substitute form requirements in the following paragraphs also apply to Forms 1099-B and 1099-DA.
Form 1099-INT, 1099-DIV, 1099-OID, or 1099-PATR. A substitute recipient statement for Form 1099-INT, 1099-DIV, 1099-OID, or 1099-PATR must comply with the following requirements.
-
Box captions and numbers that are applicable must be clearly identified, using the same wording and numbering as on the official form.
-
The recipient statement (Copy B) must contain all applicable recipient instructions as provided on the front and back of the official IRS form. You may provide those instructions on a separate sheet of paper.
-
The box caption “Federal income tax withheld” must be in boldface type or otherwise highlighted on the recipient statement.
-
The recipient statement must contain the OMB number as shown on the official IRS form. See Section 5.2.
-
The recipient statement must contain the tax year (for example, 2025), form number (for example, Form 1099-INT), and form name (for example, Interest Income) of the official IRS Form 1099. This information must be displayed prominently together in one area of the statement. For example, the tax year, form number, and form name could be shown in the upper right part of the statement. Each copy must be appropriately labeled (such as Copy B, For Recipient). See Section 4.5.2 for applicable labels and arrangement of assembly of forms. Note. Do not include the words “Substitute for” or “In lieu of” on the recipient statement.
-
Layout and format of the statement are at the discretion of the filer. However, the IRS encourages the use of boxes so that the statement has the appearance of a form and can be easily distinguished from other nontax statements.
-
Each recipient statement of Form 1099-B, 1099-DA, 1099-DIV, 1099-INT, 1099-OID, or 1099-PATR must include the direct access telephone number of an individual who can answer questions about the statement. Include that telephone number conspicuously anywhere on the recipient statement.
A mutual fund family may furnish one statement (for example, one piece of paper) on which it reports the dividend income earned by a recipient from multiple funds within the family of mutual funds, as required by Form 1099-DIV. However, each fund and its earnings must be stated separately. The statement must contain an instruction to the recipient that each fund’s dividends and name, not the name of the mutual fund family, must be reported on the recipient’s tax return. The statement cannot contain an aggregate total of all funds. In addition, a mutual fund family may furnish a single statement (as a single filer) for Form 1099-INT, 1099-DIV, or 1099-OID information (see Section 4.2.1). Each fund and its earnings must be stated separately. The statement must contain an instruction to the recipient that each fund’s earnings and name, not the name of the mutual fund family, must be reported on the recipient’s tax return. The statement cannot contain an aggregate total of all funds.
You may enter a total of the individual accounts listed on the statement only if they have been paid by the same payer. For example, if you are listing interest paid on several accounts by one financial institution on Form 1099-INT, you may also enter the total interest amount. You may also enter a date next to the CORRECTED box if that box is checked.
Statements to form recipients for Forms 1097-BTC, 1098, 1098-C, 1098-E, 1098-F, 1098-MA, 1098-Q, 1098-T, 1099-A, 1099-C, 1099-CAP, 1099-G, 1099-K, 1099-LS, 1099-LTC, 1099-MISC, 1099-NEC, 1099-Q, 1099-QA, 1099-R, 1099-S, 1099-SA, 1099-SB, 3921, 3922, 5498, 5498-ESA, 5498-QA, 5498-SA, W-2G, 1099-DIV (only for section 404(k) dividends reportable under section 6047), and 1099-INT (only for interest of $600 or more made in the course of a trade or business reportable under section 6041) can be copies of the official forms or acceptable substitutes.
Caution. The IRS does not require a donee to use Form 1098-C as the written acknowledgment for contributions of motor vehicles, boats, and airplanes. However, if you choose to use copies of Form 1098-C or an acceptable substitute as the written acknowledgment, then you must follow the requirements of this section.
To be acceptable, a substitute recipient statement must meet the following requirements.
-
The tax year, form number, and form name must be the same as on the official form and must be displayed prominently together in one area on the statement. For example, they may be shown in the upper right part of the statement.
-
The statement must contain the same information as the official IRS form, such as aggregate amounts paid to the form recipient; any backup withholding; the name, address, and TIN of the filer and of the recipient; and any other information required by the official form.
-
Each substitute recipient statement for Forms W-2G, 1097-BTC, 1098, 1098-C, 1098-E, 1098-F, 1098-T, 1099-A, 1099-C, 1099-CAP, 1099-DIV, 1099-G (excluding state and local income tax refunds), 1099-K, 1099-INT, 1099-LS, 1099-LTC, 1099-MISC (excluding fishing boat proceeds), 1099-NEC, 1099-Q, 1099-R (for qualified long-term care insurance contracts under combined arrangements only), 1099-S, 1099-SA, 1099-SB, and 5498-SA must include the direct access telephone number of an individual who can answer questions about the statement.
-
Include the telephone number conspicuously anywhere on the recipient statement. Although not required, payers reporting on Forms 1099-QA, 1099-R (payments other than qualified long-term care insurance contracts under combined arrangements), 3921, 3922, 5498, 5498-ESA, and 5498-QA are encouraged to furnish telephone numbers at which recipients of the form(s) can reach a person familiar with the information reported.
-
All applicable money amounts and information, including box numbers required to be reported to the form recipient, must be titled on the recipient statement in substantially the same manner as those on the official IRS form. The box caption “Federal income tax withheld” must be in boldface type on the recipient statement.
Exception. If you are reporting a payment as “Other income” in box 3 of Form 1099-MISC, you may substitute appropriate language for the box title. For example, for payments of accrued wages and leave to a beneficiary of a deceased employee, you might change the title of box 3 to “Beneficiary payments” or something similar.
Note. You cannot make this change on Copy A.
-
If federal income tax is withheld and shown on Form 1099-R or W-2G, Copy B and Copy C must be furnished to the recipient. If federal income tax is not withheld, only Copy C of Forms 1099-R and W-2G must be furnished. However, for Form 1099-R, instructions similar to those on the back of the official Copy B and Copy C of Form 1099-R must be furnished to the recipient. For convenience, you may choose to provide both Copies B and C of Form 1099-R to the recipient.
-
You must provide appropriate instructions to the form recipient similar to those on the official IRS form, to aid in the proper reporting on the form recipient’s income tax return. For payments reported on Forms 1099-B, 1099-CAP, and 1099-DA, the requirement to include instructions substantially similar to those on the official IRS form may be satisfied by providing form recipients with a single set of instructions for all Forms 1099-B, 1099-CAP, and 1099-DA statements required to be furnished in a calendar year.
-
If you use carbonless sets to produce recipient statements, the quality of each copy in the set must meet the following standards.
1. All copies must be clearly legible.
2. All copies must be able to be photocopied.
3. Fading must not diminish legibility and the ability to photocopy.
-
In general, black chemical transfer inks are preferred, but other colors are permitted if the above standards are met. Hot wax and cold carbon spots are not permitted on any of the internal form plies. The back of a mailer top envelope ply may contain these spots.
-
For reporting state income tax withholding and state payments, you may add an additional box(es) to recipient copies, as appropriate. In addition, the state withholding information may be provided separately and apart from the other information in the event the recipient must attach a copy to the recipient’s tax return. Note. You cannot make this change on Copy A.
-
On Copy C of Form 1099-LTC, you may reverse the location of the policyholder’s and the insured’s name, street address, city, state, and ZIP code for easier mailing.
-
If an institution insurer uses a third-party service provider to file Form 1098-T, then in addition to the institution’s or insurer’s name, address, and telephone number, the same information may be included for the third-party service provider in the space provided on the form.
-
Forms 1099-A and 1099-C transactions, if related, may be combined on Form 1099-C.
Copies B, C, D, 1, and 2, as applicable, to be furnished to recipients have been made online fillable at IRS.gov/forms-instructions for many forms referenced in these instructions. See the separate instructions for Forms 1098, 1098-E & T, 1098-F, 1098-Q, 1099-A & C, 1099-B, 1099-DA, 1099-DIV, 1099-G, 1099-INT & OID, 1099-K, 1099-LS, 1099-MISC & NEC, 1099-PATR, 1099-R & 5498, 1099-S, 1099-SB, and 3921.
A composite recipient statement is permitted for reportable payments consisting of the proceeds of brokerage and barter transactions, dividends, interest, original issue discount, patronage dividends, and royalties. The following forms may be included on a composite substitute statement, when one payer is reporting more than one of these payments during a calendar year to the same form recipient.
-
Form 1099-B.
-
Form 1099-DA.
-
Form 1099-DIV (except for section 404(k) dividends).
-
Form 1099-INT (except for interest reportable under section 6041).
-
Form 1099-MISC (only for royalties or substitute payments in lieu of dividends and interest).
-
Form 1099-OID.
-
Form 1099-PATR.
-
Form 1099-S (only for royalties).
Generally, do not include any other Form 1099 information (for example, Form 1099-A or 1099-C) on a composite statement with the information required on the forms listed in the preceding sentence.
Although the composite recipient statement may be on one sheet, the format of the composite recipient statement must satisfy the following requirements in addition to the requirements listed in Sections 4.1.2, 4.3, and 4.4, as applicable.
-
All information pertaining to a particular type of payment must be located and blocked together on the form and separate from any information covering other types of payments included on the form. For example, if you are reporting interest and dividends, the Form 1099-INT information must be presented separately from the Form 1099-DIV information.
-
The composite recipient statement must prominently display the form number and form name of the official IRS form together in one area at the beginning of each appropriate block of information. The tax year must only be placed on each block of information if it is not prominently displayed elsewhere on the page on which the information appears.
-
Any information required by the official IRS forms that would otherwise be repeated in each information block is required to be listed only once in the first information block on the composite form. For example, there is no requirement to report the name of the filer in each information block. This rule does not apply to any money amounts (for example, federal income tax withheld) or to any other information that applies to money amounts.
-
A composite statement is an acceptable substitute only if the type of payment, and the recipient’s tax obligation with respect to the payment, is as clear as if each required statement were furnished separately on an official form.
A composite recipient statement for the forms specified in Section 4.1.2 or 4.1.3 is permitted when one filer is reporting more than one type of payment during a calendar year to the same form recipient. A composite statement is not allowed for a combination of forms listed in Sections 4.1.2 and 4.1.3.
Exceptions.
-
Substitute payments in lieu of dividends or interest reported in box 8 of Form 1099-MISC may be reported on a composite substitute statement with Form 1099-DIV.
-
Form 1099-B or 1099-DA information may be reported on a composite form with the forms specified in Section 4.1.2, as described in Section 4.2.1.
-
Royalties reported on Form 1099-MISC or 1099-S may be reported on a composite form only with the forms specified in Section 4.1.2.
Although the composite recipient statement may be on one sheet, the format of the composite recipient statement must satisfy the requirements listed in Section 4.2.1 as well as the requirements in Section 4.1.3. A composite statement of Forms 1098 and 1099-INT (for interest reportable under section 6049) is not allowed.
A filer may include Form 1099-B or 1099-DA information on a composite form with the forms listed in Section 4.1.2. Therefore, supporting, explanatory, or comparable relevant information for covered and noncovered lots on the 1099-B or 1099-DA portion of the composite statement can be included. This information includes display on the payee statement of data elements such as basis for noncovered lots, explanatory remarks on permissible basis adjustments for covered lots, descriptions of the type of transaction (merger, buy to close, redemption, etc.), identification of contingent payment debt obligations, and lot relief methods.
If you wish to provide additional information to the investor on the same substitute recipient Form 1099-B or 1099-DA, the form must follow the rules set forth in this Section 4.3 and should clearly delineate how the information is presented. Any information presented should make reference to its corresponding number on the official form, as appropriate. You should clearly categorize each type of information you are reporting.
An additional separate legend is required that explains exactly which pieces of information are and are not reported to the IRS, to the extent, if any, the information is not already identified as not being reported to the IRS, as described in Section 4.1.2. It should clearly explain how the information is presented. You may present this legend in a way that is consistent with your design as long as it clearly indicates which information is being provided to the IRS. Additionally, a reminder to taxpayers that they are ultimately responsible for the accuracy of their tax returns is also required.
Form 1098 recipient statements (Copy B) must contain the following legends.
-
Form 1098:
1. “The information in boxes 1 through 9 and 11 is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if the IRS determines that an underpayment of tax results because you overstated a deduction for the mortgage interest or for these points, reported in boxes 1 and 6; or because you did not report the refund of interest (box 4); or because you claimed a nondeductible item.”
2. “Caution. The amount shown may not be fully deductible by you. Limits based on the loan amount and the cost and value of the secured property may apply. Also, you may only deduct interest to the extent it was incurred by you, actually paid by you, and not reimbursed by another person.”
-
Form 1098-C: Copy B — “In order to take a deduction of more than $500 for this contribution, you must attach this copy to your federal tax return. Unless box 5a or 5b is checked, your deduction cannot exceed the amount in box 4c.” Copy C — “This information is being furnished to the IRS unless box 7 is checked.”
-
Form 1098-E: “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if the IRS determines that an underpayment of tax results because you overstated a deduction for student loan interest.”
-
Forms 1098-F and 1098-MA: “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS.”
-
Form 1098-Q: “This information is being furnished to the IRS.”
-
Form 1098-T: “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. This form must be used to complete Form 8863 to claim education credits. Give it to the tax preparer or use it to prepare the tax return.”
-
Forms 1099-A, 1099-C, 1099-CAP, and 1099-K: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if taxable income results from this transaction and the IRS determines that it has not been reported.”
-
Forms 1099-B, 1099-DA, 1099-DIV, 1099-G, 1099-INT, 1099-MISC, 1099-NEC, 1099-OID, 1099-PATR, 1099-Q, and 1099-QA: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if this income is taxable and the IRS determines that it has not been reported.”
-
Form 1099-LS: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if this item is required to be reported and the IRS determines that it has not been reported.” Copy C — “Copy C is provided to you for information only. Only the payment recipient is required to report this information on a tax return.”
-
Form 1099-LTC: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if this item is required to be reported and the IRS determines that it has not been reported.” Copy C — “Copy C is provided to you for information only. Only the policyholder is required to report this information on a tax return.”
-
Form 1099-R: Copy B — “Report this income on your federal tax return. If this form shows federal income tax withheld in box 4, attach this copy to your return.” Copy C — “This information is being furnished to the IRS.”
-
Forms 1099-S and 1099-SB: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if this item is required to be reported and the IRS determines that it has not been reported.”
-
Form 1099-SA: Copy B — “This information is being furnished to the IRS.”
-
Form W-2G: Copy B — “This information is being furnished to the IRS. Report this income on your federal tax return. If this form shows federal income tax withheld in box 4, attach this copy to your return.” Copy C — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if this income is taxable and the IRS determines that it has not been reported.”
-
Form 1097-BTC: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if an amount of tax credit exceeding the amount reported on this form is claimed on your income tax return.”
-
Form 3921: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS. If you are required to file a return, a negligence penalty or other sanction may be imposed on you if this item is required to be reported and the IRS determines that it has not been reported.” Copy C — “This copy should be retained by the corporation whose stock has been transferred under Section 422(b).”
-
Form 3922: Copy B — “This is important tax information and is being furnished to the IRS.”
-
Form 5498: Copy B — “This information is being furnished to the IRS.” Note. If you do not provide another statement to the participant because no contributions were made for the year, the statement of the fair market value, and any required minimum distribution of the account, must contain this legend and a designation of which information is being provided to the IRS.
-
Forms 5498-ESA, 5498-QA, and 5498-SA: Copy B — “This information is being furnished to the IRS.”
Copies B, and in some cases C, D, 1, and 2 are included in the official assembly for the convenience of the filer. You are not legally required to include all these copies with the privately printed substitute forms. Furnishing Copy B, and in some cases Copy C, will satisfy the legal requirement to provide statements of information to form recipients.
Note. If an amount of federal income tax withheld is shown on Form 1099-R or W-2G, Copy B (to be attached to the tax return) and Copy C must be furnished to the recipient. Copy D (Form W-2G) may be used for payer records. Only Copy A should be filed with the IRS.
Copy A (“For Internal Revenue Service Center”) of all forms must be on top. The rest of the assembly must be arranged, from top to bottom, as follows.
| Form | Title |
|---|---|
| 1098 | Copy B “For Payer/Borrower.” |
| 1098-C | Copy B “For Donor”; Copy C “For Donor’s Records.” |
| 1098-F | Copy B “For Payer.” |
| 1098-MA | Copy B “For Homeowner.” |
| 1098-Q, 5498, and 5498-SA | Copy B “For Participant.” |
| 1098-T | Copy B “For Student.” |
| 1098-E and 1099-A | Copy B “For Borrower.” |
| 1097-BTC, 1099-PATR, 1099-Q, and 1099-QA | Copy B “For Recipient.” |
| 1099-C | Copy B “For Debtor.” |
| 1099-CAP | Copy B “For Shareholder.” |
| 1099-B, 1099-DA, 1099-DIV, 1099-G, 1099-INT, 1099-MISC, 1099-NEC, and 1099-OID | Copy 1 “For State Tax Department”; Copy B “For Recipient”; Copy 2 “To be filed with recipient's state income tax return, when required.” |
| 1099-K | Copy 1 “For State Tax Department”; Copy B “For Payee”; Copy 2 “To be filed with the recipient's state income tax return, when required.” |
| 1099-LS | Copy B “For Payment Recipient”; Copy C “For Issuer” |
| 1099-LTC | Copy B “For Policyholder”; Copy C “For Insured” |
| 1099-R | Copy 1 “For State, City, or Local Tax Department”; Copy B “Report this income on your federal tax return. If this form shows federal income tax withheld in box 4, attach this copy to your return”; Copy C “For Recipient’s Records”; Copy 2 “File this copy with your state, city, or local income tax return, when required.” |
| 1099-S | Copy B “For Transferor.” |
| 1099-SA | Copy B “For Recipient.” |
| 1099-SB | Copy B “For Seller.” |
| 3921 | Copy B “For Employee”; Copy C “For Corporation.” |
| 3922 | Copy B “For Employee.” |
| 5498-ESA and 5498-QA | Copy B “For Beneficiary.” |
| W-2G | Copy 1 “For State, City, or Local Tax Department”; Copy B “Report this income on your federal tax return. If this form shows federal income tax withheld in box 4, attach this copy to your return.”; Copy C“ For Winner’s Records”; Copy 2 “Attach this copy to your state, city, or local income tax return, if required.”; Copy D “For Payer”. |
| 1042-S | Copy B “For Recipient”; Copy C “For Recipient” and “Attach to any federal tax return you file”; Copy D “For Recipient” and “Attach to any state tax return you file” |
If you are required to furnish a written statement (Copy B or an acceptable substitute) to a recipient, then you may furnish the statement electronically instead of on paper. This includes furnishing the statement to recipients of Forms 1098, 1098-E, 1098-F, 1098-MA, 1098-Q, 1098-T, 1099-A, 1099-B, 1099-C, 1099-CAP, 1099-DA, 1099-DIV, 1099-G, 1099-INT, 1099-K, 1099-LS, 1099-LTC, 1099-MISC, 1099-NEC, 1099-OID, 1099-PATR, 1099-Q, 1099-QA, 1099-R, 1099-S, 1099-SA, 1099-SB, 1042-S, 3921, 3922, 5498, 5498-ESA, 5498-QA, and 5498-SA. It also includes Form W-2G (except for horse and dog racing, jai alai, sweepstakes, wagering pools, and lotteries).
Note. Until further guidance is issued, you cannot furnish Form 1098-C electronically. Perforation (see Section 2.1.9) does not apply to printouts of copies of forms that are furnished electronically to recipients. However, recipients should be cautioned to carefully separate the copies.
If you meet the requirements listed in Sections 4.6.2 and 4.6.3, you are treated as furnishing the statement timely.
The recipient must consent in the affirmative to receiving the statement electronically and not have withdrawn the consent before the statement is furnished. The consent by the recipient must be made electronically in a way that shows that the recipient can access the statement in the electronic format in which it will be furnished. You must notify the recipient of any hardware or software changes prior to furnishing the statement. A new consent to receive the statement electronically is required after the new hardware or software is put into service. Prior to furnishing the statements electronically, you must provide the recipient a statement with the following statements prominently displayed.
-
If the recipient does not consent to receive the statement electronically, a paper copy will be provided.
-
The scope and duration of the consent. For example, whether the consent applies to every year the statement is furnished or only for the January 31, 2026 (February 15 for Forms 1099-B, 1099-S, and 1099-MISC with payments reported in box 8 or 10), due date immediately following the date of the consent.
-
How to obtain a paper copy after giving consent.
-
How to withdraw the consent. The consent may be withdrawn at any time by furnishing the withdrawal in writing (electronically or on paper) to the person whose name appears on the statement. Confirmation of the withdrawal will also be in writing (electronically or on paper).
-
Notice of termination. The notice must state under what conditions the statements will no longer be furnished to the recipient.
-
Procedures to update the recipient’s information.
-
A description of the hardware and software required to access, print, and retain a statement, and a date the statement will no longer be available on the website.
Additionally, you must:
-
Ensure the electronic format contains all the required information and complies with the guidelines in this document;
-
Post, on or before the January 31 (February 15 for Forms 1099-MISC (with payments reported in box 8 or 10), 1099-B, 1099-DA, and 1099-S), due date, the applicable statement on a website accessible to the recipient through October 15; and
-
Inform the recipient, electronically or by mail, of the posting and how to access and print the statement.
Note. If any of these dates fall on a Saturday, Sunday, or legal holiday, the time frame will be considered met if posted by the first business day after such date.
For more information, see Regulations section 31.6051-1(j). For electronic furnishing of:
-
Forms 1098-E and 1098-T, see Regulations sections 1.6050S-2 and 1.6050S-4;
-
Form 1099-K, see Regulations section 1.6050W-2;
-
Forms 1099-QA and 5498-QA, see Regulations section 1.529A-7;
-
Forms 1099-R, 1099-SA, 1099-Q, 5498, 5498-ESA, and 5498-SA, see Notice 2004-10, 2004-1 C.B. 433; and
-
Form 1042-S, see Regulations section 1.1461-1(c)(1)(i).
Paper substitutes of Copies A, B, C, and D must be identical to the Form 1042-S and may be privately printed without prior approval from the IRS.
Caution. On the bottom of Copy B, left align the following text: (keep for your records), and right align the following text: Form 1042-S (2025).
Note. Copies A, B, C, and D of Form 1042-S may not contain multiple income types for the same recipient, that is, multiple rows of the top boxes 1–11 of the form.
Form 1042-S is subject to annual review and possible change. Withholding agents and form suppliers are cautioned against overstocking supplies of the privately printed substitutes.
Copies of the official form for the reporting year may be obtained from most IRS offices. The IRS provides only cut sheets of these forms. Continuous fan-fold/pin-fed forms are not provided.
-
Only original forms may be filed with the IRS. Photocopies are not acceptable.
-
The term “Recipient’s U.S. TIN” for an individual means the SSN, ITIN, or ATIN, consisting of nine digits separated by hyphens as follows: 000-00-0000; for all other recipients, it means the EIN or qualified intermediary employer identification number (QI-EIN). The QI-EIN designation includes a withholding foreign partnership employer identification number (WP-EIN), and a withholding foreign trust employer identification number (WT-EIN). The EIN, QI-EIN, WP-EIN, and WT-EIN consist of nine digits separated by a hyphen as follows: 00-0000000. The TIN must be in one of these formats. Note. Digits must be separated by hyphens on paper statements in the formats listed.
-
The term “Recipient’s GIIN” means the global intermediary identification number (GIIN) assigned to a recipient that is a participating foreign financial institution (FFI) (including a reporting Model 2 FFI), registered deemed-compliant FFI (including a reporting Model 1 FFI), or other entity for chapter 4 purposes.
Note. A GIIN consists of nineteen characters as follows: XXXXXX.XXXXX.XX.XXX (6 characters followed by a period, 5 characters followed by a period, 2 characters followed by a period, and 3 final characters).
-
Withholding agents are requested to type or machine print whenever possible, provide quality data entries on the forms (that is, use black ink and insert data in the middle of blocks well separated from other printing and guidelines), and take other measures to guarantee a clear, sharp image. Withholding agents are not required, however, to acquire special equipment solely for the purpose of preparing these forms.
-
The “UNIQUE FORM IDENTIFIER,” “AMENDED,” and “AMENDMENT NO.” boxes must be printed at the top center of the form under the title.
-
Substitute forms prepared in continuous or strip form must be burst and stripped to conform to the size specified for a single form before they are filed with the IRS. The dimensions are found in Section 5.1.5. Computer cards are acceptable, provided they meet all requirements regarding layout, content, and size.
-
The OMB number must be printed in the format “OMB No. 1545-XXXX.” Use the appropriate OMB number from the most recent revision of the original IRS form.
| Property | Substitute Form 1042-S Format Requirements |
|---|---|
| Printing | Privately printed substitute Forms 1042-S must be exact replicas of the official forms with respect to layout and content. The GPO symbol must be deleted. The exact dimensions are found below. The Cat. No. must be removed and replaced with the form printer’s EIN or the vendor code (preferred). See Section 2.1.10. |
| Box Entries | Only one type of income may be represented on Copies A, B, C, and D submitted to the IRS or furnished to recipients. All boxes on Copy A filed with the IRS, and Copies B, C, and D furnished to recipients on the substitute form must conform to the official IRS form. |
| Color and Quality of Ink | All printing must be in high quality nongloss black ink. |
| Typography | Type must be substantially identical in size and shape to corresponding type on the official form. All rules on the document are either 1 point (0.015 inch) or 3 point (0.045 inch). Vertical rules must be parallel to the left edge of the document; horizontal rules must be parallel to the top edge. |
| Assembly | If all four parts are present, the parts of the assembly shall be arranged from top to bottom as follows: Copy A (Original) “for Internal Revenue Service”; and Copies B, C, and D “for Recipient.” |
| Color Quality of Paper | Paper for Copy A must be white chemical wood bond, or equivalent, 20 pounds (basis 17 x 22-500), plus or minus 5% (0.05); or offset book paper, 50 pounds (basis 25 x 38-500). No optical brighteners may be added to the pulp or paper during manufacture. The paper must consist of principally bleached chemical wood pulp or recycled printed paper. It must also be suitably sized to accept ink without feathering. |
| Dimensions |
|
| Other Copies |
|
The Paperwork Reduction Act (the Act) of 1995 (P. L. 104-13) requires the following.
-
OMB approves all IRS tax forms that are subject to the Act. Each IRS form contains (in or near the upper right corner) the OMB approval number, if any. (The official OMB numbers may be found on the official IRS printed forms and are also shown on the forms in the exhibits in Part 6.)
-
Each IRS form (or its instructions) states:
1. Why the IRS needs the information,
2. How it will be used, and
3. Whether or not the information is required to be furnished to the IRS.
This information must be provided to any users of official or substitute IRS forms or instructions.
The OMB requirements for substitute IRS forms are:
-
Any substitute form or substitute statement to a recipient must show the OMB number as it appears on the official IRS form; and
-
For Copy A, the OMB number must appear exactly as shown on the official IRS form.
For any copy other than Copy A, the OMB number must use one of the following formats.
-
OMB No. 1545-xxxx (preferred).
-
OMB # 1545-xxxx (acceptable).
Caution. These requirements do not apply to substitute Forms 1042-S. See Section 5.1.4.
All substitute forms must state the Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice as listed in Section 2.1.10.
If no instructions are provided to users of your forms, you must furnish them with the exact text of the Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice.
You can order official IRS Forms (Forms 1096, 1098, 1099, W-2G, 1042-S, and most other forms mentioned in this publication), instructions, and information copies of federal tax material by going to IRS.gov/OrderForms.
Note. Some forms on the Internet are intended as information only and may not be submitted as an official IRS form (for example, most Forms 1099, W-2, and W-3). Unless otherwise instructed, Form 1096 and Copy A of 1098 series, 1099 series, 5498 series, and Forms 3921 and 3922 cannot be used for filing with the IRS when printed from a conventional printer. These forms contain drop-out ink requirements as described in Part 2 of this publication.
Exception. Forms 1097-BTC, 1098-C, 1098-MA, 1099-CAP, 1099-LTC, 1099-Q, 1099-QA, 1099-SA, 3922, 5498-ESA, 5498-QA, 5498-SA, and 1042-S can be printed in black ink as specified in Sections 2.1.1 and 5.1.5.
Exhibits A through DD illustrate some of the specifications that were discussed earlier in this revenue procedure. The dimensions apply to the actual size forms, but the exhibits have been reduced in size.
Generally, the illustrated dimensions apply to all like forms. For example, Exhibit E shows 11.00 inches from the top edge to the bottom edge of Form 1098-E and 0.85 inch between the bottom rule of the top form and the top rule of the second form on the page. These dimensions apply to all forms that are printed 3-to-a-page.
Exhibit B contains the general measurements for forms printed 2-to-a-page. All 2-to-a-page forms, except Form 1099-B, are 4.5 inches in height within the border lines. Form 1099-B is 4.67 inches in height within the border lines.
Exhibit E contains the general measurements for forms printed 3-to-a-page. All 3-to-a-page forms are 2.83 inches in height within the border lines.
The printed area of all forms is 7.3 inches wide.
All of the exhibits in this publication were updated to include all of the 2025 revisions for those forms that have been revised.
Keep in mind the following guidelines when printing substitute forms.
-
Closely follow the specifications to avoid delays in processing the forms.
-
Always use the specifications as outlined in this revenue procedure and illustrated in the exhibits.
-
Do not add the text line “Do Not Cut or Separate Forms on This Page” to the bottom form. This will be inconsistent with the specifications.
AGENCY: Internal Revenue Service (IRS), Treasury.
ACTION: Withdrawal of notices of proposed rulemaking.
SUMMARY: This document withdraws two notices of proposed rulemaking containing proposed regulations on the treatment of built-in items of income, gain, deduction, and loss taken into account by a loss corporation after an ownership change. The proposed regulations would have affected corporations that experience an ownership change under section 382(h) of the Internal Revenue Code (Code).
DATES: As of July 2, 2025, the notices of proposed rulemaking that were published in the Federal Register on September 10, 2019 (84 FR 47455), and January 14, 2020 (85 FR 2061), are withdrawn.
ADDRESSES: Send paper submissions to CC:PA:01:PR (REG-125710-18), Room 5203, Internal Revenue Service, P.O. Box 7604, Ben Franklin Station, Washington, DC 20044.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT: Lilia D. Stamm at (202) 317-3598 (not a toll-free number).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION:
On September 10, 2019, the Department of the Treasury (Treasury Department) and the IRS published a notice of proposed rulemaking (REG-125710-18) in the Federal Register (84 FR 47455) under section 382(h) (2019 proposed regulations) that would have modified §§1.382-2 and 1.382-7 of the Income Tax Regulations (26 CFR part 1). On January 14, 2020, the Treasury Department and the IRS published a notice of proposed rulemaking (REG-125710-18) in the Federal Register (85 FR 2061) under section 382(h) (2020 proposed regulations) that modified certain provisions in the 2019 proposed regulations.
The 2019 proposed regulations would have adopted as mandatory, with certain modifications, (i) the safe harbor net unrealized built-in gain (NUBIG) and net unrealized built-in loss (NUBIL) computation provided in Notice 2003-65, 2003-40 I.R.B. 747, based on the principles of section 1374 of the Code, and (ii) the “1374 approach” (as described in Notice 2003-65) with respect to the identification of recognized built-in gain (RBIG) and recognized built-in loss (RBIL).
The 2019 proposed regulations would have modified the rules in §§1.382-2 and 1.382-7: (i) to eliminate the treatment of depreciation deductions on certain built-in gain assets as RBIG, in the absence of actual gain or income recognized by the loss corporation; (ii) to exclude adequately secured nonrecourse liabilities and all recourse liabilities from the initial NUBIG/NUBIL calculation, and treat post-change cancellation-of-indebtedness income as RBIG only in certain circumstances; (iii) to introduce a “consistency rule” in order to exclude certain change-date items allocated to the pre-change period (as defined in §1.382-6(g)(2)) from the calculation of NUBIG and NUBIL; (iv) to exclude prepaid income as an item of RBIG; (v) to exclude dividends paid on stock during the recognition period (as defined in section 382(h)(7)) as RBIG; and (vi) to exclude section 382 disallowed business interest carryforwards (as defined in §1.382-2(a)(7)) as items of RBIL under section 382(h)(6)(B).
The 2019 proposed regulations reflected the view that the certainty provided by the 1374 approach would streamline the calculation of built-in gains and built-in losses for taxpayers and the administration of section 382(h) for the IRS. In developing the 2019 proposed regulations, the Treasury Department and the IRS also considered the “338 approach” (as described in Notice 2003-65) to be more complex than the 1374 approach and to result in overstatements of RBIG and RBIL.
The Treasury Department and the IRS received several comments in response to the 2019 proposed regulations, many of which were critical of the foregoing view. In response to the comments received, the Treasury Department and the IRS are withdrawing the 2019 proposed regulations and the 2020 proposed regulations.
The Treasury Department and the IRS are continuing to study the issues addressed in the 2019 proposed regulations and expect to issue a revised notice of proposed rulemaking regarding such issues. By the terms of Notice 2003-65, taxpayers may continue to rely on the approaches set forth therein for purposes of applying section 382(h) to an ownership change that occurs prior to the effective date of temporary or final regulations under section 382(h). See Notice 2003-65, Part V.
The principal author of this notice is Brian R. Loss of the Office of Associate Chief Counsel (Corporate). However, other personnel from the Treasury Department and the IRS participated in its development.
Under the authority of 26 U.S.C. 7805, the notices of proposed rulemaking (REG-125710-18) that were published in the Federal Register on September 10, 2019 (84 FR 47455), and January 14, 2020 (85 FR 2061), are withdrawn.
Edward T. Killen, Acting Chief Tax Compliance Officer.
(Filed by the Office of the Federal Register July 1, 2025, 8:45 a.m., and published in the issue of the Federal Register for July 2, 2025, 90 FR 28946)
Revenue rulings and revenue procedures (hereinafter referred to as “rulings”) that have an effect on previous rulings use the following defined terms to describe the effect:
Amplified describes a situation where no change is being made in a prior published position, but the prior position is being extended to apply to a variation of the fact situation set forth therein. Thus, if an earlier ruling held that a principle applied to A, and the new ruling holds that the same principle also applies to B, the earlier ruling is amplified. (Compare with modified, below).
Clarified is used in those instances where the language in a prior ruling is being made clear because the language has caused, or may cause, some confusion. It is not used where a position in a prior ruling is being changed.
Distinguished describes a situation where a ruling mentions a previously published ruling and points out an essential difference between them.
Modified is used where the substance of a previously published position is being changed. Thus, if a prior ruling held that a principle applied to A but not to B, and the new ruling holds that it applies to both A and B, the prior ruling is modified because it corrects a published position. (Compare with amplified and clarified, above).
Obsoleted describes a previously published ruling that is not considered determinative with respect to future transactions. This term is most commonly used in a ruling that lists previously published rulings that are obsoleted because of changes in laws or regulations. A ruling may also be obsoleted because the substance has been included in regulations subsequently adopted.
Revoked describes situations where the position in the previously published ruling is not correct and the correct position is being stated in a new ruling.
Superseded describes a situation where the new ruling does nothing more than restate the substance and situation of a previously published ruling (or rulings). Thus, the term is used to republish under the 1986 Code and regulations the same position published under the 1939 Code and regulations. The term is also used when it is desired to republish in a single ruling a series of situations, names, etc., that were previously published over a period of time in separate rulings. If the new ruling does more than restate the substance of a prior ruling, a combination of terms is used. For example, modified and superseded describes a situation where the substance of a previously published ruling is being changed in part and is continued without change in part and it is desired to restate the valid portion of the previously published ruling in a new ruling that is self contained. In this case, the previously published ruling is first modified and then, as modified, is superseded.
Supplemented is used in situations in which a list, such as a list of the names of countries, is published in a ruling and that list is expanded by adding further names in subsequent rulings. After the original ruling has been supplemented several times, a new ruling may be published that includes the list in the original ruling and the additions, and supersedes all prior rulings in the series.
Suspended is used in rare situations to show that the previous published rulings will not be applied pending some future action such as the issuance of new or amended regulations, the outcome of cases in litigation, or the outcome of a Service study.
The following abbreviations in current use and formerly used will appear in material published in the Bulletin.
A—Individual.
Acq.—Acquiescence.
B—Individual.
BE—Beneficiary.
BK—Bank.
B.T.A.—Board of Tax Appeals.
C—Individual.
C.B.—Cumulative Bulletin.
CFR—Code of Federal Regulations.
CI—City.
COOP—Cooperative.
Ct.D.—Court Decision.
CY—County.
D—Decedent.
DC—Dummy Corporation.
DE—Donee.
Del. Order—Delegation Order.
DISC—Domestic International Sales Corporation.
DR—Donor.
E—Estate.
EE—Employee.
E.O.—Executive Order.
ER—Employer.
ERISA—Employee Retirement Income Security Act.
EX—Executor.
F—Fiduciary.
FC—Foreign Country.
FICA—Federal Insurance Contributions Act.
FISC—Foreign International Sales Company.
FPH—Foreign Personal Holding Company.
F.R.—Federal Register.
FUTA—Federal Unemployment Tax Act.
FX—Foreign corporation.
G.C.M.—Chief Counsel’s Memorandum.
GE—Grantee.
GP—General Partner.
GR—Grantor.
IC—Insurance Company.
I.R.B.—Internal Revenue Bulletin.
LE—Lessee.
LP—Limited Partner.
LR—Lessor.
M—Minor.
Nonacq.—Nonacquiescence.
O—Organization.
P—Parent Corporation.
PHC—Personal Holding Company.
PO—Possession of the U.S.
PR—Partner.
PRS—Partnership.
PTE—Prohibited Transaction Exemption.
Pub. L.—Public Law.
REIT—Real Estate Investment Trust.
Rev. Proc.—Revenue Procedure.
Rev. Rul.—Revenue Ruling.
S—Subsidiary.
S.P.R.—Statement of Procedural Rules.
Stat.—Statutes at Large.
T—Target Corporation.
T.C.—Tax Court.
T.D.—Treasury Decision.
TFE—Transferee.
TFR—Transferor.
T.I.R.—Technical Information Release.
TP—Taxpayer.
TR—Trust.
TT—Trustee.
U.S.C.—United States Code.
X—Corporation.
Y—Corporation.
Z—Corporation.
The Introduction at the beginning of this issue describes the purpose and content of this publication. The weekly Internal Revenue Bulletins are available at www.irs.gov/irb/.
If you have comments concerning the format or production of the Internal Revenue Bulletin or suggestions for improving it, we would be pleased to hear from you. You can email us your suggestions or comments through the IRS Internet Home Page www.irs.gov) or write to the
Internal Revenue Service, Publishing Division, IRB Publishing Program Desk, 1111 Constitution Ave. NW, IR-6230 Washington, DC 20224.
 )
or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
)
or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.